Immunoregulation How the immune system maintains the delicate
... The return of suppressorregulatory T cells • The evidence thickened for active, transferable, antigen specific, suppressive T cell activity. • Autoimmunity was observed at an unexpected high frequency in some manipulated animals: a. thymectomized mice b. cytokine or cytokine receptor gene knockout ...
... The return of suppressorregulatory T cells • The evidence thickened for active, transferable, antigen specific, suppressive T cell activity. • Autoimmunity was observed at an unexpected high frequency in some manipulated animals: a. thymectomized mice b. cytokine or cytokine receptor gene knockout ...
Any antibody binds to only a portion of the
... protein, they may be accessible to antibodies More often, linear determinants may be inaccessible in the native conformation and appear only when the protein is denatured. ...
... protein, they may be accessible to antibodies More often, linear determinants may be inaccessible in the native conformation and appear only when the protein is denatured. ...
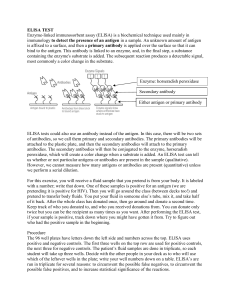
7a ELISA Test
... twice but you can be the recipient as many times as you want. After performing the ELISA test, if your sample is positive, track down where you might have gotten it from. Try to figure out who had the positive sample in the beginning. Procedure The 96 well plates have letters down the left side and ...
... twice but you can be the recipient as many times as you want. After performing the ELISA test, if your sample is positive, track down where you might have gotten it from. Try to figure out who had the positive sample in the beginning. Procedure The 96 well plates have letters down the left side and ...
Review Words for Immune System Test
... Immune Response: recognizes antigen on pathogen and produces antibodies to fight it off Antigen: protein that identifies the pathogen or donated organ as being foreign Antibodies: produced by White Blood Cells, specific to antigens Pathogen: disease causing organism, microbe, virus, bacteria, fungus ...
... Immune Response: recognizes antigen on pathogen and produces antibodies to fight it off Antigen: protein that identifies the pathogen or donated organ as being foreign Antibodies: produced by White Blood Cells, specific to antigens Pathogen: disease causing organism, microbe, virus, bacteria, fungus ...
The Immune System
... Memory cells are not active during the primary response but survive in the system for a long time This is acquired immunity ...
... Memory cells are not active during the primary response but survive in the system for a long time This is acquired immunity ...
Immune System Definition
... organisms and bacteria • Inflammatory response results as a way of “recruiting” more white blood cells • Interferon is a substance that is released by some immune cells that prevent some viruses from replicating ...
... organisms and bacteria • Inflammatory response results as a way of “recruiting” more white blood cells • Interferon is a substance that is released by some immune cells that prevent some viruses from replicating ...
Slide Presentation (Powerpoint)
... molecules over much of its surface. Because many human proteins are glycosylated, humans rarely make antibody responses to glycoslyated portions of proteins. CD4 binding site is devoid of glycosylation and relatively conserved between isolates but is masked by V1V2 loops and is in a depression which ...
... molecules over much of its surface. Because many human proteins are glycosylated, humans rarely make antibody responses to glycoslyated portions of proteins. CD4 binding site is devoid of glycosylation and relatively conserved between isolates but is masked by V1V2 loops and is in a depression which ...
Immune System – Part 2
... set of antigen receptors on cell surface Each receptor can specifically bind to a unique antigen ...
... set of antigen receptors on cell surface Each receptor can specifically bind to a unique antigen ...
Oncoimmunology
... Combination of A and B antigens make up the ABO Blood Groups (A,B,AB,O) “naturally” occurring antibody will be made against antigens that the individual does not have Usually IgM ...
... Combination of A and B antigens make up the ABO Blood Groups (A,B,AB,O) “naturally” occurring antibody will be made against antigens that the individual does not have Usually IgM ...
Lymphatic System
... particular T cell programmed to react with the antigen becomes activated – Macrophages phagocytize the antigen – Macrophages present it to the T cell ...
... particular T cell programmed to react with the antigen becomes activated – Macrophages phagocytize the antigen – Macrophages present it to the T cell ...
PHA 321 - Biosciences II
... A) activate antibodies. C) inactivate complement. B) remove antibodies. D) remove antigens. 3. The change from negative serum, without antibodies specific to an infecting agent, to positive serum, containing antibodies against that infecting agent, is called A) complement fixation. B) RIA. C) ELISA. ...
... A) activate antibodies. C) inactivate complement. B) remove antibodies. D) remove antigens. 3. The change from negative serum, without antibodies specific to an infecting agent, to positive serum, containing antibodies against that infecting agent, is called A) complement fixation. B) RIA. C) ELISA. ...
No Slide Title
... Types 4 and 1 are both active against mites, ticks, fleas • TYPE 4 activates macrophages which stimulate fibroblasts to produce granuloma and neutrophils to form intra-epidermal pustules IMMUNITY PARASITES ...
... Types 4 and 1 are both active against mites, ticks, fleas • TYPE 4 activates macrophages which stimulate fibroblasts to produce granuloma and neutrophils to form intra-epidermal pustules IMMUNITY PARASITES ...
Basic Principles of Immunology and Ag
... Essentially of Ig M and IgG classes; some IgA Characterized with specific reaction with blood group antigen epitopes/ determinants ...
... Essentially of Ig M and IgG classes; some IgA Characterized with specific reaction with blood group antigen epitopes/ determinants ...
