Somatoform disorders (part 1)
... • A false belief, not to the degree of delusion, that they have serious illness based on misinterpretation of physical signs or sensations. The belief must last at least 6 months despite the absence of pathological findings. This should not be restricted to distress about appearance. • Specify if: w ...
... • A false belief, not to the degree of delusion, that they have serious illness based on misinterpretation of physical signs or sensations. The belief must last at least 6 months despite the absence of pathological findings. This should not be restricted to distress about appearance. • Specify if: w ...
Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Abnormal Behavior: The
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
Chapter 15 Activity: DIAGNOSING Psychological Disorders
... one and her house was badly damaged. She has frequent nightmares about earthquakes, and even when awake she sometimes gets flashes as if she's reliving the experience. The slightest noise or movement around her causes her heart to pound rapidly. Post traumatic stress disorder ...
... one and her house was badly damaged. She has frequent nightmares about earthquakes, and even when awake she sometimes gets flashes as if she's reliving the experience. The slightest noise or movement around her causes her heart to pound rapidly. Post traumatic stress disorder ...
Dissociative Diso
... People with Hypochondriasis often see many doctors, looking for someone to confirm the illness. ...
... People with Hypochondriasis often see many doctors, looking for someone to confirm the illness. ...
Abnormal Psychology - North Cobb High School Class Websites
... sociocultural factors combine to interact causing psychological disorders. ...
... sociocultural factors combine to interact causing psychological disorders. ...
Theories of personality
... Your turn If you have the persistent thought that gremlins are sabotaging any airplane you are on or will be on, then you have a _____. If you cannot stop asking for more water during flights, then you have a _____. ...
... Your turn If you have the persistent thought that gremlins are sabotaging any airplane you are on or will be on, then you have a _____. If you cannot stop asking for more water during flights, then you have a _____. ...
Major Mental Illnesses
... The manic type of schizoaffective disorder often takes the form of elation, with increased self-confidence and grandiosity. The person may feel energized, but may act inappropriately in social situations, and have trouble concentrating. Symptoms of psychosis are also present, and the person’s behavi ...
... The manic type of schizoaffective disorder often takes the form of elation, with increased self-confidence and grandiosity. The person may feel energized, but may act inappropriately in social situations, and have trouble concentrating. Symptoms of psychosis are also present, and the person’s behavi ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... • Diagnosis requires that a person have at least two separate ego states (called alters) that exist independently of each other and that come forth and are in control at different times – Usually one primary personality and two to four alters at time of diagnosis – Treatment sought by the primary al ...
... • Diagnosis requires that a person have at least two separate ego states (called alters) that exist independently of each other and that come forth and are in control at different times – Usually one primary personality and two to four alters at time of diagnosis – Treatment sought by the primary al ...
Psychological Disorders
... People with social phobias often have panic attacks, or short, intense periods of fear or discomfort that feels a lot like a heart attack… Some people have such abrasive fears of social situation that they become closed off to the world. Agoraphobia is a fear of being in places or situations in whic ...
... People with social phobias often have panic attacks, or short, intense periods of fear or discomfort that feels a lot like a heart attack… Some people have such abrasive fears of social situation that they become closed off to the world. Agoraphobia is a fear of being in places or situations in whic ...
Medically Unexplained Physical Symptoms
... Intentional feigning of symptoms Aim is to receive medical care Often marked personality disorder & interpersonal difficulties (Malingering- different motive e.g: Financial Avoid court/ conscription) ...
... Intentional feigning of symptoms Aim is to receive medical care Often marked personality disorder & interpersonal difficulties (Malingering- different motive e.g: Financial Avoid court/ conscription) ...
DSM IV-TR - MsHughesPsychology
... Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging. C. The person recognizes that the fear is excessive or unreasonable. Note: In children, this feature may be absent. D. The phobic situation(s) is avoided or else is endured with intense anxiety or distress. E ...
... Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging. C. The person recognizes that the fear is excessive or unreasonable. Note: In children, this feature may be absent. D. The phobic situation(s) is avoided or else is endured with intense anxiety or distress. E ...
15 - smw15.org
... Does the behavior interfere with the person’s ability to function personally, socially, or occupationally? Many psychologists believe this is the best criterion for determining the normality of behavior ...
