The Functional Organization of Perception and Movement
... (sensory nuclei) whose axons receive stimulus information from the body’s surface. The ventral horn contains groups of motor neurons (motor nuclei) whose axons exit the spinal cord and innervate skeletal muscles. Unlike the sensory nuclei, the motor nuclei form columns that run the length of the spi ...
... (sensory nuclei) whose axons receive stimulus information from the body’s surface. The ventral horn contains groups of motor neurons (motor nuclei) whose axons exit the spinal cord and innervate skeletal muscles. Unlike the sensory nuclei, the motor nuclei form columns that run the length of the spi ...
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... o SMA: involved in programming complex sequences of movements and coordinating bilateral movements, especially selecting movements based on remembered sequences of movements. o Premotor & supplementary motor areas help in planning movement; precise control of complex sequences of voluntary movements ...
... o SMA: involved in programming complex sequences of movements and coordinating bilateral movements, especially selecting movements based on remembered sequences of movements. o Premotor & supplementary motor areas help in planning movement; precise control of complex sequences of voluntary movements ...
Neuroscience 1: Cerebral hemispheres/Telencephalon
... Neuroscience 1: Cerebral hemispheres/Telencephalon It is the primary motor area Functions for the initiate of highly skilled and fine movements 1 Lesion at this area results in apraxia—difficulty to repeat a previously learned movement a Ex: Dressing up one‘s self o Classified as Brodmann’s Area 4 ...
... Neuroscience 1: Cerebral hemispheres/Telencephalon It is the primary motor area Functions for the initiate of highly skilled and fine movements 1 Lesion at this area results in apraxia—difficulty to repeat a previously learned movement a Ex: Dressing up one‘s self o Classified as Brodmann’s Area 4 ...
- Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour
... magnetoencephalography (Nishitani and Hari, 2000). What specific aspects of an action are encoded by the mirror system? Single-unit studies in the monkey suggest that cortical representations of an action are organized around the goal or target of that action. Many F5 neurons become active during ac ...
... magnetoencephalography (Nishitani and Hari, 2000). What specific aspects of an action are encoded by the mirror system? Single-unit studies in the monkey suggest that cortical representations of an action are organized around the goal or target of that action. Many F5 neurons become active during ac ...
List 10-1
... primary motor area of the cerebral cortex? Where is the primary somatic sensory area? 2. What does the reticular activating system have to do with alertness? 3.What is the function of the limbic system? 4.What kind of information can be gained from an EEG? ...
... primary motor area of the cerebral cortex? Where is the primary somatic sensory area? 2. What does the reticular activating system have to do with alertness? 3.What is the function of the limbic system? 4.What kind of information can be gained from an EEG? ...
motor neurons
... – only these areas contain actin and myosin filaments – are innervated by gamma () efferent fibers ...
... – only these areas contain actin and myosin filaments – are innervated by gamma () efferent fibers ...
Nervous System Review PPt
... Gray Matter vs. White Matter • White matter – Composed of myelinated nerve cell processes, or axons, which connect various gray matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons – Forms the bulk of the deep parts of the brain and t ...
... Gray Matter vs. White Matter • White matter – Composed of myelinated nerve cell processes, or axons, which connect various gray matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons – Forms the bulk of the deep parts of the brain and t ...
The Nervous System Introduction Organization of Neural Tissue
... • Prefrontal cortex – Most complicated cortical region – Involved with intellect, cognition, recall and personality – Contains working memory (needed for abstract ideas), judgment, reasoning and conscience – Development depends on feedback from social environment and develops slowly ...
... • Prefrontal cortex – Most complicated cortical region – Involved with intellect, cognition, recall and personality – Contains working memory (needed for abstract ideas), judgment, reasoning and conscience – Development depends on feedback from social environment and develops slowly ...
BSCI338N, Spring 2013, Dr. Singer
... posterior limb of internal capsule → basis pedunculi (midbrain) → basis pontis (pons) → ventral column in medulla for crossing in pyramidal decussation (lateral CT) or in ventral column (anterior CT) LCT: dorsal column & lateral intermediate zone/lateral motor nuclei (LIZ/LMN) (dorsal grey matter) → ...
... posterior limb of internal capsule → basis pedunculi (midbrain) → basis pontis (pons) → ventral column in medulla for crossing in pyramidal decussation (lateral CT) or in ventral column (anterior CT) LCT: dorsal column & lateral intermediate zone/lateral motor nuclei (LIZ/LMN) (dorsal grey matter) → ...
Nervous System Notes
... The cell body is the portion of the nerve cell that surrounds the nucleus. Multipolar neurons have several branches arising form the cell body (cb). There is usually one axon (a) and many dendrites (d). Dendrites carry nerve impulses to the cell body. The axon is designed to carry nerve messages awa ...
... The cell body is the portion of the nerve cell that surrounds the nucleus. Multipolar neurons have several branches arising form the cell body (cb). There is usually one axon (a) and many dendrites (d). Dendrites carry nerve impulses to the cell body. The axon is designed to carry nerve messages awa ...
