FOSS Weather and Water Glossary FOSS Weather and
... Barometer: An instrument used to measure air pressure. Bimetallic strip: A thin piece of two different metals stuck together. The two metals expand and contract at different rates as temperature changes, which makes them useful in some thermometers, such as an oven thermometer. Blizzard: A severe st ...
... Barometer: An instrument used to measure air pressure. Bimetallic strip: A thin piece of two different metals stuck together. The two metals expand and contract at different rates as temperature changes, which makes them useful in some thermometers, such as an oven thermometer. Blizzard: A severe st ...
presentation - Outback Air Race
... Satellites provide 24 hour information on development and movement of weather systems Infra-Red Images – detect temperatures Excellent for viewing broadscale weather patterns in motion ...
... Satellites provide 24 hour information on development and movement of weather systems Infra-Red Images – detect temperatures Excellent for viewing broadscale weather patterns in motion ...
TRIP PREPERATION
... under warm air Steep slope; heavy rain Warm front: warm air advances over cold air. Slope of front gentle. Rainfall light & widespread. ...
... under warm air Steep slope; heavy rain Warm front: warm air advances over cold air. Slope of front gentle. Rainfall light & widespread. ...
Review1
... Number density (how and why it changes with altitude) Pressure (how and why it changes with altitude) Temperature (how it changes with altitude in the troposphere; Homework #3) 3. Effects of pressure and number density changes on human bodies Why is it difficult to breathe at high altitudes? ...
... Number density (how and why it changes with altitude) Pressure (how and why it changes with altitude) Temperature (how it changes with altitude in the troposphere; Homework #3) 3. Effects of pressure and number density changes on human bodies Why is it difficult to breathe at high altitudes? ...
Atmosphere Bellwork
... 4) The layer that contains 75% of our air and our weather is called is the________. 5) Earth’s atmosphere is divided up into layers that are based upon their _____ 6) Draw the diagram and label each layer with temperature curve ...
... 4) The layer that contains 75% of our air and our weather is called is the________. 5) Earth’s atmosphere is divided up into layers that are based upon their _____ 6) Draw the diagram and label each layer with temperature curve ...
Meteorology - School in the Park
... 3. Water on Earth moves between the oceans and land through the processes of evaporation and condensation. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know when liquid water evaporates, it turns into water vapor in the air and can reappear as a liquid when cooled or as a solid if cooled b ...
... 3. Water on Earth moves between the oceans and land through the processes of evaporation and condensation. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know when liquid water evaporates, it turns into water vapor in the air and can reappear as a liquid when cooled or as a solid if cooled b ...
Meteorology Test
... 7) Air in a low pressure converges and is forced to rise. This air rises to its dew point, condenses, and creates clouds. 8) Conduction, Radiation, and Convection 9) Right; left 10) Near the poles; there is no Coriolis force at the equator. 11) Occluded, Stationary, Warm, Cold ...
... 7) Air in a low pressure converges and is forced to rise. This air rises to its dew point, condenses, and creates clouds. 8) Conduction, Radiation, and Convection 9) Right; left 10) Near the poles; there is no Coriolis force at the equator. 11) Occluded, Stationary, Warm, Cold ...
Climate
... Earth moves about 1 million miles to/from the Sun per year because of the orbit Earth is 93 million miles from the Sun Earth is closest to the sun in winter and farthest from the sun during summer Tilt of the earth causes the seasons / is the direction of the tilt NH is tilted most toward the Sun – ...
... Earth moves about 1 million miles to/from the Sun per year because of the orbit Earth is 93 million miles from the Sun Earth is closest to the sun in winter and farthest from the sun during summer Tilt of the earth causes the seasons / is the direction of the tilt NH is tilted most toward the Sun – ...
Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere
... The flow of air caused by differences in heating and the Coriolis effect creates distinct wind patterns on Earth’s surface. ...
... The flow of air caused by differences in heating and the Coriolis effect creates distinct wind patterns on Earth’s surface. ...
Th, January 29th
... The Southern oscillation is a phenomenon that refers to the see-saw effect of surface air pressures in the Eastern and Western Pacific Ocean. For Example, when air pressure recordings are high in Tahiti, they are low in Eastern Australia. Also noted was a cycle of varying Pacific Ocean temperatures ...
... The Southern oscillation is a phenomenon that refers to the see-saw effect of surface air pressures in the Eastern and Western Pacific Ocean. For Example, when air pressure recordings are high in Tahiti, they are low in Eastern Australia. Also noted was a cycle of varying Pacific Ocean temperatures ...
