PLANCK`S CONSTANT AND THE PHOTO
... thermal equilibrium and applying the statistical methods of Boltzmann Planck was able to derive his already empirically determined formula now known as Planck's law. I(T,λ) ...
... thermal equilibrium and applying the statistical methods of Boltzmann Planck was able to derive his already empirically determined formula now known as Planck's law. I(T,λ) ...
Physics - Aurora City Schools
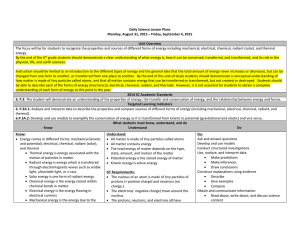
... immediately begin working on the “Question of the Day”. If you are tardy three times in a given SEMESTER, you will receive a detention. Any tardy beyond the third will also result in a detention Be prepared for class. Bring all necessary materials (see list above) and any assignments that are due ...
... immediately begin working on the “Question of the Day”. If you are tardy three times in a given SEMESTER, you will receive a detention. Any tardy beyond the third will also result in a detention Be prepared for class. Bring all necessary materials (see list above) and any assignments that are due ...
Electrical Potential Energy & Electrical Potential
... Electrical Potential The potential of a point is relative to zero potential, which is located infinitely far away. When more than one charge is present, the potential is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to each of the charges, individually. ...
... Electrical Potential The potential of a point is relative to zero potential, which is located infinitely far away. When more than one charge is present, the potential is the algebraic sum of the potentials due to each of the charges, individually. ...
Word - Structured Independent Learning
... Louis de Broglie proposed a hypothesis that was related to which of the following statements? A. ...
... Louis de Broglie proposed a hypothesis that was related to which of the following statements? A. ...
Energy
... • The energy source for nearly all ecosystems is the sun • The energy source for nearly all cellular processes is ATP ...
... • The energy source for nearly all ecosystems is the sun • The energy source for nearly all cellular processes is ATP ...
Energy
... energy changes and spontaneity of reactions. • In thermodynamics we are also interested in how far a particular reaction goes, and the yield of the reaction as well as factors that will affect these. • There are various forms of energy; light, sound, electrical, heat, nuclear and chemical energy. • ...
... energy changes and spontaneity of reactions. • In thermodynamics we are also interested in how far a particular reaction goes, and the yield of the reaction as well as factors that will affect these. • There are various forms of energy; light, sound, electrical, heat, nuclear and chemical energy. • ...
Electric Potential, Energy, and Capacitance
... b) What is the potential difference between the plates? c) If the proton is released from rest at the positive plate, what speed will it have just before it hits the negative plate? ...
... b) What is the potential difference between the plates? c) If the proton is released from rest at the positive plate, what speed will it have just before it hits the negative plate? ...
4-3 Power Point
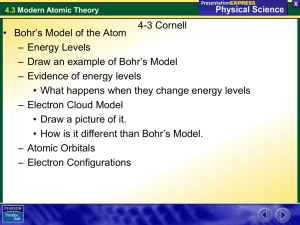
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom The movement of electrons between energy levels explains the light you see when fireworks explode. • Heat causes some electrons to move to higher energy levels. • When those electrons move back to lower energy levels, they release energy. Some of that energy is released as v ...
... Bohr’s Model of the Atom The movement of electrons between energy levels explains the light you see when fireworks explode. • Heat causes some electrons to move to higher energy levels. • When those electrons move back to lower energy levels, they release energy. Some of that energy is released as v ...
B - s3.amazonaws.com
... charges anywhere in the interior. Net charges can only be on the surface(s). ...
... charges anywhere in the interior. Net charges can only be on the surface(s). ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... The kinetic energy of a system, K, is the sum of the kinetic energies Ki 1/2mivi2 of all the particles in the system. The potential energy of a system, U, is the interaction energy of the system. The change in potential energy, U, is 1 times the work done by the interaction forces: ...
... The kinetic energy of a system, K, is the sum of the kinetic energies Ki 1/2mivi2 of all the particles in the system. The potential energy of a system, U, is the interaction energy of the system. The change in potential energy, U, is 1 times the work done by the interaction forces: ...
Energy and Power - Effingham County Schools
... Light energy is energy that is visible to the eye. It represents a very small portion of all radiant energy, which collectively is known as the electromagnetic spectrum ...
... Light energy is energy that is visible to the eye. It represents a very small portion of all radiant energy, which collectively is known as the electromagnetic spectrum ...
posted
... electron has its maximum speed at this point. When the electron moves past the center of the ring the force on it is opposite to its motion and it slows down. 23.31.IDENTIFY: The voltmeter measures the potential difference between the two points. We must relate this quantity to the linear charge den ...
... electron has its maximum speed at this point. When the electron moves past the center of the ring the force on it is opposite to its motion and it slows down. 23.31.IDENTIFY: The voltmeter measures the potential difference between the two points. We must relate this quantity to the linear charge den ...
Word
... cannot be constant (so the answer is not A). The rate of rotation will decrease, thus the rate of cutting magnetic flux lines will also decrease, so B and C which show initial increases are not relevant. This leaves D as the correct answer. (b) Either relatively large total mass (due to batteries, e ...
... cannot be constant (so the answer is not A). The rate of rotation will decrease, thus the rate of cutting magnetic flux lines will also decrease, so B and C which show initial increases are not relevant. This leaves D as the correct answer. (b) Either relatively large total mass (due to batteries, e ...
Thermochemistry
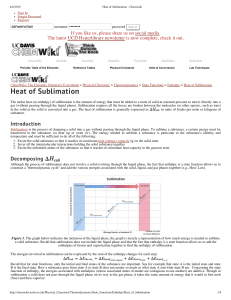
... – to take into account the chemical energy, define a reference state (p=1atm, T=25C) and let enthalpy of formation for the element in their naturally occurring state zero. – NASA has a dada base for most elements and compounds ...
... – to take into account the chemical energy, define a reference state (p=1atm, T=25C) and let enthalpy of formation for the element in their naturally occurring state zero. – NASA has a dada base for most elements and compounds ...
Electric Potential and Capacitance
... Does not depend on Q or V Proportional to area Inversely proportional to distance between ...
... Does not depend on Q or V Proportional to area Inversely proportional to distance between ...
MP350 Classical Mechanics Jon-Ivar Skullerud October 16, 2014
... all phenomena. The movement of animals, the vegetative growth of plants . . . are only its consequences; and the spectacle of the universe becomes so much the grander, so much more beautiful, the worthier of its Author, when one knows that a small number of laws, most wisely established, suffice for ...
... all phenomena. The movement of animals, the vegetative growth of plants . . . are only its consequences; and the spectacle of the universe becomes so much the grander, so much more beautiful, the worthier of its Author, when one knows that a small number of laws, most wisely established, suffice for ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.