Ch 20 Thermodynamics
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
... Ch 20: Thermodynamics: First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. ∆E= q + w (q=heat, w=work, E=internal energy) E univ= E sys + E surr Heat gained by system is lost by surroundings and vice-versa. Total energy of Universe is constant ∆E s ...
Slide 1
... collection panels with a total area of 4.0 m2. If the sun’s radiation is incident perpendicular to the panels and is completely absorbed find the average solar power absorbed and the average force associated with the radiation pressure. The intensity (I or Saverage) of sunlight prior to passing thro ...
... collection panels with a total area of 4.0 m2. If the sun’s radiation is incident perpendicular to the panels and is completely absorbed find the average solar power absorbed and the average force associated with the radiation pressure. The intensity (I or Saverage) of sunlight prior to passing thro ...
pages 15
... increase in temperature. Waste heat from a power plant, for example, will raise the temperature of cooling water drawn into its condenser. The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1 degree is called the specific heat. The specific heat of water is the bas ...
... increase in temperature. Waste heat from a power plant, for example, will raise the temperature of cooling water drawn into its condenser. The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1 degree is called the specific heat. The specific heat of water is the bas ...
documentstyle[12pt]{article}
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
... The study of thermodynamics is concerned with the ways energy is stored within a body and how energy transformations, which involve heat and work, may take place. One of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an energy interaction, e ...
18_lecture_acl
... • Any charges placed on a conductor will arrange themselves in a stable, unmoving distribution: electrostatic equilibrium. • For a conductor in electrostatic equilibrium: 1) The E-field inside it is zero (no field lines) 2) Any net charge must reside on the surface 3) Just outside the surface, E is ...
... • Any charges placed on a conductor will arrange themselves in a stable, unmoving distribution: electrostatic equilibrium. • For a conductor in electrostatic equilibrium: 1) The E-field inside it is zero (no field lines) 2) Any net charge must reside on the surface 3) Just outside the surface, E is ...
Energy
... forward. The original source of energy was the Sun, so the car is driving on solar energy that has been converted into other forms by plants and burning. Using Energy Video ...
... forward. The original source of energy was the Sun, so the car is driving on solar energy that has been converted into other forms by plants and burning. Using Energy Video ...
Thermodynamics
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. – All of these are considered microstates of a system. ...
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. – All of these are considered microstates of a system. ...
6.8A Potential Kinetic Energy
... Potential energy is stored energy—energy ready to go. A lawn mower filled with gasoline, a car on top of a hill, and students waiting to go home from school are all examples of potential energy. Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potential energy. Most of the energy under our con ...
... Potential energy is stored energy—energy ready to go. A lawn mower filled with gasoline, a car on top of a hill, and students waiting to go home from school are all examples of potential energy. Water stored behind a dam at a hydroelectric plant has potential energy. Most of the energy under our con ...
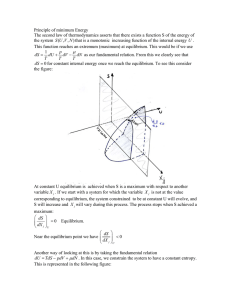
Principle of minimum Energy The second law of thermodynamics
... It follows that the change in F is the work reversibly done by or on the system under constant temperature.(isothermal reversible work). As we can see this reversible work is more negative than the corresponding irreversible work. (if the system does work on the bath, it does more work reversibly t ...
... It follows that the change in F is the work reversibly done by or on the system under constant temperature.(isothermal reversible work). As we can see this reversible work is more negative than the corresponding irreversible work. (if the system does work on the bath, it does more work reversibly t ...
$doc.title
... where ε is the atomic energy and −t / is the rate at which an electron tunnels between the two atoms. The parameter t is positive ( t > 0 ). This Hamiltonian is expressed in the basis ...
... where ε is the atomic energy and −t / is the rate at which an electron tunnels between the two atoms. The parameter t is positive ( t > 0 ). This Hamiltonian is expressed in the basis ...
Lecture 06 - Potential
... When one (external agent) moves a test charge from one point in a field to another, the external agent must do work. This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the ...
... When one (external agent) moves a test charge from one point in a field to another, the external agent must do work. This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the ...
b - UCSC Physics
... same (VB = VC). In which process was more work done by the gas? Answer: Work W = ∫ PdV = the area under the curve. The area under curve AB is ...
... same (VB = VC). In which process was more work done by the gas? Answer: Work W = ∫ PdV = the area under the curve. The area under curve AB is ...
13 particle accelerators
... as expected, but for relativistic particles the centre-of-mass energy is considerably reduced. For example, taking the proton mass be be approximately 1 GeV/c2 , the if we have an accelerator that can accelerate protons up to an energy of 100 GeV, the total centre-of-mass energy achieved is only abo ...
... as expected, but for relativistic particles the centre-of-mass energy is considerably reduced. For example, taking the proton mass be be approximately 1 GeV/c2 , the if we have an accelerator that can accelerate protons up to an energy of 100 GeV, the total centre-of-mass energy achieved is only abo ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.





![documentstyle[12pt]{article}](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010234315_1-392ad57a1bf5b2aaeca94206588a5307-300x300.png)