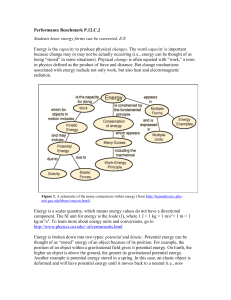
4.1 Forms of Energy Assignment
... (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate; the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Whenever you hear a sound, some sort of energy is being converted into sound energy. Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you t ...
... (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate; the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Whenever you hear a sound, some sort of energy is being converted into sound energy. Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you t ...
printer-friendly version
... frequency. For example, high frequency light, such as x-rays have greater photon energies than low frequency light such as radio. The total energy transferred by an individual photon is calculated using Einstein’s photoelectric effect equation. Details about the photoelectric effect can be found at ...
... frequency. For example, high frequency light, such as x-rays have greater photon energies than low frequency light such as radio. The total energy transferred by an individual photon is calculated using Einstein’s photoelectric effect equation. Details about the photoelectric effect can be found at ...
PPT
... • What is the electric field between the plates in each case? • What (and where) is the charge density on the plates in case (1)? • What happens to an electron released midway between the plates in case (1)? ...
... • What is the electric field between the plates in each case? • What (and where) is the charge density on the plates in case (1)? • What happens to an electron released midway between the plates in case (1)? ...
Flux, Intensity, Brilliance and all those extremely
... synchrotron facility one simply adds the contribution from each electron. The average power emitted by a storage ring with beam current, I, is then: P(kW ) 8.85 10 2 ...
... synchrotron facility one simply adds the contribution from each electron. The average power emitted by a storage ring with beam current, I, is then: P(kW ) 8.85 10 2 ...
Entropy and Free Energy
... has a fundamental molecular significance: It is a measure of the disorder of a system. This disorder can be asymmetry or displacement. This significance is relevant in the sub-atomic nature of the physical universe as well. Boltzmann proposed that entropy is related to the number of different micros ...
... has a fundamental molecular significance: It is a measure of the disorder of a system. This disorder can be asymmetry or displacement. This significance is relevant in the sub-atomic nature of the physical universe as well. Boltzmann proposed that entropy is related to the number of different micros ...
Electric potential - Mona Shores Blogs
... capacitor can effect the capacitance of the system. • A dielectric is an insulating material that is placed in between plates of a capacitor to increase its capacitance. – Insulators are used because the plates can realign the charges on the surface of the insulator space for the charge to be stored ...
... capacitor can effect the capacitance of the system. • A dielectric is an insulating material that is placed in between plates of a capacitor to increase its capacitance. – Insulators are used because the plates can realign the charges on the surface of the insulator space for the charge to be stored ...
Heat
... Question Which of the following is/are true if no energy is added as heat during the expansion of an ideal gas? (Select all that apply.) The temperature of the gas must change because of changes in internal energy. ...
... Question Which of the following is/are true if no energy is added as heat during the expansion of an ideal gas? (Select all that apply.) The temperature of the gas must change because of changes in internal energy. ...
Thermodynamic system
... • Temperature quantifies the kinetic energy of microscopic thermal motion (recall the equipartition theorem) • Heat is energy transfer between two systems (apart from work) • Temperature is a state variable, heat is not (depends on process path) • Isothermal vs. adiabatic process: – if system is the ...
... • Temperature quantifies the kinetic energy of microscopic thermal motion (recall the equipartition theorem) • Heat is energy transfer between two systems (apart from work) • Temperature is a state variable, heat is not (depends on process path) • Isothermal vs. adiabatic process: – if system is the ...
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
... of relatively slow processes. “Slow” means slow compared to the rate of atomic and molecular relaxation processes (which often are fast on the human time scale of seconds and milliseconds). Slow processes have to be slow enough so that an initially homogeneous system remains homogeneous in this proc ...
... of relatively slow processes. “Slow” means slow compared to the rate of atomic and molecular relaxation processes (which often are fast on the human time scale of seconds and milliseconds). Slow processes have to be slow enough so that an initially homogeneous system remains homogeneous in this proc ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
Electrical Energy
... the particles that make up an object. • Chemical Energy is the energy of a chemical compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged. • Electrical Energy is the energy of moving ...
... the particles that make up an object. • Chemical Energy is the energy of a chemical compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged. • Electrical Energy is the energy of moving ...
AOSS_401_20070919_L06_Thermo_Energy
... • We have formed equations to predict changes in motion (conservation of momentum) and density (conservation of mass) • We need one more equation to describe either the time rate of change of pressure or temperature (they are linked through the ideal gas law) • Conservation of energy is the basic pr ...
... • We have formed equations to predict changes in motion (conservation of momentum) and density (conservation of mass) • We need one more equation to describe either the time rate of change of pressure or temperature (they are linked through the ideal gas law) • Conservation of energy is the basic pr ...
Interaction of Radiation with Matter
... The energy loss increases with β, however even at relativistic energies the energy loss is small compared to collision loss. Advantage : very accurate β measurement of relativistic particles, since cone angle of radiation (θ ) depends on β. The radiation is observed only for β above threshold. The C ...
... The energy loss increases with β, however even at relativistic energies the energy loss is small compared to collision loss. Advantage : very accurate β measurement of relativistic particles, since cone angle of radiation (θ ) depends on β. The radiation is observed only for β above threshold. The C ...
Chapter 24 Capacitance, Dielectrics, Electric Energy Storage
... In this second experiment, we charge a capacitor, disconnect it, and then insert the dielectric. In this case, the charge remains constant. Since the dielectric increases the capacitance, the potential across the capacitor ...
... In this second experiment, we charge a capacitor, disconnect it, and then insert the dielectric. In this case, the charge remains constant. Since the dielectric increases the capacitance, the potential across the capacitor ...
Sustainable Energy Handbook
... Change of atomic composition: energy is involved when an atom loses an electron or when an atomic nucleus breaks up or merge with another one Change of the energy or of the number of photons: laser and micro wave ...
... Change of atomic composition: energy is involved when an atom loses an electron or when an atomic nucleus breaks up or merge with another one Change of the energy or of the number of photons: laser and micro wave ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
... causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When Joe pushes a book across the table, the energy from his moving arm is transferred from his body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting ...
c - Telkom University
... The Relativistic Doppler Effect Equations (2.32) and (2.33) can be combined into one equation if we agree to use a + sign for β (+v/c) when the source and receiver are approaching each other and a – sign for β (– v/c) when they are receding. The final equation becomes ...
... The Relativistic Doppler Effect Equations (2.32) and (2.33) can be combined into one equation if we agree to use a + sign for β (+v/c) when the source and receiver are approaching each other and a – sign for β (– v/c) when they are receding. The final equation becomes ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.