Immunology: Specific Immunity
... carried out only by those T cells and B cells which are programmed to react to that antigen, that is, have a surface receptor with the proper fit to react with that antigen. • Both B cells and T cells, when stimulated to multiply, produce memory cells which are long lived. These are the cells that a ...
... carried out only by those T cells and B cells which are programmed to react to that antigen, that is, have a surface receptor with the proper fit to react with that antigen. • Both B cells and T cells, when stimulated to multiply, produce memory cells which are long lived. These are the cells that a ...
Immune Systm.graffle
... The ability of the body to defend itself against pathogens or poisons depends on the immune system. The T helper cells have the ability to recognize antigens (foreign substance). Once this is done, other cells (B cells) must make special molecules out of protein that attach to the antigen. These spe ...
... The ability of the body to defend itself against pathogens or poisons depends on the immune system. The T helper cells have the ability to recognize antigens (foreign substance). Once this is done, other cells (B cells) must make special molecules out of protein that attach to the antigen. These spe ...
Document
... DNA hybridization of Ig genes can diagnose B-cell leukemias Peripheral blood from healthy patient is made up of mostly neutrophils Peripheral blood from a leukemia patient has an abnormally high proportion of B-cells. Cancer cells are derived from one clonal line of B-cell which has V and C chains ...
... DNA hybridization of Ig genes can diagnose B-cell leukemias Peripheral blood from healthy patient is made up of mostly neutrophils Peripheral blood from a leukemia patient has an abnormally high proportion of B-cells. Cancer cells are derived from one clonal line of B-cell which has V and C chains ...
Immunology Review
... Cell Mediated Immunity • Controlled by T lymphocytes. – Influence other parts of the immune system (including the humoral response) through the release of cytokines. ...
... Cell Mediated Immunity • Controlled by T lymphocytes. – Influence other parts of the immune system (including the humoral response) through the release of cytokines. ...
Immune System
... by white blood cells to attach and attack an antigen • Primary immune response – the reaction of the immune system to the first exposure to an antigen – takes 7 – 10 days • Secondary immune response – the reaction of the immune system to a repeat exposure to an antigen – much, much quicker ...
... by white blood cells to attach and attack an antigen • Primary immune response – the reaction of the immune system to the first exposure to an antigen – takes 7 – 10 days • Secondary immune response – the reaction of the immune system to a repeat exposure to an antigen – much, much quicker ...
Chapter 13 Antigen - Shandong University
... determinants between different microbes, so the antiserum against one kind of Ag can also react with another Ag and cause a cross reaction. ---In clinic, existence of cross reaction may lead to wrong diagnosis. ...
... determinants between different microbes, so the antiserum against one kind of Ag can also react with another Ag and cause a cross reaction. ---In clinic, existence of cross reaction may lead to wrong diagnosis. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (b) Write briefly on the history of immunology. 12. (a) Describe the structure of antibody with diagram. Or (b) What is antigen? Cite the factors that contribute to antigenicity? 13. (a) What is agglutination? Describe the process of blood grouping. Or (b) Write the principle and process of immunoel ...
... (b) Write briefly on the history of immunology. 12. (a) Describe the structure of antibody with diagram. Or (b) What is antigen? Cite the factors that contribute to antigenicity? 13. (a) What is agglutination? Describe the process of blood grouping. Or (b) Write the principle and process of immunoel ...
BSC 361
... temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B-cells PMN's=polymorphonuclear luekocytes-includes neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils Mononuclear cells-includes lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages Immune r ...
... temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B-cells PMN's=polymorphonuclear luekocytes-includes neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils Mononuclear cells-includes lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages Immune r ...
Serum Sickness
... Serum sickness is a reaction similar to an allergy. Specifically, type III hypersensitivity reaction to certain medications, injected proteins used to treat immune conditions, or antiserum ▪ Antiserum: liquid part of blood that contains antibodies that help protect against infectious or poisonous ...
... Serum sickness is a reaction similar to an allergy. Specifically, type III hypersensitivity reaction to certain medications, injected proteins used to treat immune conditions, or antiserum ▪ Antiserum: liquid part of blood that contains antibodies that help protect against infectious or poisonous ...
Chapter 2 Antigen
... 1. Antigen determinants(epitope) The portion of antigen molecules which can be specifically bound by antibody or antigenic receptor of lymphocytes. Polypeptide antigen----5-23 amino acid residues Polysaccharide antigen----5-7 monosaccharides Nuclear acid antigen----6-8 nucleotide ...
... 1. Antigen determinants(epitope) The portion of antigen molecules which can be specifically bound by antibody or antigenic receptor of lymphocytes. Polypeptide antigen----5-23 amino acid residues Polysaccharide antigen----5-7 monosaccharides Nuclear acid antigen----6-8 nucleotide ...
Introduction to Immunology BIOS 486A/586A
... secrete their antigen receptor as a soluble molecule (antibody). Antibody recognizes and binds the immunogen resulting in direct neutralization of toxicity or infectivity; promotes phagocytosis and digestion of the antigen directly or via serum complement activation. ...
... secrete their antigen receptor as a soluble molecule (antibody). Antibody recognizes and binds the immunogen resulting in direct neutralization of toxicity or infectivity; promotes phagocytosis and digestion of the antigen directly or via serum complement activation. ...
Exam 2
... MHC o What is haplotype? o Which MHC reacts with what population of T cells? o On what cells do you find Class I MHC? Class II MHC? o Antigen presentation – review both the cystolic and endocytic pathways ...
... MHC o What is haplotype? o Which MHC reacts with what population of T cells? o On what cells do you find Class I MHC? Class II MHC? o Antigen presentation – review both the cystolic and endocytic pathways ...