Psychiatry and Medicine
... • The sudden onset of severe chest pain frequently causes anxiety. • In severe infarcts, delirium is frequent. • A sizable minority of patients show denial with little distress, if denial persist it may lead to non-compliant with treatment. • In the weeks after an infarct patients frequently describ ...
... • The sudden onset of severe chest pain frequently causes anxiety. • In severe infarcts, delirium is frequent. • A sizable minority of patients show denial with little distress, if denial persist it may lead to non-compliant with treatment. • In the weeks after an infarct patients frequently describ ...
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
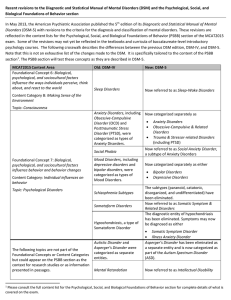
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
Blue and Red Gradient
... The only diagnosis that is appropriate of Susan is that of separation anxiety disorder; Susan's mom is reported to suffer from panic disorder and the dad from depression. Each disorder is associated significantly with SAD in off-spring and a history of both further increases the risk ...
... The only diagnosis that is appropriate of Susan is that of separation anxiety disorder; Susan's mom is reported to suffer from panic disorder and the dad from depression. Each disorder is associated significantly with SAD in off-spring and a history of both further increases the risk ...
Psychological Disorders
... Medical (physical) conditions influencing Axis 1 & 2 disorders Axis 4 Psychosocial & environmental stress influencing Axis 1 & 2 disorders Axis 5 Global Assessment of Functioning score: highest level of functioning patient has achieved in work, relationships, and activities ...
... Medical (physical) conditions influencing Axis 1 & 2 disorders Axis 4 Psychosocial & environmental stress influencing Axis 1 & 2 disorders Axis 5 Global Assessment of Functioning score: highest level of functioning patient has achieved in work, relationships, and activities ...
Chapter 4 Reading Guide
... A. Understanding Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD—Causes 1. Explain how we learn fear from the learning perspective. ...
... A. Understanding Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD—Causes 1. Explain how we learn fear from the learning perspective. ...
Students with Mental Disorders
... Anxiety in childhood predicts anxiety disorders, major depression, suicide attempts, and psychiatric hospitalization in adulthood. ...
... Anxiety in childhood predicts anxiety disorders, major depression, suicide attempts, and psychiatric hospitalization in adulthood. ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Feelings of worthlessness Loss of interest in family & friends Loss of interest in activities ...
... Feelings of worthlessness Loss of interest in family & friends Loss of interest in activities ...
Depression and anxiety in dissociative (conversion) disorder
... Conversion disorder is judged to be caused by psychological factors as the illness is preceded by conflicts or other stressors. The symptoms are not intentionally produced, are not caused by substance use, and the gain is primarily psychological and not social, monetary, or legal.1 As the duration o ...
... Conversion disorder is judged to be caused by psychological factors as the illness is preceded by conflicts or other stressors. The symptoms are not intentionally produced, are not caused by substance use, and the gain is primarily psychological and not social, monetary, or legal.1 As the duration o ...
Mental Health in Children and Adolescents
... Flashbacks, hallucinations, nightmares, recollections, reenactment, or repetitive play referencing the event Emotional distress from reminders of the event Physical reactions from reminders of the event Fear of certain places, things, or situations that remind them of the event Denial of the event A ...
... Flashbacks, hallucinations, nightmares, recollections, reenactment, or repetitive play referencing the event Emotional distress from reminders of the event Physical reactions from reminders of the event Fear of certain places, things, or situations that remind them of the event Denial of the event A ...
Schizophrenic Disorders
... E. The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition. F. If there is a history of autism spectrum disorder or a communication disorder of childhood onset, the additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is mad ...
... E. The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition. F. If there is a history of autism spectrum disorder or a communication disorder of childhood onset, the additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is mad ...
Anxiety Disorders in the Elderly
... may underestimate the true rates. The evidence from case reports, and nonpsychiatric patient and volunteer samples, suggests that panic in old age is less common than in early adulthood, is more common in women and widows and is symptomatically less severe than in early onset cases (Sheikh et al, ...
... may underestimate the true rates. The evidence from case reports, and nonpsychiatric patient and volunteer samples, suggests that panic in old age is less common than in early adulthood, is more common in women and widows and is symptomatically less severe than in early onset cases (Sheikh et al, ...
Best Practices for People with Mild Autism Spectrum
... 2. Excessive adherence to routines, ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior, or excessive resistance to change; (such as motoric rituals, insistence on same route or food, repetitive questioning or extreme distress at small changes); 3. Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnor ...
... 2. Excessive adherence to routines, ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior, or excessive resistance to change; (such as motoric rituals, insistence on same route or food, repetitive questioning or extreme distress at small changes); 3. Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnor ...
Psychology is defined as the science of
... One of the negative effects of labeling a person with a mental illness is: a. because of the media's influence, most people think those with a mental illness are extremely passive and peaceful. b. labels help mental health professionals communicate with each other. c. labels influence expectations a ...
