Slide 1
... No! These are not isolated systems. Energy comes into them in the form of food, sunlight, and air, and energy also leaves them. The second law of thermodynamics is the one that defines the arrow of time – processes will occur that are not reversible, and movies that run backward will look silly. ...
... No! These are not isolated systems. Energy comes into them in the form of food, sunlight, and air, and energy also leaves them. The second law of thermodynamics is the one that defines the arrow of time – processes will occur that are not reversible, and movies that run backward will look silly. ...
Ch15Thermo (1)
... No! These are not isolated systems. Energy comes into them in the form of food, sunlight, and air, and energy also leaves them. The second law of thermodynamics is the one that defines the arrow of time – processes will occur that are not reversible, and movies that run backward will look silly. ...
... No! These are not isolated systems. Energy comes into them in the form of food, sunlight, and air, and energy also leaves them. The second law of thermodynamics is the one that defines the arrow of time – processes will occur that are not reversible, and movies that run backward will look silly. ...
Untitled
... When is the potential energy the greatest in a roller coaster? A. at the bottom of the first hill B. at the top of the first hill C. at the top of the second hill D. at the bottom of the second ...
... When is the potential energy the greatest in a roller coaster? A. at the bottom of the first hill B. at the top of the first hill C. at the top of the second hill D. at the bottom of the second ...
Synoptic physics paraphrased
... protons increases the electrostatic force repulsive forces within the nucleus increase, and this affects all the nucleons. However the strong with not increase with distance because of its short range. This is why forces tending to disintegrate the nucleus become more dominate and the nucleus become ...
... protons increases the electrostatic force repulsive forces within the nucleus increase, and this affects all the nucleons. However the strong with not increase with distance because of its short range. This is why forces tending to disintegrate the nucleus become more dominate and the nucleus become ...
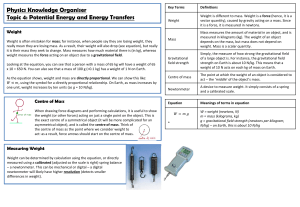
4 Potential energy and elasticity
... The extension of an elastic object, like a spring, is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided the limit of proportionality of the spring is not exceeded. This also works with the compression of an object – you can use the equations below too, ‘e’ just means the amount of compressi ...
... The extension of an elastic object, like a spring, is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided the limit of proportionality of the spring is not exceeded. This also works with the compression of an object – you can use the equations below too, ‘e’ just means the amount of compressi ...
Vocabulary Lists
... objects is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along a line joining their centers. (NOTE: The objects are point masses. If they are not point masses but are very far apart, that is, the distance between ...
... objects is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and acts along a line joining their centers. (NOTE: The objects are point masses. If they are not point masses but are very far apart, that is, the distance between ...
Form of Intensity of the Moving Charge Electric Field is
... It's own kinetic energy of the electron (proton). Kinetic energy of electron (proton) Tkin ad = mc2 [ln |1+v/c|- (v/c) / (1+v/c) ] against direction of motion of electron (proton), where v is velocity of electron (proton) and m is mass of electron (proton. Represents the wave energy, which creates e ...
... It's own kinetic energy of the electron (proton). Kinetic energy of electron (proton) Tkin ad = mc2 [ln |1+v/c|- (v/c) / (1+v/c) ] against direction of motion of electron (proton), where v is velocity of electron (proton) and m is mass of electron (proton. Represents the wave energy, which creates e ...
Unit 10 Worksheet 5
... 9a. Describe the motion of a negative charge placed at point E. How do you know? ...
... 9a. Describe the motion of a negative charge placed at point E. How do you know? ...
Modern Physics Notes
... Time intervals are not absolute, after all, as has been assumed in classical physics. a. Inertial reference frame or “observer” An inertial observer is a coordinate system for space-time; it records the position (x) and time (t) of any event. [We’ll restrict our attention to one spatial dimension, a ...
... Time intervals are not absolute, after all, as has been assumed in classical physics. a. Inertial reference frame or “observer” An inertial observer is a coordinate system for space-time; it records the position (x) and time (t) of any event. [We’ll restrict our attention to one spatial dimension, a ...
Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization
... « Maxwell’s equations show us that light is a smooth and continuous wave, and we often describe EMR in terms of its wave-like properties. . ...
... « Maxwell’s equations show us that light is a smooth and continuous wave, and we often describe EMR in terms of its wave-like properties. . ...
Ue and Voltage
... • The longer the hill the more work you do: more distance • The taller the hill, the more work you do: more force The work, W, done on an object by an agent exerting a constant force is the product of the component of the force in the direction of the displacement and the magnitude of the displaceme ...
... • The longer the hill the more work you do: more distance • The taller the hill, the more work you do: more force The work, W, done on an object by an agent exerting a constant force is the product of the component of the force in the direction of the displacement and the magnitude of the displaceme ...
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
... volume, Maintaining isothermal conditions for a system. Lecture #7 (On PPT) Phase diagrams and tables, PV, TV and PT diagrams, P-V-T surfaces (for substances which expand and contract on freezing, respectively), Reading phase diagrams, latent heat of fusion and evaporation, triple point, concept of ...
... volume, Maintaining isothermal conditions for a system. Lecture #7 (On PPT) Phase diagrams and tables, PV, TV and PT diagrams, P-V-T surfaces (for substances which expand and contract on freezing, respectively), Reading phase diagrams, latent heat of fusion and evaporation, triple point, concept of ...
Test Review # 2 - Evan`s Chemistry Corner
... of atoms with more electrons. The wave mechanical model solved the problem. Thinking of the electron as a standing wave also helps to explain why the electron’s energy is quantized. The wave mechanical model describes the location of electrons a their most probable location rather than as orbits wit ...
... of atoms with more electrons. The wave mechanical model solved the problem. Thinking of the electron as a standing wave also helps to explain why the electron’s energy is quantized. The wave mechanical model describes the location of electrons a their most probable location rather than as orbits wit ...
energy is transferred - iGCSE Science Courses
... gravitational potential, chemical, elastic (strain), nuclear and internal energy that have occurred as a result of an event or process • Recognise that energy is transferred during events and processes, including examples of transfer by forces ...
... gravitational potential, chemical, elastic (strain), nuclear and internal energy that have occurred as a result of an event or process • Recognise that energy is transferred during events and processes, including examples of transfer by forces ...
Grade 12 Unit 3 - Amazon Web Services
... of an object in motion, and potential kinetic energy is energy due to an object’s position or height above the earth. There are two types of potential energy: gravitational and elastic. In this text, we will only be using the formula concerned with gravitational energy. Mechanical energy is the sum ...
... of an object in motion, and potential kinetic energy is energy due to an object’s position or height above the earth. There are two types of potential energy: gravitational and elastic. In this text, we will only be using the formula concerned with gravitational energy. Mechanical energy is the sum ...
Ch 20 Thermodynamics
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.