Imaging the premotor areas Nathalie Picard* and Peter L Strick
... studies were matched in size in the anterior–posterior axis. Dotted lines in (b) represent the estimated locations of levels indicated in (a). Activations related to conflict monitoring are located at the rostral edge of activations found during word generation. This topography suggests that the RCZ ...
... studies were matched in size in the anterior–posterior axis. Dotted lines in (b) represent the estimated locations of levels indicated in (a). Activations related to conflict monitoring are located at the rostral edge of activations found during word generation. This topography suggests that the RCZ ...
Central Nervous System I. Brain - Function A. Hindbrain 1. Medulla
... indicating intense pain or extreme pleasure and rage. One part of the limbic system in conjunction with parts of the cerebrum function in memory. People with damage to certain parts of the limbic system are forgetful and cannot commit things to memory. 3. Basal Cerebral Ganglia (Basal Cerebral Nucl ...
... indicating intense pain or extreme pleasure and rage. One part of the limbic system in conjunction with parts of the cerebrum function in memory. People with damage to certain parts of the limbic system are forgetful and cannot commit things to memory. 3. Basal Cerebral Ganglia (Basal Cerebral Nucl ...
ppt
... • Findings consistent with hemorrhage of genetically-based, cavernous angioma (small tumor of vessel wall) in right, language dominant hemisphere • Depression is irrelevant in this context ...
... • Findings consistent with hemorrhage of genetically-based, cavernous angioma (small tumor of vessel wall) in right, language dominant hemisphere • Depression is irrelevant in this context ...
Reflex Arcs
... (optional step) Interneurons in the CNS (a reflex center) to Motor neurons to Effector ...
... (optional step) Interneurons in the CNS (a reflex center) to Motor neurons to Effector ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... • Nodes of Ranvier are gaps between Schwann cells in myelin sheath that speed up transmission • Neurilemma is a protective membrane that helps in re-generation of a neuron. Not found in Grey matter. ...
... • Nodes of Ranvier are gaps between Schwann cells in myelin sheath that speed up transmission • Neurilemma is a protective membrane that helps in re-generation of a neuron. Not found in Grey matter. ...
[PDF]
... is mapped onto the cortical sheet. Optimizing local continuity then becomes a matter of fitting together disparate pieces in the best compromise possible. For example, at the columnar level, the primary visual cortex represents not only the positions of stimuli on the retina but also the orientation ...
... is mapped onto the cortical sheet. Optimizing local continuity then becomes a matter of fitting together disparate pieces in the best compromise possible. For example, at the columnar level, the primary visual cortex represents not only the positions of stimuli on the retina but also the orientation ...
2. Parkinsons diseas and Movement Disorders. 1998
... arrangement in which the head region lies above the lateral sulcus, the lowest part representing the throat A 2, tongue A3 and the lips. Dorsally follows the region for the hand, arm, trunk and leg, which extends across the upper margin onto the medial surface. This produces a homunculuswhich stands ...
... arrangement in which the head region lies above the lateral sulcus, the lowest part representing the throat A 2, tongue A3 and the lips. Dorsally follows the region for the hand, arm, trunk and leg, which extends across the upper margin onto the medial surface. This produces a homunculuswhich stands ...
ch_12_lecture_outline_a
... • Thin (2–4 mm) superficial layer of gray matter • 40% of the mass of the brain ...
... • Thin (2–4 mm) superficial layer of gray matter • 40% of the mass of the brain ...
powerpoint lecture
... – Motor areas—control voluntary movement – Sensory areas—conscious awareness of sensation – Association areas—integrate diverse information ...
... – Motor areas—control voluntary movement – Sensory areas—conscious awareness of sensation – Association areas—integrate diverse information ...
Biology 358 — Neuroanatomy First Exam
... somesthetic cortex of the cerebrum. Within the brain this tract gives off collateral branches to the basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum and reticular formation. This tract is concerned with fine motor control, and would be found within all segments of the spinal cord. PT ...
... somesthetic cortex of the cerebrum. Within the brain this tract gives off collateral branches to the basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum and reticular formation. This tract is concerned with fine motor control, and would be found within all segments of the spinal cord. PT ...
Notes: Divisions of the Nervous System
... • Cerebrum – involved in memory, learning, speech, emotions & controls complex behaviors – Divided into “hemispheres” • Left hemisphere controls movement on the right side of the body & vise versa ...
... • Cerebrum – involved in memory, learning, speech, emotions & controls complex behaviors – Divided into “hemispheres” • Left hemisphere controls movement on the right side of the body & vise versa ...
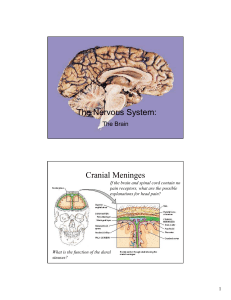
The Nervous System: Cranial Meninges
... Which ventricle is found in the diencephalon? Describe the structure and function of the reticular formation (RAS). ...
... Which ventricle is found in the diencephalon? Describe the structure and function of the reticular formation (RAS). ...
Motor cortex

Motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.Classically the motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the dorsal precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus.
















![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008803536_1-596eb89655aa0d1d0994e74af33d6baf-300x300.png)