Toxic Weeds Identification Guide
... the edge of the leaf, there are blunt teeth. In the first year, leaves form a rosette or clump at soil level. These lower leaves have a stalk (petiole), whereas those on the flowering stem do not. The underside of the leaf is noticeably soft or downy – being covered with many small hair like structu ...
... the edge of the leaf, there are blunt teeth. In the first year, leaves form a rosette or clump at soil level. These lower leaves have a stalk (petiole), whereas those on the flowering stem do not. The underside of the leaf is noticeably soft or downy – being covered with many small hair like structu ...
Transplant Sweet Alyssum - Edible Schoolyard Pittsburgh
... Seed Needs for Germination A seed contains the beginnings of a new plant. In simple terms, seeds contain three main parts – the outer seed coat, an embryo (or immature plant) and a large food store. Seeds remain in a stage of dormancy until presented with the proper conditions for germination. In or ...
... Seed Needs for Germination A seed contains the beginnings of a new plant. In simple terms, seeds contain three main parts – the outer seed coat, an embryo (or immature plant) and a large food store. Seeds remain in a stage of dormancy until presented with the proper conditions for germination. In or ...
Volume : 6(2) pp. 201 - 203, 2014 PDF
... house plant with a tight swollen spherical base made up of many overlapping scales (Fig. 1). It is a very slow growing. At maturity of 5-6 years some bulbs tend to split and produce smaller bulbs to form clumps. During winters when in dormancy, the outer scales shrivel and turn brown and assume pape ...
... house plant with a tight swollen spherical base made up of many overlapping scales (Fig. 1). It is a very slow growing. At maturity of 5-6 years some bulbs tend to split and produce smaller bulbs to form clumps. During winters when in dormancy, the outer scales shrivel and turn brown and assume pape ...
Plants notes
... Movement of Water and Nutrients Plants take up water and minerals through their roots, but they make food in their leaves. Most plants have specialized tissues that carry water and nutrients from the soil and distribute products of photosynthesis throughout the plant body. Simpler plants carry out t ...
... Movement of Water and Nutrients Plants take up water and minerals through their roots, but they make food in their leaves. Most plants have specialized tissues that carry water and nutrients from the soil and distribute products of photosynthesis throughout the plant body. Simpler plants carry out t ...
Iolanthe Magnolia - Garden Supply Co
... purple eyes held atop the branches in early spring before the leaves. It has green foliage throughout the season. The large pointy leaves turn coppery-bronze in fall. The fruits are red pods displayed from early to late fall. The furrowed gray bark is not particularly outstanding. Landscape Attribut ...
... purple eyes held atop the branches in early spring before the leaves. It has green foliage throughout the season. The large pointy leaves turn coppery-bronze in fall. The fruits are red pods displayed from early to late fall. The furrowed gray bark is not particularly outstanding. Landscape Attribut ...
Plant Parts and Functions
... Fertilisation • Pollen grains germinate on the stigma, growing down the style to reach an ovule. • Fertilised ovules develop into seeds. • The carpel enlarges to form the flesh of the fruit and to protect the ovary. ...
... Fertilisation • Pollen grains germinate on the stigma, growing down the style to reach an ovule. • Fertilised ovules develop into seeds. • The carpel enlarges to form the flesh of the fruit and to protect the ovary. ...
Chapter 24 - GEOCITIES.ws
... b. Seed Dispersal- two methods i. Dispersal by animals- these seeds are typically contained in fleshy nutritious fruits ii. Dispersal by wind and water-are typically lightweight, allowing them to be carried in the air or float on the surface of water. 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants ...
... b. Seed Dispersal- two methods i. Dispersal by animals- these seeds are typically contained in fleshy nutritious fruits ii. Dispersal by wind and water-are typically lightweight, allowing them to be carried in the air or float on the surface of water. 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants ...
The Effects of Two Levels of Salinity on Wisconsin Fast Plants
... Our study of the Wisconsin Fast Plants corroborated other scientific studies that exhibited decreased plant height and a reduced amount of leaves in other species of plants (Qados, 2011). Rameeh and Gerami’s (2015) experiment with Rapeseed showing that increased level of salinity caused decreased gr ...
... Our study of the Wisconsin Fast Plants corroborated other scientific studies that exhibited decreased plant height and a reduced amount of leaves in other species of plants (Qados, 2011). Rameeh and Gerami’s (2015) experiment with Rapeseed showing that increased level of salinity caused decreased gr ...
Red Fountain Bamboo
... vigorous variety Ornamental Features: Red Fountain Bamboo's narrow leaves remain light green in color throughout the year. Neither the flowers nor the fruit are ornamentally significant. The stems are dark red but aren't particularly outstanding. ...
... vigorous variety Ornamental Features: Red Fountain Bamboo's narrow leaves remain light green in color throughout the year. Neither the flowers nor the fruit are ornamentally significant. The stems are dark red but aren't particularly outstanding. ...
Layers of Light - Hardy Plant Society
... In June, richly-coloured heucheras begin to throw up their beaded stalks. My favourite of these is dark-leaved Heuchera ‘Prince'. In summer, it produces long stiff stems bearing large (for a heuchera) creamy lime-green flowers, which contrast perfectly with the purple-black sheen of its ruffled-edge ...
... In June, richly-coloured heucheras begin to throw up their beaded stalks. My favourite of these is dark-leaved Heuchera ‘Prince'. In summer, it produces long stiff stems bearing large (for a heuchera) creamy lime-green flowers, which contrast perfectly with the purple-black sheen of its ruffled-edge ...
