Note Packet
... Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from place to place. If you throw a stone into a pond, circular waves move along the surface since some of the stones kinetic energy was transferred. The substance through which waves travel is called a medium. This can be solid, liquid or gas. Light does ...
... Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from place to place. If you throw a stone into a pond, circular waves move along the surface since some of the stones kinetic energy was transferred. The substance through which waves travel is called a medium. This can be solid, liquid or gas. Light does ...
Forms of Energy - Net Start Class
... Did you know that a match also has potential energy? It is in the form of chemical energy. This energy comes from the bonds between the atoms in molecules. Atoms bond when they share electrons or when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Bonds with more electrons have more energy. Whe ...
... Did you know that a match also has potential energy? It is in the form of chemical energy. This energy comes from the bonds between the atoms in molecules. Atoms bond when they share electrons or when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Bonds with more electrons have more energy. Whe ...
Chapter 6 lecture notes
... The system is described by a set of variables that represent the state of the system—these are called state variable. Common state variables are temperature, pressure, and volume. The distinguishing feature of state variables is that when a change of state occurs, the path taken in the change does n ...
... The system is described by a set of variables that represent the state of the system—these are called state variable. Common state variables are temperature, pressure, and volume. The distinguishing feature of state variables is that when a change of state occurs, the path taken in the change does n ...
JEE-Main-2015-Physics-Triumph-Academy
... 8 1028 m3 , the resistivity of the material is close to ...
... 8 1028 m3 , the resistivity of the material is close to ...
The Ideal Gas Law and the Kinetic Theory of Gasses
... transferred by heat also depends on the initial, final and intermediate states of the system. So we now have two ways energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings: 1. Work is done by the system on its surroundings 2. The system transfers heat to the surroundings. This will lead us the ...
... transferred by heat also depends on the initial, final and intermediate states of the system. So we now have two ways energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings: 1. Work is done by the system on its surroundings 2. The system transfers heat to the surroundings. This will lead us the ...
Is there a negative absolute temperature?
... bottom to top) or SB with one particle larger, i.e., N = 2, 3, 6, etc. Temperature for N=1 cannot be properly defined. ...
... bottom to top) or SB with one particle larger, i.e., N = 2, 3, 6, etc. Temperature for N=1 cannot be properly defined. ...
List of Required Definitions
... objects is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along a line joining their centers. (NOTE: The objects are point masses. If they are not point masses but are very far apart, that is, the distance between ...
... objects is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along a line joining their centers. (NOTE: The objects are point masses. If they are not point masses but are very far apart, that is, the distance between ...
Potential energy - Peoria Public Schools
... has due to its position, condition, or chemical composition. ...
... has due to its position, condition, or chemical composition. ...
Energy exists in different forms.
... Suppose you are holding a soccer ball in your hands. Even if the ball is not moving, it has energy because it has the potential to fall. Potential energy is the stored energy that an object has due to its position or chemical composition. The ball’s position above the ground gives it potential energ ...
... Suppose you are holding a soccer ball in your hands. Even if the ball is not moving, it has energy because it has the potential to fall. Potential energy is the stored energy that an object has due to its position or chemical composition. The ball’s position above the ground gives it potential energ ...
6-5 Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential energy can
... Potential energy is a property of a system as a whole, not just of the object (because it depends on external forces). If ...
... Potential energy is a property of a system as a whole, not just of the object (because it depends on external forces). If ...
What is energy?
... • On Earth the acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2, and has the symbol g. • Like all forms of energy, gravitational potential energy is measured in joules. ...
... • On Earth the acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2, and has the symbol g. • Like all forms of energy, gravitational potential energy is measured in joules. ...
AP Physics: Volume 2
... *Solids are either crystalline or amorphous. *Crystalline Solids- The atoms have an ordered structure. Ex. Salt (Pg. 257) *Amorphus Solids- Atoms are arranged randomly Ex. Glass *Liquids are always at a higher temperature then the solid form of the same substance. The high temperature causes the mol ...
... *Solids are either crystalline or amorphous. *Crystalline Solids- The atoms have an ordered structure. Ex. Salt (Pg. 257) *Amorphus Solids- Atoms are arranged randomly Ex. Glass *Liquids are always at a higher temperature then the solid form of the same substance. The high temperature causes the mol ...
GRB prompt emission
... frame we see the unshocked gas ahead of us approaching at speed vu and the hot shocked gas streaming behind us at speed vd=1/4 vu. Consider now electrons initially at rest in the unshocked gas frame. They see the shock approaching at vu but they also see the hot shocked gas approaching at 3/4 vu. As ...
... frame we see the unshocked gas ahead of us approaching at speed vu and the hot shocked gas streaming behind us at speed vd=1/4 vu. Consider now electrons initially at rest in the unshocked gas frame. They see the shock approaching at vu but they also see the hot shocked gas approaching at 3/4 vu. As ...
Quantum Numbers
... • The p sublevel has three orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are six columns in the “p” block. • The d sublevel has five orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are ten columns in the “d” block. • The f sublevel has seven orbitals, each of which ...
... • The p sublevel has three orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are six columns in the “p” block. • The d sublevel has five orbitals, each of which can hold 2 electrons. That is why there are ten columns in the “d” block. • The f sublevel has seven orbitals, each of which ...
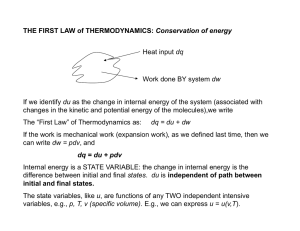
THE FIRST LAW of THERMODYNAMICS: Conservation of energy
... Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since dq = dw = 0, du = 0. Under these conditions, its clear that the volume of the gas changed, as ...
... Consider a gas expanding into an evacuated cylinder (vacuum). Since p is zero, no mechanical work is done and dw = 0. Imagine that the process is also adiabatic (perfectly insulated walls), so dq = 0. Since dq = dw = 0, du = 0. Under these conditions, its clear that the volume of the gas changed, as ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.