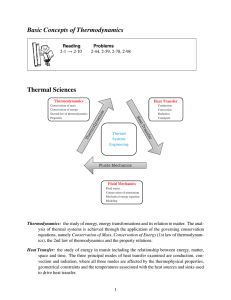
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... Heat Transfer: the study of energy in transit including the relationship between energy, matter, space and time. The three principal modes of heat transfer examined are conduction, convection and radiation, where all three modes are affected by the thermophysical properties, geometrical constraints ...
... Heat Transfer: the study of energy in transit including the relationship between energy, matter, space and time. The three principal modes of heat transfer examined are conduction, convection and radiation, where all three modes are affected by the thermophysical properties, geometrical constraints ...
relative - Purdue Physics
... • The result applies to all clocks, even biological ones • At Fermilab, pi mesons traveling close to c can travel for several kilometers in the lab, even though they typically decay in 26 ns (in their own “rest frame”) and you would naively expect them to travel only a distance d = c x 26E-9s where ...
... • The result applies to all clocks, even biological ones • At Fermilab, pi mesons traveling close to c can travel for several kilometers in the lab, even though they typically decay in 26 ns (in their own “rest frame”) and you would naively expect them to travel only a distance d = c x 26E-9s where ...
Vortices with Character - CMSA
... Infinite 1D wire Key measurement. Single-electron tunneling into middle of the wire, with applied voltage V. Differential conductance measures energy spectrum G(E) of one-electron Green’s function at E=eV. Proximity induced superconductivity gives an energy gap Δ for all excitations. G(E) = 0 for E ...
... Infinite 1D wire Key measurement. Single-electron tunneling into middle of the wire, with applied voltage V. Differential conductance measures energy spectrum G(E) of one-electron Green’s function at E=eV. Proximity induced superconductivity gives an energy gap Δ for all excitations. G(E) = 0 for E ...
Chapter 4 Energy and Potential
... position. If the source released its hold on the charge, the charge would accelerate, turning its potential energy into kinetic energy. The potential energy of a system is found by finding the work done by an external source in positioning the charge. ...
... position. If the source released its hold on the charge, the charge would accelerate, turning its potential energy into kinetic energy. The potential energy of a system is found by finding the work done by an external source in positioning the charge. ...
Chapter 4 notes
... • As it falls, it loses height so its gravitational potential energy decreases. • This potential energy is transformed into ______ energy as the velocity of the apple increases. ...
... • As it falls, it loses height so its gravitational potential energy decreases. • This potential energy is transformed into ______ energy as the velocity of the apple increases. ...
Powerpoint
... Storage of Electric Energy The energy density, defined as the energy per unit volume, is the same no matter the origin of the electric field: ...
... Storage of Electric Energy The energy density, defined as the energy per unit volume, is the same no matter the origin of the electric field: ...
Ch. 27: Quantum Physics
... learning Newton's laws and their consequences was wasted? I'll answer the second question first. No. Well maybe a little more explanation is required. The effects of relativity manifest themselves when things move at speeds near to the speed of light, 3×108m/s. Everyday objects on Earth move at spee ...
... learning Newton's laws and their consequences was wasted? I'll answer the second question first. No. Well maybe a little more explanation is required. The effects of relativity manifest themselves when things move at speeds near to the speed of light, 3×108m/s. Everyday objects on Earth move at spee ...
Ch. 16 Electrical Energy and Capacitance
... Potential energy of a pair of charges If two charges are a distance r apart you can find the potential energy of the pair. This is equivalent to finding the work needed to bring the pair together from infinity (very far apart). ...
... Potential energy of a pair of charges If two charges are a distance r apart you can find the potential energy of the pair. This is equivalent to finding the work needed to bring the pair together from infinity (very far apart). ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields
... 's are not quantities but 3D differential operators, and 's are 3D "cross products" mixing up (screwing up?) x, y, z components If they are so complex and hard to use, why bother? Because together they describe essentially everything! AND they allow for quantitative numerical calculations But, for t ...
... 's are not quantities but 3D differential operators, and 's are 3D "cross products" mixing up (screwing up?) x, y, z components If they are so complex and hard to use, why bother? Because together they describe essentially everything! AND they allow for quantitative numerical calculations But, for t ...
