video slide
... widely divergent species provide information in many fields of biology • The more similar the nucleotide sequences between two species, the more closely related these species are in their evolutionary history • Comparative genome studies confirm the relevance of research on simpler organisms to ...
... widely divergent species provide information in many fields of biology • The more similar the nucleotide sequences between two species, the more closely related these species are in their evolutionary history • Comparative genome studies confirm the relevance of research on simpler organisms to ...
video slide - Morgan Community College
... widely divergent species provide information in many fields of biology • The more similar the nucleotide sequences between two species, the more closely related these species are in their evolutionary history • Comparative genome studies confirm the relevance of research on simpler organisms to ...
... widely divergent species provide information in many fields of biology • The more similar the nucleotide sequences between two species, the more closely related these species are in their evolutionary history • Comparative genome studies confirm the relevance of research on simpler organisms to ...
DNA Technology - De Anza College
... How is the stone washed denim look achieved? Via genetic engineering… • Recombinant DNA techniques are used • To clone cellulase genes in bacteria • To produce large quantities of cellulase To sell to textile manufacturers ...
... How is the stone washed denim look achieved? Via genetic engineering… • Recombinant DNA techniques are used • To clone cellulase genes in bacteria • To produce large quantities of cellulase To sell to textile manufacturers ...
Chapter 5 - FIU Faculty Websites
... Sequence should be known It should grow to high copy number in the host cell. (relax plasmid) Replicon sequence (ori + regulatory sequence) It should contain a selectable marker that allows cells containing the plasmid to be isolated. It should also contain a second selectable gene that is inac ...
... Sequence should be known It should grow to high copy number in the host cell. (relax plasmid) Replicon sequence (ori + regulatory sequence) It should contain a selectable marker that allows cells containing the plasmid to be isolated. It should also contain a second selectable gene that is inac ...
Student Genetic recombination
... bacteria as a defense mechanism against phages. The enzymes act like scissors, cutting up the DNA of the phage and thereby inactivating it. Importantly, restriction enzymes do not cut randomly; rather, they cut at specific DNA target sequences, which is one of the key features that make them suitabl ...
... bacteria as a defense mechanism against phages. The enzymes act like scissors, cutting up the DNA of the phage and thereby inactivating it. Importantly, restriction enzymes do not cut randomly; rather, they cut at specific DNA target sequences, which is one of the key features that make them suitabl ...
PART I
... provide material for analysis, sequencing etc. Producing many identical copies of the same recombinant molecule is called cloning. Cloning can be done in vitro, by a process called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and in vivo. Cloning in vivo can be done in ...
... provide material for analysis, sequencing etc. Producing many identical copies of the same recombinant molecule is called cloning. Cloning can be done in vitro, by a process called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and in vivo. Cloning in vivo can be done in ...
file - ORCA - Cardiff University
... 11. The library can now be screened to identify protein variants with the required properties. ...
... 11. The library can now be screened to identify protein variants with the required properties. ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard
... into the plasmid, the recombined DNA is ___________ into a bacterial cell. • An advantage to using bacterial cells to clone DNA is that they reproduce quickly; therefore, millions of bacteria are produced and each bacterium contains hundreds of recombinant DNA __________________ ...
... into the plasmid, the recombined DNA is ___________ into a bacterial cell. • An advantage to using bacterial cells to clone DNA is that they reproduce quickly; therefore, millions of bacteria are produced and each bacterium contains hundreds of recombinant DNA __________________ ...
MCB 421-2006: Homologous Recombination
... RecG and RUV proteins 1) work at the stage of recombinational repair that is different from the stage at which RecBC and RecFOR work; 2) define the two alternative pathways of the stage. If we combine the results of epistatic analysis with the previous results of the substrate analysis above, we arr ...
... RecG and RUV proteins 1) work at the stage of recombinational repair that is different from the stage at which RecBC and RecFOR work; 2) define the two alternative pathways of the stage. If we combine the results of epistatic analysis with the previous results of the substrate analysis above, we arr ...
