Thermodynamic Processes
... Mechanical energy is transferred to the atoms and molecules throughout (a system) the entire roller coaster. Thus, the roller coaster’s internal energy increases by an amount equal to the decrease in the mechanical energy. ...
... Mechanical energy is transferred to the atoms and molecules throughout (a system) the entire roller coaster. Thus, the roller coaster’s internal energy increases by an amount equal to the decrease in the mechanical energy. ...
Forms of Energy-Chart add pictures
... Electrical Energy is what is stored in a battery, and can be used to power a cell phone or start a car. Electrical energy is delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Lightning is an example of electrical energy in nature, so powerful that it is not confi ...
... Electrical Energy is what is stored in a battery, and can be used to power a cell phone or start a car. Electrical energy is delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Lightning is an example of electrical energy in nature, so powerful that it is not confi ...
Chapter 8 Test Study Guide
... The energy associated with moving charges, or electric current-electrical energy The energy of radiation, including visible light and microwaves –electromagnetic energy The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom-nuclear energy Know how to use the following equations. kinetic energy = ½ x mass x spe ...
... The energy associated with moving charges, or electric current-electrical energy The energy of radiation, including visible light and microwaves –electromagnetic energy The energy stored in the nucleus of an atom-nuclear energy Know how to use the following equations. kinetic energy = ½ x mass x spe ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Energy and Its Conservation Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two ...
... Energy and Its Conservation Thermal Energy: The kinetic energy of molecular motion and is measured by finding the temperature of an object Heat: The amount of thermal energy transferred from one object to another as the result of a temperature difference between the two ...
Schrodinger equation (PPT - 7.3MB)
... A system is completely described by a wave function ψ, representing an observer's subjective knowledge of the system. The description of nature is essentially probabilistic, with the probability of an event related to the square of the amplitude of the wave function related to it. It is not possible ...
... A system is completely described by a wave function ψ, representing an observer's subjective knowledge of the system. The description of nature is essentially probabilistic, with the probability of an event related to the square of the amplitude of the wave function related to it. It is not possible ...
state of matter - Mayfield City Schools
... -What we’ve learned thus far about heat and thermal energy is summed up in the laws of thermodynamics. The word thermodynamics stems from Greek for “movement of heat.” -When thermal energy transfers as heat, it does so without net loss or gain. The energy lost from one place is gained by the other. ...
... -What we’ve learned thus far about heat and thermal energy is summed up in the laws of thermodynamics. The word thermodynamics stems from Greek for “movement of heat.” -When thermal energy transfers as heat, it does so without net loss or gain. The energy lost from one place is gained by the other. ...
chapter 5 thermochemistry
... Another common energy unit is the calorie (cal), which was originally defined as the quantity of energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C: When we study thermodynamic properties, we define a specific amount of matter as the system. Everything outside the system is the surr ...
... Another common energy unit is the calorie (cal), which was originally defined as the quantity of energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C: When we study thermodynamic properties, we define a specific amount of matter as the system. Everything outside the system is the surr ...
Grade 7 Question bank
... 1. Define the following: a) Energy b) Work done c) Renewable energy resources d) Kinetic energy e) Non renewable energy f) Potential energy ...
... 1. Define the following: a) Energy b) Work done c) Renewable energy resources d) Kinetic energy e) Non renewable energy f) Potential energy ...
Photon model of light - High Point University
... There are two models of light that are useful to explain various experiments. One model of light describes it as an electromagnetic wave made up of a propagating wave made up of an oscillating electric field and oscillating magnetic field (in a plane perpendicular to the electric field). The color o ...
... There are two models of light that are useful to explain various experiments. One model of light describes it as an electromagnetic wave made up of a propagating wave made up of an oscillating electric field and oscillating magnetic field (in a plane perpendicular to the electric field). The color o ...
09_H1Phy_DHS_Prelim_..
... Research for the best properties of the material is carried out using life-sized models of children with accelerometers inside the skulls of the models. As part of the investigation, the resilience is measured using the pendulum device shown in the diagram below. The pendulum is drawn back to a spec ...
... Research for the best properties of the material is carried out using life-sized models of children with accelerometers inside the skulls of the models. As part of the investigation, the resilience is measured using the pendulum device shown in the diagram below. The pendulum is drawn back to a spec ...
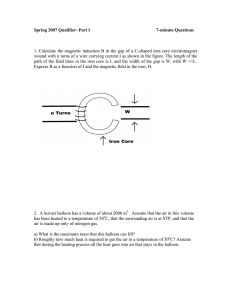
Spring 2007 Qualifier- Part I 7-minute Questions
... air is made up only of nitrogen gas. a) What is the maximum mass that this balloon can lift? b) Roughly how much heat is required to get the air to a temperature of 50oC? Assume that during the heating process all the heat goes into air that stays in the balloon. ...
... air is made up only of nitrogen gas. a) What is the maximum mass that this balloon can lift? b) Roughly how much heat is required to get the air to a temperature of 50oC? Assume that during the heating process all the heat goes into air that stays in the balloon. ...
Chapter 5 Guided Reading - Breathitt County Schools
... Fusion is the joining of nuclei and fission is the splitting of nuclei. Fission is the joining of nuclei and fusion is the splitting of nuclei. Fission releases energy and fusion absorbs energy. Fusion is the splitting of nuclei and fission is the joining of nuclei. ...
... Fusion is the joining of nuclei and fission is the splitting of nuclei. Fission is the joining of nuclei and fusion is the splitting of nuclei. Fission releases energy and fusion absorbs energy. Fusion is the splitting of nuclei and fission is the joining of nuclei. ...
Energy
... as thermal energy. Mass into Energy: Nuclear fusion is an example. Remember e=mc2. A little mass = a lot of energy Two hydrogen nuclei come together and combine to ...
... as thermal energy. Mass into Energy: Nuclear fusion is an example. Remember e=mc2. A little mass = a lot of energy Two hydrogen nuclei come together and combine to ...
3.3.2 kinetic potential energy
... Use the equation for kinetic energy. Solve problems involving exchange between kinetic and gravitational potential energy. Apply the principle of conservation of energy to determine the speed of an object falling. ...
... Use the equation for kinetic energy. Solve problems involving exchange between kinetic and gravitational potential energy. Apply the principle of conservation of energy to determine the speed of an object falling. ...
Slide 1
... FREQUENCY (f): number of crests that pass through a point each second. It is measured in units of hertz (Hz), which are the number of cycles per second. AMPLITUDE: A measure of the strength of the wave. ...
... FREQUENCY (f): number of crests that pass through a point each second. It is measured in units of hertz (Hz), which are the number of cycles per second. AMPLITUDE: A measure of the strength of the wave. ...
New Energy transfer
... Energy transfer • Example: The battery transfers stored chemical energy as electrical energy. The electrical energy is transferred to the surroundings by the lamp as light energy and thermal energy (heat energy). ...
... Energy transfer • Example: The battery transfers stored chemical energy as electrical energy. The electrical energy is transferred to the surroundings by the lamp as light energy and thermal energy (heat energy). ...
Forms of Energy
... Collected from organic waste that can be burned to produce energy Can be converted to methane or ethanol (car fuel) Renewable energy source and cheap Burning biomass does produce pollution and foul ...
... Collected from organic waste that can be burned to produce energy Can be converted to methane or ethanol (car fuel) Renewable energy source and cheap Burning biomass does produce pollution and foul ...
Name: Date: ______ Bill Nye - Phases of Matter http://www
... 1. Everything you can touch is made of __________________________ . 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Ai ...
... 1. Everything you can touch is made of __________________________ . 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Ai ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.