Trauma And First Responders
... Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. Vol. 19 (5), 503-507. Bisson, J. I., McFarlane, A. C., & Rose, S. (2000). Psychological debriefing. In E. F. Foa, T. M. Keane, & M. J. Friedman (Eds.) Effective treatments for PTSD (pp. 39-59, 317-319). New York: Guilford. Bohl, N. (1995). Professional ...
... Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. Vol. 19 (5), 503-507. Bisson, J. I., McFarlane, A. C., & Rose, S. (2000). Psychological debriefing. In E. F. Foa, T. M. Keane, & M. J. Friedman (Eds.) Effective treatments for PTSD (pp. 39-59, 317-319). New York: Guilford. Bohl, N. (1995). Professional ...
A Survival Guide to the DSM-5
... hyperactivity disorder, combined presentation, moderate (principal diagnosis) and V62.3 academic or educational problem (reason for visit) ...
... hyperactivity disorder, combined presentation, moderate (principal diagnosis) and V62.3 academic or educational problem (reason for visit) ...
Research-Based Direction for the Use of Amino
... actually affect and shape brain structures, and create enduring neuronal pathways. In turn, these pathways create automatic responses which can be changed, but only with focused attention, practice, and new interpersonal experiences, such as those created in long-term therapy. In the DSM IV (Diagnos ...
... actually affect and shape brain structures, and create enduring neuronal pathways. In turn, these pathways create automatic responses which can be changed, but only with focused attention, practice, and new interpersonal experiences, such as those created in long-term therapy. In the DSM IV (Diagnos ...
Somatic Symptom Disorders: a new approach in DSM-5
... The somatic symptoms workgroup sharply reduced the number of diagnoses, either by elimination or by regrouping. For factitious disorder, the variants were reduced from 2 to 1. For psychological factors affected medical condition (PFAMC), the 6 subtypes were entirely eliminated in favor of one diagno ...
... The somatic symptoms workgroup sharply reduced the number of diagnoses, either by elimination or by regrouping. For factitious disorder, the variants were reduced from 2 to 1. For psychological factors affected medical condition (PFAMC), the 6 subtypes were entirely eliminated in favor of one diagno ...
Anxiety and anxiety disorders
... the body via the nervous system and hormones to get ready for 'fight or flight.' This causes an increase in breathing and heart rate and a change in blood flow throughout the body, to prepare it for movement. It can also be accompanied by unpleasant feelings such as dizziness, nausea and perspiratio ...
... the body via the nervous system and hormones to get ready for 'fight or flight.' This causes an increase in breathing and heart rate and a change in blood flow throughout the body, to prepare it for movement. It can also be accompanied by unpleasant feelings such as dizziness, nausea and perspiratio ...
Doctor Letter - What is Misophonia?
... over their reactions. They realize that their sensitivities to these sounds are irrational, but their brains appear to get hijacked and their emotional centers activated, perhaps related to a brain error involving the normal fight or flight response that all humans experience in a threatening situat ...
... over their reactions. They realize that their sensitivities to these sounds are irrational, but their brains appear to get hijacked and their emotional centers activated, perhaps related to a brain error involving the normal fight or flight response that all humans experience in a threatening situat ...
The RNBC Stress and Anxiety Clinic
... disorders, especially for those children who struggle with social-emotional learning deficits. She has extensive experience using CBT, mindfulness, stress reduction methods, and hypnotherapy, and works closely with families and schools, as needed. Her research includes efficacy assessment of treatme ...
... disorders, especially for those children who struggle with social-emotional learning deficits. She has extensive experience using CBT, mindfulness, stress reduction methods, and hypnotherapy, and works closely with families and schools, as needed. Her research includes efficacy assessment of treatme ...
Mood & Disruptive Behavior Disorders in Children & Adolescents
... opiate-like substance in the brain, is released in animals during social behavior. Additionally, there is evidence that the beta-endorphin levels in autistic individuals is elevated so they do not need to rely on social interaction for pleasure. Some research on the drug, naltrexone, which blocks th ...
... opiate-like substance in the brain, is released in animals during social behavior. Additionally, there is evidence that the beta-endorphin levels in autistic individuals is elevated so they do not need to rely on social interaction for pleasure. Some research on the drug, naltrexone, which blocks th ...
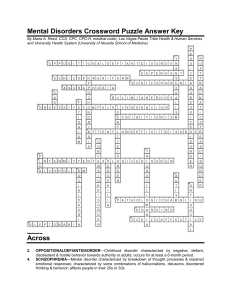
Mental Disorders Crossword Puzzle Answer Key Across
... with an inability to discard or part with them; has been upgraded to a full blown diagnostic category in DSM-5 HYPOCHONDRIASIS—Type of mental illness where a person has symptoms of medical illness but can't be explained by actual physical disorder; characterized by excessive preoccupation or worry a ...
... with an inability to discard or part with them; has been upgraded to a full blown diagnostic category in DSM-5 HYPOCHONDRIASIS—Type of mental illness where a person has symptoms of medical illness but can't be explained by actual physical disorder; characterized by excessive preoccupation or worry a ...
Personality Disorder
... • Histrionic Personality Disorder – the person engages in attentiongrabbing emotional outbursts and tries to gain other’s approval • Narcissistic Personality Disorder – the person is very self-absorbed and have delusions of grandeur • Borderline Personality Disorder – the person has unstable emotion ...
... • Histrionic Personality Disorder – the person engages in attentiongrabbing emotional outbursts and tries to gain other’s approval • Narcissistic Personality Disorder – the person is very self-absorbed and have delusions of grandeur • Borderline Personality Disorder – the person has unstable emotion ...
disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence
... of an extreme autistic aloneness that, whenever possible, disregards, ignores, shuts out anything that comes to the child from the outside • Prior to age three • Abnormal functioning in at least one area: – social interaction – language by social communication – symbolic/imaginative play ...