Treatment of lactose intolerance via β-galactosidase - Blogs at H-SC
... need to be mindful to bring the pills and ingest them prior to any time they wished to consume lactose. Although there are some limited treatment options for lactose intolerance, cures do not yet exist. Because hypolactasia is a genetic disorder, a cure would require gene therapy, in which a functio ...
... need to be mindful to bring the pills and ingest them prior to any time they wished to consume lactose. Although there are some limited treatment options for lactose intolerance, cures do not yet exist. Because hypolactasia is a genetic disorder, a cure would require gene therapy, in which a functio ...
פרויקט מחקר - בנימין קפא
... • The WT strains morphology is round throughout all the streaks. • In the case of a severe mutation (terD) the morphology is severe in the early passages and it improved during the passages which is believed to be due to an elongation of the telomeres in a recombination pathway. The telomeres shorte ...
... • The WT strains morphology is round throughout all the streaks. • In the case of a severe mutation (terD) the morphology is severe in the early passages and it improved during the passages which is believed to be due to an elongation of the telomeres in a recombination pathway. The telomeres shorte ...
Biotechnology - Department of Plant Biology
... visible at the right) do not make ßpresence of ß-galactosidase. Those galactosidase, because their gene for that colonies of bacteria that contain intact ßenzyme has been interrupted by the insertion galactosidase genes will synthesize ßof a foreign piece of DNA. galactosidase and turn blue. Colonie ...
... visible at the right) do not make ßpresence of ß-galactosidase. Those galactosidase, because their gene for that colonies of bacteria that contain intact ßenzyme has been interrupted by the insertion galactosidase genes will synthesize ßof a foreign piece of DNA. galactosidase and turn blue. Colonie ...
2. Biotechnology
... 65. You have a cDNA of unknown sequence in a plasmid vector. How could you do a PCR amplification of the cDNA without first determining its end sequences? 66. What aspects of PCR make it particularly useful in forensic investigations? How do the same properties make PCR particularly susceptible to c ...
... 65. You have a cDNA of unknown sequence in a plasmid vector. How could you do a PCR amplification of the cDNA without first determining its end sequences? 66. What aspects of PCR make it particularly useful in forensic investigations? How do the same properties make PCR particularly susceptible to c ...
Bacteria / Monerans
... – Methanogens are found in anaerobic environments.such as marshes and in the intestinal tracts of animals. They produce methane as a result of cellular respiration. – Halophiles are found in environments with high salt concentration such as the great salt lake or soil with a high salt concentration. ...
... – Methanogens are found in anaerobic environments.such as marshes and in the intestinal tracts of animals. They produce methane as a result of cellular respiration. – Halophiles are found in environments with high salt concentration such as the great salt lake or soil with a high salt concentration. ...
DNA
... lytic bacteriophage that is now carrying donor bacterial DNA due to an error in maturation during the lytic life cycle. specialized transduction: A DNA fragment is transferred from one bacterium to another by a temperate bacteriophage that is now carrying donor bacterial DNA due to an error in spon ...
... lytic bacteriophage that is now carrying donor bacterial DNA due to an error in maturation during the lytic life cycle. specialized transduction: A DNA fragment is transferred from one bacterium to another by a temperate bacteriophage that is now carrying donor bacterial DNA due to an error in spon ...
Investigating a Eukaryotic Genome
... in the Student pages. As a control, students also set up a ligation reaction that contains no insert. By using this control in a transformation reaction, they can get a background reading of the frequency of vector reclosure without insert by counting any resulting colonies. Since the vector is tre ...
... in the Student pages. As a control, students also set up a ligation reaction that contains no insert. By using this control in a transformation reaction, they can get a background reading of the frequency of vector reclosure without insert by counting any resulting colonies. Since the vector is tre ...
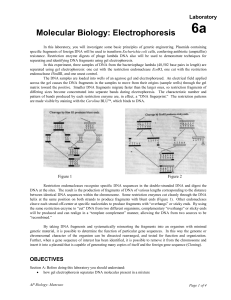
Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
Microbiology - Imperial Valley College
... restriction enzyme come together, they can join by base pairing. The joined fragments will usually form either a linear molecule or a circular one, as shown here for a plasmid. Other combinations of fragments can also occur. ...
