Bad Meteorology: The reason clouds form when air cools is because
... The idea that it is the air which determines the amount of water vapor which can be present through some sort of holding capacity is an eighteenth century idea which was shown to be false both empirically and theoretically about two hundred years ago! The fact that it is still taught in our schools ...
... The idea that it is the air which determines the amount of water vapor which can be present through some sort of holding capacity is an eighteenth century idea which was shown to be false both empirically and theoretically about two hundred years ago! The fact that it is still taught in our schools ...
145KB - NZQA
... In general candidates showed good understanding of the life cycle and characteristics of stars but were less able to answer questions about planetary systems. ...
... In general candidates showed good understanding of the life cycle and characteristics of stars but were less able to answer questions about planetary systems. ...
4.2 effects of air pollutants on human and environment
... CO2 and the Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect occurs when radiant energy is retained in the atmosphere and warms it Some atmospheric scientists think that global warming is already under way There are many natural sources that contribute significantly to “greenhouse” gas production that canno ...
... CO2 and the Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect occurs when radiant energy is retained in the atmosphere and warms it Some atmospheric scientists think that global warming is already under way There are many natural sources that contribute significantly to “greenhouse” gas production that canno ...
Outside-class project#9a questions
... (2) How do supercell thunderstorms differ from ordinary cell (air mass) thunderstorms? Be certain to specify which thunderstorm type is likely to have a longer lifespan and which is likely to meet the “severe” criteria. Your explanation should include reasons why there are differences in lifespan an ...
... (2) How do supercell thunderstorms differ from ordinary cell (air mass) thunderstorms? Be certain to specify which thunderstorm type is likely to have a longer lifespan and which is likely to meet the “severe” criteria. Your explanation should include reasons why there are differences in lifespan an ...
Definition: A group of organs working together to bring about the
... gas exchange? Through which vessel does this process occur? ...
... gas exchange? Through which vessel does this process occur? ...
Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
... 11) Which of these pairs of processes, working together, will make the atmosphere most unstable? a) cool the surface and cool the air aloft b) cool the surface and warm the air aloft c) warm the surface and warm the air aloft d) warm the surface and cool the air aloft 12) A stable atmosphere is ...
... 11) Which of these pairs of processes, working together, will make the atmosphere most unstable? a) cool the surface and cool the air aloft b) cool the surface and warm the air aloft c) warm the surface and warm the air aloft d) warm the surface and cool the air aloft 12) A stable atmosphere is ...
4th Grade Weather and Water Cycle Vocabulary
... What do we call the process by which a gas changes into a liquid? ...
... What do we call the process by which a gas changes into a liquid? ...
Climate
... ____________________________________________ - The ratio between the _____________________ amount of water ____________________ in the air to the _________________________ amount of water vapor the air can ___________________ at ant given temperature. ...
... ____________________________________________ - The ratio between the _____________________ amount of water ____________________ in the air to the _________________________ amount of water vapor the air can ___________________ at ant given temperature. ...
ES Chapter 3 PPT
... The Composition of the Earth • The mantle is the layer of rock between the Earth’s crust and core. • The mantle is made of rocks of medium density, and makes up 64 percent of the mass of the Earth. • The core is the central part of the Earth below the mantle, and is composed of the ...
... The Composition of the Earth • The mantle is the layer of rock between the Earth’s crust and core. • The mantle is made of rocks of medium density, and makes up 64 percent of the mass of the Earth. • The core is the central part of the Earth below the mantle, and is composed of the ...
NC Earth Science Final Exam Review and Key
... How do Kepler’s laws describe planetary orbits (esp. Earth’s)? 1st Law (Law of Orbits): All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun as one focus. (Earth orbit is an ellipse.) 2nd Law (Law of Areas): A line that connects a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time. (Earth sweeps o ...
... How do Kepler’s laws describe planetary orbits (esp. Earth’s)? 1st Law (Law of Orbits): All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun as one focus. (Earth orbit is an ellipse.) 2nd Law (Law of Areas): A line that connects a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time. (Earth sweeps o ...
File
... • Relative humidity is a ratio of the air’s actual water-vapor content compared with the amount of water vapor air can hold at that temperature and pressure. • To summarize, when the water-vapor content of air remains constant, lowering air temperature causes an increase in relative humidity, and ra ...
... • Relative humidity is a ratio of the air’s actual water-vapor content compared with the amount of water vapor air can hold at that temperature and pressure. • To summarize, when the water-vapor content of air remains constant, lowering air temperature causes an increase in relative humidity, and ra ...
The Royal Meteorological Society
... about 0.7 °C over the past three decades. • The UK has experienced nine of the 10 warmest years on record since 1990. • Sea levels around the UK have risen 10 cm since ...
... about 0.7 °C over the past three decades. • The UK has experienced nine of the 10 warmest years on record since 1990. • Sea levels around the UK have risen 10 cm since ...
Intro Meteorology - LunsfordEnvironmentalScience
... towards cooler latitudes Simple wind system: surface winds blow from the polar high to the equatorial low The air at the equator heats up, becomes less dense and returns to the poles at the top of the troposphere where it cools and sinks This is model of simple earth with no rotation—How is th ...
... towards cooler latitudes Simple wind system: surface winds blow from the polar high to the equatorial low The air at the equator heats up, becomes less dense and returns to the poles at the top of the troposphere where it cools and sinks This is model of simple earth with no rotation—How is th ...