... of an extreme autistic aloneness that, whenever possible, disregards, ignores, shuts out anything that comes to the child from the outside • Prior to age three • Abnormal functioning in at least one area: – social interaction – language by social communication – symbolic/imaginative play ...
anxiety and brain injury - ABI Partnership Project
... It is common to experience a range of these symptoms following a trauma but generally the majority of symptoms will diminish in the days and weeks to follow. It is also quite common to experience a range of these symptoms as a direct result of sustaining a traumatic brain injury. Common outcomes of ...
... It is common to experience a range of these symptoms following a trauma but generally the majority of symptoms will diminish in the days and weeks to follow. It is also quite common to experience a range of these symptoms as a direct result of sustaining a traumatic brain injury. Common outcomes of ...
PsychAP Notes pt 11
... is a genetic predisposition to Schizophrenia. A traumatic life will trigger that genetic predisposition. If they get assaulted or are in a car accident or take a lot of drugs, it may trigger the disorder. The Systems Theory (biopsychosocial model) is a model in which biological, psychological, and s ...
... is a genetic predisposition to Schizophrenia. A traumatic life will trigger that genetic predisposition. If they get assaulted or are in a car accident or take a lot of drugs, it may trigger the disorder. The Systems Theory (biopsychosocial model) is a model in which biological, psychological, and s ...
Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood
... Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, or Adolescence Mental Retardation; Learning Disorders Communication Disorders Autistic Spectrum Disorders Attention-Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders of Infancy or Early Childhood Tic Disorders Other Disor ...
... Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, or Adolescence Mental Retardation; Learning Disorders Communication Disorders Autistic Spectrum Disorders Attention-Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders of Infancy or Early Childhood Tic Disorders Other Disor ...
Treatment of Young Children with Separation Anxiety
... more of the following symptoms develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes • Palpitations, sweating, trembling, shaking, shortness of breath, feeling of choking, chest pain or discomfort, nausea or abdominal distress, feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint, feelings of unreality, fea ...
... more of the following symptoms develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes • Palpitations, sweating, trembling, shaking, shortness of breath, feeling of choking, chest pain or discomfort, nausea or abdominal distress, feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint, feelings of unreality, fea ...
Workbook Assignment 4 Chapters 12 and 13 to correspond with
... 2. What normal traits do people with antisocial personality disorder seem to lack? ...
... 2. What normal traits do people with antisocial personality disorder seem to lack? ...
DSM-5 - Wiley
... distress and mood changes. For children and adolescents, mood may be reported as irritable. Presentation may differ from what is seen in an adult. May be confused with DMDD where the mood is consistently agitated for at least a year and does not take on a cyclic pattern in which the individual seems ...
... distress and mood changes. For children and adolescents, mood may be reported as irritable. Presentation may differ from what is seen in an adult. May be confused with DMDD where the mood is consistently agitated for at least a year and does not take on a cyclic pattern in which the individual seems ...
Slide 1
... Risk Factors Biological Factors: a) Neuroendocrinology – dysregulation of HPA axis cortisol production b) Sleep architecture – increased REM density c) Neurotransmitters – dysregulation of serotonin and norepinephrine d) Structural and functional brain correlates ...
... Risk Factors Biological Factors: a) Neuroendocrinology – dysregulation of HPA axis cortisol production b) Sleep architecture – increased REM density c) Neurotransmitters – dysregulation of serotonin and norepinephrine d) Structural and functional brain correlates ...
Somatoform Disorders
... One study showed 95% of patients with somatization disorder had been to health care provider in past 6 months vs. 56% of other community residents Typically episodes of illness are secondary to period of stress ...
... One study showed 95% of patients with somatization disorder had been to health care provider in past 6 months vs. 56% of other community residents Typically episodes of illness are secondary to period of stress ...
Psychological Disorders - Welcome to AP Psychology
... person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have somatoform disorder are not faking their symptoms. The pain that they feel i ...
... person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have somatoform disorder are not faking their symptoms. The pain that they feel i ...
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology
... • Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder in which the anxiety suddenly escalates at times into a terrifying panic attack, a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
... • Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder in which the anxiety suddenly escalates at times into a terrifying panic attack, a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch16
... personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal personality disorder, antisocial personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, histrionic personality, narcissistic personality disorder, avoidant personality disorder, dependent personality disorder and obsessivecompulsive pe ...
... personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal personality disorder, antisocial personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, histrionic personality, narcissistic personality disorder, avoidant personality disorder, dependent personality disorder and obsessivecompulsive pe ...
Podcast Script – Information about MDD for Parents and
... treatments, which I will describe in detail through their reports. The first group of treatments is medication. Several different pills can be taken to help people with depression depending on their symptoms. Therapy is a second type of treatment. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, is a therapy i ...
... treatments, which I will describe in detail through their reports. The first group of treatments is medication. Several different pills can be taken to help people with depression depending on their symptoms. Therapy is a second type of treatment. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, or CBT, is a therapy i ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... Somatoform Disorders • Psychological factors produce physical symptoms in the Somatoform Disorders: – Conversion disorder involves a change in sensory/motor function – Somatization disorder involves recurrent, multiple somatic complaints – In pain disorder, chronic pain results in distress – Body d ...
... Somatoform Disorders • Psychological factors produce physical symptoms in the Somatoform Disorders: – Conversion disorder involves a change in sensory/motor function – Somatization disorder involves recurrent, multiple somatic complaints – In pain disorder, chronic pain results in distress – Body d ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.