... restriction enzyme come together, they can join by base pairing. The joined fragments will usually form either a linear molecule or a circular one, as shown here for a plasmid. Other combinations of fragments can also occur. ...
13.2 abbreviated Interactive Text
... vitamins in certain crops. That will help provide better nutrition. Some plants have already been developed that produce toxins to make them resistant to insects. That will limit the use of dangerous pesticides. ...
... vitamins in certain crops. That will help provide better nutrition. Some plants have already been developed that produce toxins to make them resistant to insects. That will limit the use of dangerous pesticides. ...
Re-Purification of Plasmid DNA Prepared by Methods other
... If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, store the eluate at 4°C. Storage periods longer than overnight are not recommended. 7. Precipitate DNA by adding 3.5 ml or 10.5 ml (0.7 volumes) room-temperature isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at 15,000 x g for 30 mi ...
... If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, store the eluate at 4°C. Storage periods longer than overnight are not recommended. 7. Precipitate DNA by adding 3.5 ml or 10.5 ml (0.7 volumes) room-temperature isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at 15,000 x g for 30 mi ...
mutation
... 7. Name three cellular uses of general recombination. 8. What are the constraints of genetic crossovers in general recombination? 9. Describe recombination, its main steps, and the key enzymes involved. I will NOT ask about inner strand versus outer strand resolution. 10. What is complementation and ...
... 7. Name three cellular uses of general recombination. 8. What are the constraints of genetic crossovers in general recombination? 9. Describe recombination, its main steps, and the key enzymes involved. I will NOT ask about inner strand versus outer strand resolution. 10. What is complementation and ...
Microbial Gene Transfer: An Ecological
... recipient. A significant effect of temperature was observed, with no transfer below 10 °C. Natural transformation of indigenous marine bacteria has been demonstrated by Frischer et al. (1994) using plasmid multimers of pQSR50. Plasmid multimers were used to ensure internal homology and thus provide ...
... recipient. A significant effect of temperature was observed, with no transfer below 10 °C. Natural transformation of indigenous marine bacteria has been demonstrated by Frischer et al. (1994) using plasmid multimers of pQSR50. Plasmid multimers were used to ensure internal homology and thus provide ...
Author`s personal copy
... Some bacteria are able to take up DNA from their general environment (transformation), including DNA that encodes resistance determinants. Resistance genes are rarely found in bacteriophages, but they can move DNA between cells (transduction), and their mechanisms for integration into host chromosom ...
... Some bacteria are able to take up DNA from their general environment (transformation), including DNA that encodes resistance determinants. Resistance genes are rarely found in bacteriophages, but they can move DNA between cells (transduction), and their mechanisms for integration into host chromosom ...
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that may benefit the survival of the organism, for example antibiotic resistance. While the chromosomes are big and contain all the essential information for living, plasmids usually are very small and contain only additional information. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms.Plasmids are considered replicons, a unit of DNA capable of replicating autonomously within a suitable host. However, plasmids, like viruses, are not generally classified as life. Plasmids can be transmitted from one bacterium to another (even of another species) via three main mechanisms: transformation, transduction, and conjugation. This host-to-host transfer of genetic material is called horizontal gene transfer, and plasmids can be considered part of the mobilome. Unlike viruses (which encase their genetic material in a protective protein coat called a capsid), plasmids are ""naked"" DNA and do not encode genes necessary to encase the genetic material for transfer to a new host. However, some classes of plasmids encode the conjugative ""sex"" pilus necessary for their own transfer. The size of the plasmid varies from 1 to over 200 kbp, and the number of identical plasmids in a single cell can range anywhere from one to thousands under some circumstances.The relationship between microbes and plasmid DNA is neither parasitic nor mutualistic, because each implies the presence of an independent species living in a detrimental or commensal state with the host organism. Rather, plasmids provide a mechanism for horizontal gene transfer within a population of microbes and typically provide a selective advantage under a given environmental state. Plasmids may carry genes that provide resistance to naturally occurring antibiotics in a competitive environmental niche, or the proteins produced may act as toxins under similar circumstances, or allow the organism to utilize particular organic compounds that would be advantageous when nutrients are scarce.