Heat in the Atmosphere
... Solar energy that reaches the Earth and is reflected back depending on characteristics such as color, texture, composition, volume, mass, transparency, state of matter, intensity of light, and amount of time ...
... Solar energy that reaches the Earth and is reflected back depending on characteristics such as color, texture, composition, volume, mass, transparency, state of matter, intensity of light, and amount of time ...
Meteorology
... • Temp can reach up to 1,800°C • Suns radiation strikes this layer first • Thermometer would read 0°C, Why? • Density and distance between molecules. Molecules have a lot of energy but there isn’t a lot of molecules and they are spread out • Temperature = Average amount of energy of motion of ...
... • Temp can reach up to 1,800°C • Suns radiation strikes this layer first • Thermometer would read 0°C, Why? • Density and distance between molecules. Molecules have a lot of energy but there isn’t a lot of molecules and they are spread out • Temperature = Average amount of energy of motion of ...
WHAT IS WEATHER?
... influences the weather that we notice. Weather can be hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, and clear or cloudy. There are certain things that are involved in weather, and these are: temperature, humidity, cloudiness, precipitation, wind and pressure. Humidity is the amount of water that is prese ...
... influences the weather that we notice. Weather can be hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, and clear or cloudy. There are certain things that are involved in weather, and these are: temperature, humidity, cloudiness, precipitation, wind and pressure. Humidity is the amount of water that is prese ...
chapter 4 - Maritime Safety Queensland
... warm and cold air. As the warm air rises, the cold air rushes in to take its place and, at the same time, a rotation is imparted to the path of cold air by the effect of the earth’s rotation. Cyclones require vast amounts of water vapour to maintain intensity and tend to decay into rain depressions ...
... warm and cold air. As the warm air rises, the cold air rushes in to take its place and, at the same time, a rotation is imparted to the path of cold air by the effect of the earth’s rotation. Cyclones require vast amounts of water vapour to maintain intensity and tend to decay into rain depressions ...
Extreme Weater - Department of Meteorology and Climate Science
... KATRINA… WHY??? Katrina wasn’t an exceptionally strong storm at landfall… but it hit the worst possible place… New Orleans! ...
... KATRINA… WHY??? Katrina wasn’t an exceptionally strong storm at landfall… but it hit the worst possible place… New Orleans! ...
Met10_lecture_01 - Department of Meteorology and Climate
... - The weight of all the air on earth is 5600 trillion tons. The weight of the air molecules acts as a force on earth and us. The amount of force exerted over an area of surface is called atmospheric pressure or air pressure. The pressure at any level in the atmosphere may be measured as total mass o ...
... - The weight of all the air on earth is 5600 trillion tons. The weight of the air molecules acts as a force on earth and us. The amount of force exerted over an area of surface is called atmospheric pressure or air pressure. The pressure at any level in the atmosphere may be measured as total mass o ...
wind energy training datasheet
... Weather hazards This module looks at several of the main weather hazards, how they affect the wind energy industry and what can be done to moderate their affects. ...
... Weather hazards This module looks at several of the main weather hazards, how they affect the wind energy industry and what can be done to moderate their affects. ...
Climate Science Study Guide
... _____ 14. A storm surge is a dangerous part of a. a tornado b. a thunderstorm. c. the water cycle. d. a hurricane. _____ 15. Which describes an altocumulus cloud? a. high, feathery cloud b. puffy mid-level cloud c. low storm cloud d. high cloud made of ice crystals _____ 16. Isobars help meteorolog ...
... _____ 14. A storm surge is a dangerous part of a. a tornado b. a thunderstorm. c. the water cycle. d. a hurricane. _____ 15. Which describes an altocumulus cloud? a. high, feathery cloud b. puffy mid-level cloud c. low storm cloud d. high cloud made of ice crystals _____ 16. Isobars help meteorolog ...
Lecture 10: Extreme Weather - Department of Meteorology and
... KATRINA… WHY??? Katrina wasn’t an exceptionally strong storm at landfall… but it hit the worst possible place… New Orleans! ...
... KATRINA… WHY??? Katrina wasn’t an exceptionally strong storm at landfall… but it hit the worst possible place… New Orleans! ...
Lec 18 - Agro Meteorology - Development of e
... monsoon. It consists of series of cyclones that arise in India Ocean. These travel in northeast direction and enter the Peninsular India along its west coast. The most important of these cyclones usually occur from June to September resulting in summer monsoon or southwest monsoon. This is followed ...
... monsoon. It consists of series of cyclones that arise in India Ocean. These travel in northeast direction and enter the Peninsular India along its west coast. The most important of these cyclones usually occur from June to September resulting in summer monsoon or southwest monsoon. This is followed ...
Climate models and assessment of climate change
... tropics get higher solar radiation hot air rises, reducing surface pressure and increasing pressure higher up forces air towards poles lower surface pressure at poles makes air sink moves back towards tropics ...
... tropics get higher solar radiation hot air rises, reducing surface pressure and increasing pressure higher up forces air towards poles lower surface pressure at poles makes air sink moves back towards tropics ...
Chapter 1 - The Atmosphere
... Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted on an object by the weight of the atmosphere above it. The cause is the transfer of momentum by the random motion of air molecules. ...
... Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted on an object by the weight of the atmosphere above it. The cause is the transfer of momentum by the random motion of air molecules. ...
Q: What is Weather
... Temperature: Average energy of molecules or atoms in a material Heat: Total energy of molecules or atoms in a material Can have large amount of heat but low temperatures Can have high temperatures but little heat Heat and Temperature are of course closely related Add heat -> molecules move faster -> ...
... Temperature: Average energy of molecules or atoms in a material Heat: Total energy of molecules or atoms in a material Can have large amount of heat but low temperatures Can have high temperatures but little heat Heat and Temperature are of course closely related Add heat -> molecules move faster -> ...
Correctly define: air mass, air pressure, anemometer, barometer
... ¾ Explain where the energy for Earth’s weather originates. ¾ Describe the basic direction all weather moves in the United States. STATION MODELS: ¾ Locate and decode information from a weather station model. ¾ Label a weather station model based on provided data in the correct formats. MOISTURE: ¾ N ...
... ¾ Explain where the energy for Earth’s weather originates. ¾ Describe the basic direction all weather moves in the United States. STATION MODELS: ¾ Locate and decode information from a weather station model. ¾ Label a weather station model based on provided data in the correct formats. MOISTURE: ¾ N ...
raven ch5
... Weather and Climate Rain shadows Mountains cause air to rise . As the air rises it takes moisture with it, which forms a cloud when temperatures decreases (with greater elevation), and precipitation occurs. As the air moves down the other side of the mountain it is warmed. This decreases the chance ...
... Weather and Climate Rain shadows Mountains cause air to rise . As the air rises it takes moisture with it, which forms a cloud when temperatures decreases (with greater elevation), and precipitation occurs. As the air moves down the other side of the mountain it is warmed. This decreases the chance ...
A Thin Blue Veil Reading
... densest layer, however, containing four-‐fifths (80%) of the total mass of the atmosphere. Earth's surface (land and water) absorbs heat from the Sun and warms the air above it. Because air in th ...
... densest layer, however, containing four-‐fifths (80%) of the total mass of the atmosphere. Earth's surface (land and water) absorbs heat from the Sun and warms the air above it. Because air in th ...
Chapter 15 study guide
... The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surround Earth. Earth's atmosphere traps energy from the sun which allows water to exist as a liquid. The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen. Ozone is a form of oxygen with three oxygen atoms in each molecule. Air contains gase ...
... The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surround Earth. Earth's atmosphere traps energy from the sun which allows water to exist as a liquid. The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen. Ozone is a form of oxygen with three oxygen atoms in each molecule. Air contains gase ...
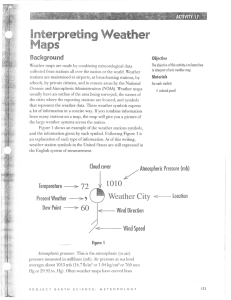
Fryterprettng V/eathen - Mrs. Battistone`s Earth Science Class
... that represent the weather data. These weather symbols express a lot of information in a concise way. If you combine information from many stations on a map, the map will give you a picture of the large weather systems across the nation. Figrue 1 shows an example of the weather stations symbols, inf ...
... that represent the weather data. These weather symbols express a lot of information in a concise way. If you combine information from many stations on a map, the map will give you a picture of the large weather systems across the nation. Figrue 1 shows an example of the weather stations symbols, inf ...
CE Weather Wind and Pressure
... There are two features of wind that we can measure: the direction that it is moving in and the speed that it is travelling in. The photograph on the right shows the equipment that is used to measure wind on a weather station. The arrow on the left points the direction that the wind is coming from. T ...
... There are two features of wind that we can measure: the direction that it is moving in and the speed that it is travelling in. The photograph on the right shows the equipment that is used to measure wind on a weather station. The arrow on the left points the direction that the wind is coming from. T ...
AOS Mini Vignette
... Solar flares release high speed particles that reach the Martian surface more easily than the same particles can reach Earth because Earth’s thicker atmosphere serves as a natural shield. ...
... Solar flares release high speed particles that reach the Martian surface more easily than the same particles can reach Earth because Earth’s thicker atmosphere serves as a natural shield. ...
4th Grade Weather and Water Cycle Vocabulary
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
... What do we call the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface? ...
Earth`s Atmosphere Study Guide
... Why is the thermosphere said to be the hottest layer when it feels so cold up there? __________________________________________________________________ How much of the sun’s energy does Earth’s surface absorb? _______ What happens to the rest of it? __________________________________________________ ...
... Why is the thermosphere said to be the hottest layer when it feels so cold up there? __________________________________________________________________ How much of the sun’s energy does Earth’s surface absorb? _______ What happens to the rest of it? __________________________________________________ ...
Extreme Weather on Earth Overview
... Tornado: clouds, strong wind, rain, hail Hurricane or cyclone: strong wind, heavy rain Blizzard: heavy snow, ice, cold temperatures Dust storm: strong winds, arid conditions ...
... Tornado: clouds, strong wind, rain, hail Hurricane or cyclone: strong wind, heavy rain Blizzard: heavy snow, ice, cold temperatures Dust storm: strong winds, arid conditions ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.