Component 4: Oils, Earth and Atmosphere
... When we cook food chemical reactions cause p____________ changes to the food. When v____________ oil is used to cook food it causes different changes than when it is cooked in water. This is because vegetable oil has a h____________ boiling point compared to water. Food cooked in vegetable oil cooks ...
... When we cook food chemical reactions cause p____________ changes to the food. When v____________ oil is used to cook food it causes different changes than when it is cooked in water. This is because vegetable oil has a h____________ boiling point compared to water. Food cooked in vegetable oil cooks ...
MOMS SM1 2015 Test
... 19. What is the charge of an atom's nucleus? ○ A. Positive ○ B. Negative ○ C. No charge ○ D. Changes between positive and negative 20. Which of the following options describe a metal's properties the best. ○ A. Shiny, conducts heat and electricity, malleable, ductile ○ B. Hard and dull, does not co ...
... 19. What is the charge of an atom's nucleus? ○ A. Positive ○ B. Negative ○ C. No charge ○ D. Changes between positive and negative 20. Which of the following options describe a metal's properties the best. ○ A. Shiny, conducts heat and electricity, malleable, ductile ○ B. Hard and dull, does not co ...
Key terms are bolded. 1.
... 107. What is the difference between point and nonpoint pollution? What are examples of each? Include sedimentation and stormwater runoff in your answer. o Point pollution is delivered directly into the water source. Nonpoint pollution reaches water source from runoff and erosion. Stormwater carries ...
... 107. What is the difference between point and nonpoint pollution? What are examples of each? Include sedimentation and stormwater runoff in your answer. o Point pollution is delivered directly into the water source. Nonpoint pollution reaches water source from runoff and erosion. Stormwater carries ...
AOS Mini Vignette
... x that of Earth. Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) come from outside the solar system but generally from within our Milky Way galaxy. GCR levels on Mars are higher than Earth because Mars lacks a magnetic field and has a thinner atmosphere than Earth. The magnetic fields deflect GCR towards Earth’s pole. ...
... x that of Earth. Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) come from outside the solar system but generally from within our Milky Way galaxy. GCR levels on Mars are higher than Earth because Mars lacks a magnetic field and has a thinner atmosphere than Earth. The magnetic fields deflect GCR towards Earth’s pole. ...
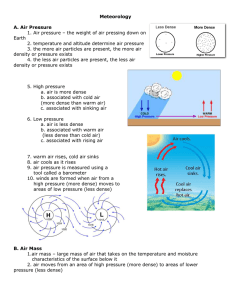
Meteorology A. Air Pressure 1. Air pressure – the
... b. Oxygen (28%) c. trace gases (1%) – argon, methane, hydrogen, and helium 2. atmosphere also contains ozone (O3) which absorbs UV radiation ...
... b. Oxygen (28%) c. trace gases (1%) – argon, methane, hydrogen, and helium 2. atmosphere also contains ozone (O3) which absorbs UV radiation ...
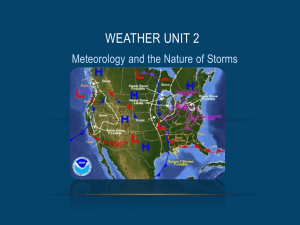
Weather maps
... High Pressure and Clear Weather High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud ...
... High Pressure and Clear Weather High pressure areas are produced by cooler, heavier, sinking air. This air contains less moisture and is more stable. In the summer, high pressure usually means sustained sunshine, few clouds, low winds, high temperatures, and dry weather. In winter, the lack of cloud ...
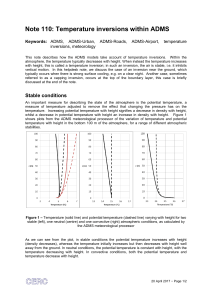
Note 110: Temperature inversions within ADMS
... Another form of temperature inversion which can play an important role within dispersion calculations is when a temperature inversion occurs at the top of the boundary layer; this is sometimes called a capping inversion. In these conditions, the inversion acts as a cap to the boundary layer and make ...
... Another form of temperature inversion which can play an important role within dispersion calculations is when a temperature inversion occurs at the top of the boundary layer; this is sometimes called a capping inversion. In these conditions, the inversion acts as a cap to the boundary layer and make ...
Meteorology Frameworks Kindergarten Students know
... closures (discussed above), they can predict stormy or fair weather from high-pressure closures. Very small changes in temperature and pressure, however, may significantly ...
... closures (discussed above), they can predict stormy or fair weather from high-pressure closures. Very small changes in temperature and pressure, however, may significantly ...
Notes
... Processes that lift air ‐ In general, the tendency is for air to resist vertical movement; air locate near the surface tends to stay near the surface, and air aloft tends to stay aloft. • In most cases when you see clouds forming, there is some mechanical phenomenon at work that forces the air t ...
... Processes that lift air ‐ In general, the tendency is for air to resist vertical movement; air locate near the surface tends to stay near the surface, and air aloft tends to stay aloft. • In most cases when you see clouds forming, there is some mechanical phenomenon at work that forces the air t ...
Changes In The Earth And It`s Atmosphere
... Scientists now accept Wegener’s theory because they know that the Earth’s ................................................ and upper part of the mantle are cracked into tectonic plates. The tectonic plates move at relative speeds of a few centimetres per year because of convection currents in the Ea ...
... Scientists now accept Wegener’s theory because they know that the Earth’s ................................................ and upper part of the mantle are cracked into tectonic plates. The tectonic plates move at relative speeds of a few centimetres per year because of convection currents in the Ea ...
Atmosphere of Earth

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).The common name air is given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for the survival of terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and artificial atmospheres.The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.