Thermodynamic Characteristics of Solid
... In conclusion, it is worth noting that the essential feature of the considered phenomenon has been discovered. It is about the quantum nature and it appears that the reality, as considered in the macroscopic scale, also possesses quantum energetic nature. Thus not only the microscopic world is quant ...
... In conclusion, it is worth noting that the essential feature of the considered phenomenon has been discovered. It is about the quantum nature and it appears that the reality, as considered in the macroscopic scale, also possesses quantum energetic nature. Thus not only the microscopic world is quant ...
physical world
... In that case, the two objects will fall almost at the same rate, giving the basic law that acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the object. With the basic law thus found, we can go back to the feather, introduce corrections due to air resistance, modify the existing theory and t ...
... In that case, the two objects will fall almost at the same rate, giving the basic law that acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the object. With the basic law thus found, we can go back to the feather, introduce corrections due to air resistance, modify the existing theory and t ...
Physics Booklet for Form 3
... How to read a Vernier scale? .............................................................................................................. 5 Measurement of volume .................................................................................................................... 7 Volumes of liquid ...
... How to read a Vernier scale? .............................................................................................................. 5 Measurement of volume .................................................................................................................... 7 Volumes of liquid ...
Physical Science Common Core Curriculum Standards
... spacing between the particles. change the substance is gaining The density of a substance can be calculated from the or loosing potential energy, which slope of a mass vs. volume graph. indicates a change in the position Differences in densities can be determined by of the particles. interpretin ...
... spacing between the particles. change the substance is gaining The density of a substance can be calculated from the or loosing potential energy, which slope of a mass vs. volume graph. indicates a change in the position Differences in densities can be determined by of the particles. interpretin ...
Cellular Thermodynamics
... molecule is heat. If it is accelerated by interaction with another molecule, has work been done on it, or has heat been given to it? For a large collection of molecules, however, collective organized motion (say a current of air) can do work, whereas random individual motion (in a hot, stationary ga ...
... molecule is heat. If it is accelerated by interaction with another molecule, has work been done on it, or has heat been given to it? For a large collection of molecules, however, collective organized motion (say a current of air) can do work, whereas random individual motion (in a hot, stationary ga ...
E - 101physics
... Interestingly, it was found that Kmax does not depend upon the intensity of the incident light. • It is difficult to explain this observation with classical physics where light is viewed as a continuous wave. • In classical physics, the electrons would be viewed as oscillating under the influence of ...
... Interestingly, it was found that Kmax does not depend upon the intensity of the incident light. • It is difficult to explain this observation with classical physics where light is viewed as a continuous wave. • In classical physics, the electrons would be viewed as oscillating under the influence of ...
Electrical Potential
... Batteries supply energy to maintain a potential difference across the circuit. 1) A 12V battery means that the + terminal has an electric potential that is 12V higher than the – terminal. 2) Charges flow through the external circuit (the wire) from high to low potential. 3) As the charges flow throu ...
... Batteries supply energy to maintain a potential difference across the circuit. 1) A 12V battery means that the + terminal has an electric potential that is 12V higher than the – terminal. 2) Charges flow through the external circuit (the wire) from high to low potential. 3) As the charges flow throu ...
Algebra-based Physics II The Nature of Atom
... 1. Electrons travel in fixed orbits around the proton, each orbit being defined by a unique radius and energy. These orbits are called stationary orbits or states, and while in these orbits, the electrons do not emit radiation. How can we have radiationless orbits??? This goes against classical phys ...
... 1. Electrons travel in fixed orbits around the proton, each orbit being defined by a unique radius and energy. These orbits are called stationary orbits or states, and while in these orbits, the electrons do not emit radiation. How can we have radiationless orbits??? This goes against classical phys ...
Entropy, free energy and equilibrium
... Various spontaneities: dispersal Matter disperses – gas fills a container, two liquids mix Heat disperses – hot object cools on cold surface Motion disperses – a ball stops bouncing The reverses of these three well known processes never occur spontaneously ...
... Various spontaneities: dispersal Matter disperses – gas fills a container, two liquids mix Heat disperses – hot object cools on cold surface Motion disperses – a ball stops bouncing The reverses of these three well known processes never occur spontaneously ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.