... One of the negative effects of labeling a person with a mental illness is: a. because of the media's influence, most people think those with a mental illness are extremely passive and peaceful. b. labels help mental health professionals communicate with each other. c. labels influence expectations a ...
The Mind Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
... • Mild depressive illness supportive psychotherapy • For moderate to severe depressive illnesses (having more than the minimal number of diagnostic criteria) or non-responders to brief supportive therapy consider SSRI, CBT/IPT or a combination. ...
... • Mild depressive illness supportive psychotherapy • For moderate to severe depressive illnesses (having more than the minimal number of diagnostic criteria) or non-responders to brief supportive therapy consider SSRI, CBT/IPT or a combination. ...
Types of Mood Disorders
... Factors that place people at increased risk of developing major depression include: ...
... Factors that place people at increased risk of developing major depression include: ...
Somatoform Disorder
... somatoform disorder. A type of disease this is characterized under it is hypochondria. When you’re fearful and precautious. You usually deal with: Depression, anxiety, pains, ect. ...
... somatoform disorder. A type of disease this is characterized under it is hypochondria. When you’re fearful and precautious. You usually deal with: Depression, anxiety, pains, ect. ...
The Numbers Count: Mental Disorders in America
... Horne RL. Binge eating disorder: its further validation in a multisite study. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 1993 Mar;13(2):137-53. 16. American Psychiatric Association Work Group on Eating Disorders. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with eating disorders (revision). Amer ...
... Horne RL. Binge eating disorder: its further validation in a multisite study. International Journal of Eating Disorders. 1993 Mar;13(2):137-53. 16. American Psychiatric Association Work Group on Eating Disorders. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with eating disorders (revision). Amer ...
Psychodynamic Treatment of Panic Disorder
... relationships with significant others, usually parents or other caregivers. In either case, significant others are perceived as ‘‘unreliable,’’ prone to abandoning and rejecting the child. In response to perceived rejection or unavailability, and due to the narcissistic injury of dependency, the chi ...
... relationships with significant others, usually parents or other caregivers. In either case, significant others are perceived as ‘‘unreliable,’’ prone to abandoning and rejecting the child. In response to perceived rejection or unavailability, and due to the narcissistic injury of dependency, the chi ...
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Overview
... genetic component. • There is a genetic relationship between Tourette disorder and both ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. • Atypical antipsychotic agents and typical agents are the most effective treatments for Tourette disorder. • In milder cases, medication such as clonidine also are helpful ...
... genetic component. • There is a genetic relationship between Tourette disorder and both ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. • Atypical antipsychotic agents and typical agents are the most effective treatments for Tourette disorder. • In milder cases, medication such as clonidine also are helpful ...
Specific Phobias
... The description and treatment of specific phobias, or fear of specific objects or situations, are embedded in the history of psychiatry and psychology. Indeed, Freud’s classic analytic case of “Little Hans” illustrated a common form of specific phobia (animal type).1 As opposed to psychodynamic theo ...
... The description and treatment of specific phobias, or fear of specific objects or situations, are embedded in the history of psychiatry and psychology. Indeed, Freud’s classic analytic case of “Little Hans” illustrated a common form of specific phobia (animal type).1 As opposed to psychodynamic theo ...
Does This Patient Have Generalized Anxiety or Panic Disorder? The
... which contributes to underrecognition of these conditions and can result in unnecessary and costly diagnostic testing.6 When diagnosed, both GAD and panic disorder can be treated successfully with medication and/or psychotherapy. Furthermore, care management trials have shown that screening, coupled ...
... which contributes to underrecognition of these conditions and can result in unnecessary and costly diagnostic testing.6 When diagnosed, both GAD and panic disorder can be treated successfully with medication and/or psychotherapy. Furthermore, care management trials have shown that screening, coupled ...
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... The steps in the management of such patients can be :summarized as follows Check the diagnosis and comorbidity, especially depressive disorder, substance abuse, or a physical cause such as thyrotoxicosis. If any of these are present, treat ...
... The steps in the management of such patients can be :summarized as follows Check the diagnosis and comorbidity, especially depressive disorder, substance abuse, or a physical cause such as thyrotoxicosis. If any of these are present, treat ...
nur201moduleC
... Crises are personal by nature. Crises are acute, not chronic, and are resolved in one way or another within a brief period. A crisis situation contains the potential for psychological growth or deterioration. ...
... Crises are personal by nature. Crises are acute, not chronic, and are resolved in one way or another within a brief period. A crisis situation contains the potential for psychological growth or deterioration. ...
Substance Abuse
... • For dual diagnosis patients, psychotherapy has significant advantages over substance abuse counseling alone, and can be incorporated into the substance abuse treatment. ...
... • For dual diagnosis patients, psychotherapy has significant advantages over substance abuse counseling alone, and can be incorporated into the substance abuse treatment. ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.