Introduction to Meteorology Homework #1 Answers 1. What is
... 31. Low latitudes (tropics) tend to gain more energy than they lose (heat surplus) since they receive more direct sunlight and high latitudes lose more energy to space than they gain (deficit). So that the temperature imbalance does not become extreme (unstable), atmospheric and oceanic circulations ...
... 31. Low latitudes (tropics) tend to gain more energy than they lose (heat surplus) since they receive more direct sunlight and high latitudes lose more energy to space than they gain (deficit). So that the temperature imbalance does not become extreme (unstable), atmospheric and oceanic circulations ...
Air and Weather - Beaver Dam Elementary
... Air Temperature How hot or cold air is Air Pressure Force of air pushing on an area Precipitation ANY form of water that falls from clouds ...
... Air Temperature How hot or cold air is Air Pressure Force of air pushing on an area Precipitation ANY form of water that falls from clouds ...
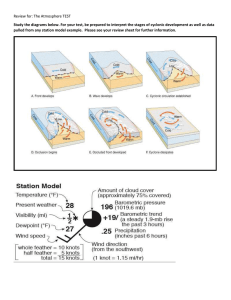
Review for: The Atmosphere TEST Study the diagrams below. For
... Measures temperature, pressure and humidity in the upper atmosphere What are the 2 most common abundant gasses in the atmosphere? The temperature at which condensation occurs Particles of dust around which cloud droplets form The deflection of Earth’s atmosphere due to its rotation Current short ter ...
... Measures temperature, pressure and humidity in the upper atmosphere What are the 2 most common abundant gasses in the atmosphere? The temperature at which condensation occurs Particles of dust around which cloud droplets form The deflection of Earth’s atmosphere due to its rotation Current short ter ...
AOSC200_summer_lect1 - UMD | Atmospheric and Oceanic
... 1. Troposphere- literally means region where air “turns over” -temperature usually decreases (on average ~6.5°C/km) with altitude Tropopause 2. Stratosphere- layer above the tropopause, little mixing occurs in the stratosphere, unlike the troposphere, where “turbulent mixing” is common Stratopause ...
... 1. Troposphere- literally means region where air “turns over” -temperature usually decreases (on average ~6.5°C/km) with altitude Tropopause 2. Stratosphere- layer above the tropopause, little mixing occurs in the stratosphere, unlike the troposphere, where “turbulent mixing” is common Stratopause ...
Atmosphere and Wind PowerPoint
... Does air have volume (takes up space)? yes Does air have mass? yes Layer of air that surrounds earth- atmosphere ...
... Does air have volume (takes up space)? yes Does air have mass? yes Layer of air that surrounds earth- atmosphere ...
Weather Study Kit - Home Science Tools
... You can either use the thermometer in the mini weather station or the separate thermometer to take daily and hourly measurements of the outside air temperature. To use the mini weather station thermometer, follow the instructions on the box to install the station and try to pick a location where the ...
... You can either use the thermometer in the mini weather station or the separate thermometer to take daily and hourly measurements of the outside air temperature. To use the mini weather station thermometer, follow the instructions on the box to install the station and try to pick a location where the ...
The Early Atmosphere - Leon County Schools
... Air is very thin Temperature decreases. Where meteors burn up and make shooting stars. ...
... Air is very thin Temperature decreases. Where meteors burn up and make shooting stars. ...
Overview of the Earth`s Atmosphere
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
Worksheet 2
... Contour lines are lines of equal temperature Isotherms are used to identify temperature gradients and, consequently, frontal systems ...
... Contour lines are lines of equal temperature Isotherms are used to identify temperature gradients and, consequently, frontal systems ...
Lesson 5
... A weather watch is issued when severe weather conditions are possible over a large area. People should have a plan of action in case of a storm. A weather warning is issued when weather conditions that pose a threat to life and property are happening or are about to happen. ...
... A weather watch is issued when severe weather conditions are possible over a large area. People should have a plan of action in case of a storm. A weather warning is issued when weather conditions that pose a threat to life and property are happening or are about to happen. ...
Y7GeU2B Weather typesPP Wk4
... Weather can be described using terms such as wet or fine, warm or cold, windy or calm, so why is there a need to measure the weather? For most people, a description of the weather is adequate but for many businesses more detailed and accurate measurements are required. The science of studying weathe ...
... Weather can be described using terms such as wet or fine, warm or cold, windy or calm, so why is there a need to measure the weather? For most people, a description of the weather is adequate but for many businesses more detailed and accurate measurements are required. The science of studying weathe ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.