... Does the behavior interfere with the person’s ability to function personally, socially, or occupationally? Many psychologists believe this is the best criterion for determining the normality of behavior ...
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... -persistent irrational fears of common events or objects -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, un ...
... -persistent irrational fears of common events or objects -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, un ...
Psychopathology
... Paranoid Schizophrenia is characterized by an array of hallucinations and delusions, but unlike the jumble of the hebephrenic, these are wellorganized into one or more unifying themes. Four common delusions: Delusions of Persecution – the paranoid believes that some person or group is determined to ...
... Paranoid Schizophrenia is characterized by an array of hallucinations and delusions, but unlike the jumble of the hebephrenic, these are wellorganized into one or more unifying themes. Four common delusions: Delusions of Persecution – the paranoid believes that some person or group is determined to ...
MODERN INDICATIONS FOR THE USE OF OPIPRAMOL
... during pharmacotherapy in the outpatient is that opipramol is used in very small doses and the drug is takien over too short a period (Prusiński 2003b). Except from the traditional form of the drug introduced in the 60s, a search for new pharmacological options has been made. The appearance of susta ...
... during pharmacotherapy in the outpatient is that opipramol is used in very small doses and the drug is takien over too short a period (Prusiński 2003b). Except from the traditional form of the drug introduced in the 60s, a search for new pharmacological options has been made. The appearance of susta ...
Child and Adolescent Anxiety Disorders
... repeatedly for no apparent reason, often accompanied by intense physical symptoms such as dizziness, abdominal distress, chest pain, pounding heart, and shortness of breath.This is differentiated from a generalized anxiety attack because there’s no apparent reason, and no identifiable worry that bro ...
... repeatedly for no apparent reason, often accompanied by intense physical symptoms such as dizziness, abdominal distress, chest pain, pounding heart, and shortness of breath.This is differentiated from a generalized anxiety attack because there’s no apparent reason, and no identifiable worry that bro ...
Perspectives on Psychological Disorders
... • A mood disorder in which periods of mania and depression alternate, sometimes with periods of normal mood intervening. ...
... • A mood disorder in which periods of mania and depression alternate, sometimes with periods of normal mood intervening. ...
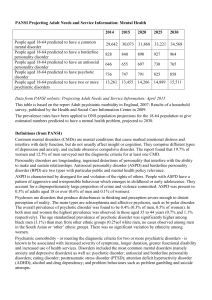
Mental Health Projections: PANSI 2015
... estimated numbers predicted to have a mental health problem, projected to 2030. Definitions (from PANSI) Common mental disorders (CMDs) are mental conditions that cause marked emotional distress and interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise differen ...
... estimated numbers predicted to have a mental health problem, projected to 2030. Definitions (from PANSI) Common mental disorders (CMDs) are mental conditions that cause marked emotional distress and interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise differen ...
Drug treatment for Anxiety Disorders
... Tolerance will inevitably develop and she will need increasing doses of xanax. Iatrogenic dependence will occur She is very sensitive to the side effect of SSRI. Initially SSRIs can increase anxiety and she will need to start on a lower dose before increasing. Correct approach Stopping xanax abruptl ...
... Tolerance will inevitably develop and she will need increasing doses of xanax. Iatrogenic dependence will occur She is very sensitive to the side effect of SSRI. Initially SSRIs can increase anxiety and she will need to start on a lower dose before increasing. Correct approach Stopping xanax abruptl ...
Module 17 + 18 Practice Questions: 30 points total
... C) What might be considered abnormal in one culture could be normal in another culture. D) The frequency of mental disorders differ among the countries of the world. ____ 23. A cultural variable that may explain the differences in the percentage of men and percentage of women reporting depression is ...
... C) What might be considered abnormal in one culture could be normal in another culture. D) The frequency of mental disorders differ among the countries of the world. ____ 23. A cultural variable that may explain the differences in the percentage of men and percentage of women reporting depression is ...
Somatoform Disorders
... Clinical Description • Pain that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • There may have been clear physical reasons for the pain initially, but psychological factors play a major role in maintaining it. • The pain is real & it hurts regardless of the cause • Whatever it ...
... Clinical Description • Pain that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • There may have been clear physical reasons for the pain initially, but psychological factors play a major role in maintaining it. • The pain is real & it hurts regardless of the cause • Whatever it ...