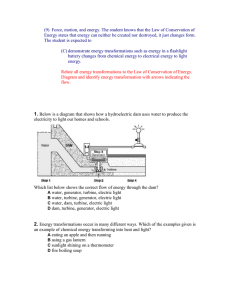
Lesson 1 What Are Some Forms of Energy? Fast Fact A Balancing
... wires glow. This is because some of the electrical energy is changed into light energy. Where does the electrical energy used by the toaster come from? Your home is connected to a system of electrical lines and cables that lead to a generating station. There, electrical energy is generated, or produ ...
... wires glow. This is because some of the electrical energy is changed into light energy. Where does the electrical energy used by the toaster come from? Your home is connected to a system of electrical lines and cables that lead to a generating station. There, electrical energy is generated, or produ ...
(9) Force, motion, and energy - 2010
... B It is converted to chemical energy. C It is converted to kinetic energy. D It is converted to potential energy. 17. Which energy transformation occurs when wood logs are burning in a fireplace? A. electrical energy → heat energy B. chemical energy → light energy C. light energy → heat energy D. he ...
... B It is converted to chemical energy. C It is converted to kinetic energy. D It is converted to potential energy. 17. Which energy transformation occurs when wood logs are burning in a fireplace? A. electrical energy → heat energy B. chemical energy → light energy C. light energy → heat energy D. he ...
Work and Energy - college physics
... and end points of the motion D. the work done moving an object depends on the mass of the object and not on the start and finish points ...
... and end points of the motion D. the work done moving an object depends on the mass of the object and not on the start and finish points ...
Pifer.weebly.com – Physical Science page Types of Energy Chapter
... (Potential energy is energy that is stored – not in motion) In order for work to be done, an object has to supply a _________ for another object to be ________________ (moved from its place) Does the hammer have more potential energy when it is resting on the ground or when it is raised above his he ...
... (Potential energy is energy that is stored – not in motion) In order for work to be done, an object has to supply a _________ for another object to be ________________ (moved from its place) Does the hammer have more potential energy when it is resting on the ground or when it is raised above his he ...
chapter20 - HCC Learning Web
... The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy. It is a special cases when only the internal energy changes and the only energy transfers are by heat and work. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that ...
... The First Law of Thermodynamics is a special case of the Law of Conservation of Energy. It is a special cases when only the internal energy changes and the only energy transfers are by heat and work. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that ...
Section 2. Mechanics Course Notes
... straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational field without air resistance If a body falls in a vacuum near the Earths surface it has an acceleration g of freefall ...
... straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational field without air resistance If a body falls in a vacuum near the Earths surface it has an acceleration g of freefall ...
The Theory of Lorentz and The Principle of Reaction
... If electromagnetic energy is neither created nor destroyed anywhere, then the last term disappears; then, the center of gravity of the system consisting of the matter and energy (regarded as a fictional fluid) has motion which is linear and uniform. Let us suppose, now, that at certain locations, th ...
... If electromagnetic energy is neither created nor destroyed anywhere, then the last term disappears; then, the center of gravity of the system consisting of the matter and energy (regarded as a fictional fluid) has motion which is linear and uniform. Let us suppose, now, that at certain locations, th ...
Energy - Hazlet.org
... Heat energy causes changes in temperature and phase of matter. (like ice to water and water to steam) ...
... Heat energy causes changes in temperature and phase of matter. (like ice to water and water to steam) ...
1. Teach for 10-15 minutes to explain:
... Where q is the charge of the ion and V is the electric potential near the surface of the charged sphere. This electric potential depends on the total charge of the charged sphere and its radius. c. Although we cannot measure the gravitational potential energy directly, we can measure the height as a ...
... Where q is the charge of the ion and V is the electric potential near the surface of the charged sphere. This electric potential depends on the total charge of the charged sphere and its radius. c. Although we cannot measure the gravitational potential energy directly, we can measure the height as a ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science Safety
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
Lecture 2: Energy Balance - San Jose State University
... What is the source of global energy? What is the difference between icesheet and ocean in terms of their reflections on ...
... What is the source of global energy? What is the difference between icesheet and ocean in terms of their reflections on ...
Energy and Its Forms
... Analyze how potential energy is related to an object’s position and give examples of gravitational and elastic potential energy. Give examples of the major forms of energy and explain how each is produced. ...
... Analyze how potential energy is related to an object’s position and give examples of gravitational and elastic potential energy. Give examples of the major forms of energy and explain how each is produced. ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.