Energy: Forms and Conversions
... Yields about 240 kJ/mole energy leading to a high pressure gas. This energy shows as the kinetic energy This energy can be used directly as mechanical energy (car) or converted to other useful energy, such as electrical energy ...
... Yields about 240 kJ/mole energy leading to a high pressure gas. This energy shows as the kinetic energy This energy can be used directly as mechanical energy (car) or converted to other useful energy, such as electrical energy ...
Notes
... On a roller coaster the greatest kinetic energy is at the lowest point This is where the roller coaster has the highest velocity (fastest) ...
... On a roller coaster the greatest kinetic energy is at the lowest point This is where the roller coaster has the highest velocity (fastest) ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... particle are related by ϵ = cp, where c is the speed of light. ...
... particle are related by ϵ = cp, where c is the speed of light. ...
Chapter3 Energy and energy transfer
... Both are recognized at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. That is, both heat and work are boundary phenomena. Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. Both are associated with a process, not a state. Unlike properties, heat or work has no meaning at a state. Both are path ...
... Both are recognized at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. That is, both heat and work are boundary phenomena. Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. Both are associated with a process, not a state. Unlike properties, heat or work has no meaning at a state. Both are path ...
ENERGY UNIT Answer Key
... 3. What type of energy can be divided into kinetic and potential energy? __ Mechanical__ 4. What is kinetic energy? __Energy in the form of motion____ 5. What is potential energy? __Energy due to an object’s position or location. Stored energy.__ 6. Give three examples of electromagnetic energy. Vis ...
... 3. What type of energy can be divided into kinetic and potential energy? __ Mechanical__ 4. What is kinetic energy? __Energy in the form of motion____ 5. What is potential energy? __Energy due to an object’s position or location. Stored energy.__ 6. Give three examples of electromagnetic energy. Vis ...
Six Forms of Energy-Explain Powerpoint
... Mechanical Energy 3. Student Discussion: Why are these pictures examples of Mechanical Energy? Can these pictures be examples of any other forms of energy? ...
... Mechanical Energy 3. Student Discussion: Why are these pictures examples of Mechanical Energy? Can these pictures be examples of any other forms of energy? ...
Lecture 1: The basics - University of Warwick
... operation of a fusion reactor is hindered by several, in itself rather interesting, physics phenomena The cost argument isn’t all that clear, since the cost of the energy will be largely determined by the cost of the reactor. ...
... operation of a fusion reactor is hindered by several, in itself rather interesting, physics phenomena The cost argument isn’t all that clear, since the cost of the energy will be largely determined by the cost of the reactor. ...
Types of Energy and Energy Conversions Web/Text
... Answer the following questions after completing the 5 activities. 1. "Energy cannot be created nor destroyed in any chemical reaction. It can only be changed from one form to another." This is known as the Law of: A. Energy Transformation B. Conservation of Energy C. Energy Transfer ...
... Answer the following questions after completing the 5 activities. 1. "Energy cannot be created nor destroyed in any chemical reaction. It can only be changed from one form to another." This is known as the Law of: A. Energy Transformation B. Conservation of Energy C. Energy Transfer ...
The Laws of Thermodinamics
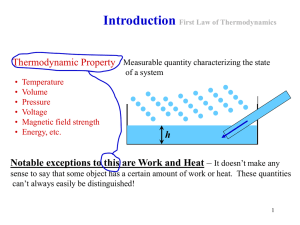
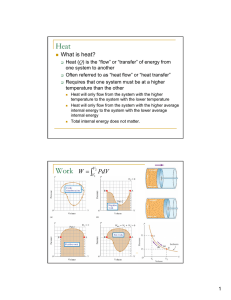
... W= -P ΔV –can be used to calculate the work done on the system only when the pressure of the gas remain ct. during the expansion or compression ISOBARIC PROCESS- a process in which the pressure remain constant • The area under the graph in a PV diagram is equal in magnitude to do work done on a gas ...
... W= -P ΔV –can be used to calculate the work done on the system only when the pressure of the gas remain ct. during the expansion or compression ISOBARIC PROCESS- a process in which the pressure remain constant • The area under the graph in a PV diagram is equal in magnitude to do work done on a gas ...
Heat Work
... When temperature changes, internal energy has changed – may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the system ΔU = Q ...
... When temperature changes, internal energy has changed – may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the system ΔU = Q ...
Electric Potential Energy v2
... Since there is an attractive and repulsive field and there is a linear relationship, the sum of the attractive and repulsive forces are a constant ...
... Since there is an attractive and repulsive field and there is a linear relationship, the sum of the attractive and repulsive forces are a constant ...
Other types of energy!
... Sound energy needs a medium/matter to travel through – solid, liquid or gas ...
... Sound energy needs a medium/matter to travel through – solid, liquid or gas ...
energy - s3.amazonaws.com
... -vibration that moves through matter to our ears - energy stored in chemical bonds and released in chemical reactions - energy generated through electricity - energy released during a nuclear reaction (fusion or fission of an atom) (heat)- energy that changes the temperature of an object…… include a ...
... -vibration that moves through matter to our ears - energy stored in chemical bonds and released in chemical reactions - energy generated through electricity - energy released during a nuclear reaction (fusion or fission of an atom) (heat)- energy that changes the temperature of an object…… include a ...
Energy Forms
... Stored energy that could cause change in the future. Potential energy often changes or transfers into kinetic energy. Types of potential energy: elasticity gravitational compressed spring chemical magnetic atoms being brought together ...
... Stored energy that could cause change in the future. Potential energy often changes or transfers into kinetic energy. Types of potential energy: elasticity gravitational compressed spring chemical magnetic atoms being brought together ...
Standard 2 Key
... The energy level of an atom is a measure of the relative amount of energy absorbed by electron waves. Energy is absorbed or released by electron waves in the form of photons or quanta (small packets of energy). Light is absorbed as electrons increase in energy. Light is emitted when electrons decrea ...
... The energy level of an atom is a measure of the relative amount of energy absorbed by electron waves. Energy is absorbed or released by electron waves in the form of photons or quanta (small packets of energy). Light is absorbed as electrons increase in energy. Light is emitted when electrons decrea ...
QM1
... Inverse Photoelectric Effect Conservation of energy requires that the electron kinetic energy equal the maximum photon energy (neglect the work function because it’s small compared to the electron potential energy). This yields the Duane-Hunt limit, first found experimentally. The photon wavelength ...
... Inverse Photoelectric Effect Conservation of energy requires that the electron kinetic energy equal the maximum photon energy (neglect the work function because it’s small compared to the electron potential energy). This yields the Duane-Hunt limit, first found experimentally. The photon wavelength ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.