Growing and Flowing Study Guide answer key
... fertilizes the ovules. The ovary becomes a fruit, and the ovules become seeds. ...
... fertilizes the ovules. The ovary becomes a fruit, and the ovules become seeds. ...
Scouring-rush Horsetail Scientific Name
... averages a third of an inch in diameter. Noticeably spotted are the jointed unions that are located down the plant. The stems are hollow and don’t branch off into additional stems. Also, scouringrush horsetail has rough ridges that run longitudinal along the stem. Although not covered in leaves, tin ...
... averages a third of an inch in diameter. Noticeably spotted are the jointed unions that are located down the plant. The stems are hollow and don’t branch off into additional stems. Also, scouringrush horsetail has rough ridges that run longitudinal along the stem. Although not covered in leaves, tin ...
Lesquerella perforata - Wikipedia, the free
... This very rare plant is threatened by the loss and degradation of its habitat. [2] It is federally listed as an endangered species. This is an annual herb growing mostly erect to a height of 10 to 15 centimeters. The leaves are auriculate (earshaped), up to 5 centimeters long by 1.5 wide, and h ...
... This very rare plant is threatened by the loss and degradation of its habitat. [2] It is federally listed as an endangered species. This is an annual herb growing mostly erect to a height of 10 to 15 centimeters. The leaves are auriculate (earshaped), up to 5 centimeters long by 1.5 wide, and h ...
What are several commercial uses for plant growth regulators?
... are pyramidal in shape. • Apical dominance can be overcome by simply cutting off the dominant stem, losing the source of the auxin. ...
... are pyramidal in shape. • Apical dominance can be overcome by simply cutting off the dominant stem, losing the source of the auxin. ...
Lesson 2
... the crown where leaf growth initiated. Sheath rolled or folded around each other and support leaf blades. When older leaf dies, new leaf develops with in the sheath of the next oldest leaf and emerges at the top of the plant. Besides the crown, there is the meristematic tissue at base of leaf blade ...
... the crown where leaf growth initiated. Sheath rolled or folded around each other and support leaf blades. When older leaf dies, new leaf develops with in the sheath of the next oldest leaf and emerges at the top of the plant. Besides the crown, there is the meristematic tissue at base of leaf blade ...
Plantae: Divisions 1. Mosses and liverworts :Division Bryophyte
... -was propagated in a Chinese monastery and is now adays only rarely found in the wild -tolerant to air pollution 6. Gnetophyta: small group of gymnosperms -Ephedra spp is a dessert shrub that produces ephedrine (antihistimine) Angiosperms: Flowering plants Most wide spread and diverse plants on eart ...
... -was propagated in a Chinese monastery and is now adays only rarely found in the wild -tolerant to air pollution 6. Gnetophyta: small group of gymnosperms -Ephedra spp is a dessert shrub that produces ephedrine (antihistimine) Angiosperms: Flowering plants Most wide spread and diverse plants on eart ...
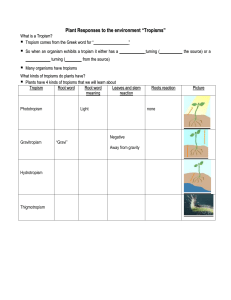
Tropism - My Teacher Site
... C. when organisms move toward or away D. they are natural occurrences Qu e s t i o n 2 What does positive phototropism mean? A. the organism moves toward light B. moves away from light C. moves toward the picture D. moves away from the picture Qu e s t i o n 3 What does part of the plant has a posit ...
... C. when organisms move toward or away D. they are natural occurrences Qu e s t i o n 2 What does positive phototropism mean? A. the organism moves toward light B. moves away from light C. moves toward the picture D. moves away from the picture Qu e s t i o n 3 What does part of the plant has a posit ...
plant diversity ii
... (undifferentiated) cells meristems. Can undergo cell division to produce new organs through life of plant. Elongate and differentiate into cell types depending on tissue of plant. ...
... (undifferentiated) cells meristems. Can undergo cell division to produce new organs through life of plant. Elongate and differentiate into cell types depending on tissue of plant. ...
Concepts of Micropropagation
... Organogensis refers to that period of time during development when the organs are being formed. After an egg has been fertilized, and has been implanted in the uterus, the developing form is known as the embryo. Organogenesis takes place during this embryonic phase. In fact, most organogenesis has b ...
... Organogensis refers to that period of time during development when the organs are being formed. After an egg has been fertilized, and has been implanted in the uterus, the developing form is known as the embryo. Organogenesis takes place during this embryonic phase. In fact, most organogenesis has b ...
Plants Powerpoint
... (undifferentiated) cells meristems. Can undergo cell division to produce new organs through life of plant. Elongate and differentiate into cell types depending on tissue of plant. ...
... (undifferentiated) cells meristems. Can undergo cell division to produce new organs through life of plant. Elongate and differentiate into cell types depending on tissue of plant. ...
two parts/categories roots shoots stem leaves flowers roots The
... Figure 2. Cross section of monocot stem. Vascular bundles are randomly arranged. Within the vascular bundle the phloem (yellow in line drawing) is to the outside and the xylem (blue in line drawing) is to the inside of each bundle. In herbaceous dicot stems, the vascular system makes a ring, with th ...
... Figure 2. Cross section of monocot stem. Vascular bundles are randomly arranged. Within the vascular bundle the phloem (yellow in line drawing) is to the outside and the xylem (blue in line drawing) is to the inside of each bundle. In herbaceous dicot stems, the vascular system makes a ring, with th ...
Plant morphology

Plant morphology or phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level. Plant morphology is useful in the visual identification of plants.