Chapter 14 Powerpoint
... • Specific Phobias – fear of objects or specific situations or events • Agoraphobia – fear of being in a place or situation ...
... • Specific Phobias – fear of objects or specific situations or events • Agoraphobia – fear of being in a place or situation ...
What is Abnormality?
... You can have a pre-disposition to a disorder without ever manifesting it. You can also have very stressful circumstances and never develop a disorder. ...
... You can have a pre-disposition to a disorder without ever manifesting it. You can also have very stressful circumstances and never develop a disorder. ...
Causes of Anxiety Disorders
... o Panic attacks—sudden episode of helpless terror with high physiological arousal o Very frightening—sufferers live in of having them o often develops as a result Cognitive-behavioral Theory of Panic Disorder: o Sufferers tend to misinterpret the physical signs of as and dangerous o This interpretat ...
... o Panic attacks—sudden episode of helpless terror with high physiological arousal o Very frightening—sufferers live in of having them o often develops as a result Cognitive-behavioral Theory of Panic Disorder: o Sufferers tend to misinterpret the physical signs of as and dangerous o This interpretat ...
The APA is offering a number of “emerging measures” for... clinical evaluation. These patient assessment measures were developed to be
... symptoms of panic disorder in children and adolescents. The measure was designed to be completed by the child upon receiving a diagnosis of panic disorder (or clinically significant panic disorder symptoms) and thereafter, prior to follow-up visits with the clinician. Each item asks the child receiv ...
... symptoms of panic disorder in children and adolescents. The measure was designed to be completed by the child upon receiving a diagnosis of panic disorder (or clinically significant panic disorder symptoms) and thereafter, prior to follow-up visits with the clinician. Each item asks the child receiv ...
Severity Measure for Panic Disorder, Adult
... The Severity Measure for Panic Disorder—Adult is a 10-item measure that assesses the severity of symptoms of panic disorder in individuals age 18 and older. The measure was designed to be completed by an individual upon receiving a diagnosis of panic disorder (or clinically significant panic disorde ...
... The Severity Measure for Panic Disorder—Adult is a 10-item measure that assesses the severity of symptoms of panic disorder in individuals age 18 and older. The measure was designed to be completed by an individual upon receiving a diagnosis of panic disorder (or clinically significant panic disorde ...
PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2 Current
... » Exposure to trigger leads to anxiety about being humiliated or embarrassed socially. » Onset often adolescence » Diagnosed as either generalized or specific 33% also diagnosed with Avoidant Personality Disorder » Overlap in genetic vulnerability for both disorders ...
... » Exposure to trigger leads to anxiety about being humiliated or embarrassed socially. » Onset often adolescence » Diagnosed as either generalized or specific 33% also diagnosed with Avoidant Personality Disorder » Overlap in genetic vulnerability for both disorders ...
anxiety disorders - Psychology for you and me
... cued by the presence, or thoughts, of particular stimuli or that occurs without obvious cues and is spontaneous and unpredictable. During these episodes, the person experiences the urge to flee, or the feeling that they need to escape. The symptoms may be misdiagnose as a serious medical condition ( ...
... cued by the presence, or thoughts, of particular stimuli or that occurs without obvious cues and is spontaneous and unpredictable. During these episodes, the person experiences the urge to flee, or the feeling that they need to escape. The symptoms may be misdiagnose as a serious medical condition ( ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Hypochondriasis • Physical complaints without a clear medical cause and severe anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious illness • Medical reassurance does not seem to help • Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders ...
... Hypochondriasis • Physical complaints without a clear medical cause and severe anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious illness • Medical reassurance does not seem to help • Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders ...
Psychological Issues of Adolescence
... Adolescent challenges include-‐availability and normality of early sexual activity, teen drinking and drug use, difficulty getting into a good college and paying for it, anticipation of entering a depressed job ...
... Adolescent challenges include-‐availability and normality of early sexual activity, teen drinking and drug use, difficulty getting into a good college and paying for it, anticipation of entering a depressed job ...
Mental Illness
... Experiencing feelings of sadness, loneliness, and hopelessness for an extended period of time. Bi-Polar Disorder aka Manic-Depressive Experiencing exaggerated feelings of euphoria, irritability, depression, exaggerated mood ...
... Experiencing feelings of sadness, loneliness, and hopelessness for an extended period of time. Bi-Polar Disorder aka Manic-Depressive Experiencing exaggerated feelings of euphoria, irritability, depression, exaggerated mood ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
... C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
Mood Disorders09
... compulsions are rituals or behavior that is performed to try to prevent or reduce the obsessive thoughts. Disorder that affects men and women equally, 1 in 50 often show up in teens, early adulthood. Obsessions-uncontrollable thoughts or impulses occur repeatedly Compulsions-performed behaviors or r ...
... compulsions are rituals or behavior that is performed to try to prevent or reduce the obsessive thoughts. Disorder that affects men and women equally, 1 in 50 often show up in teens, early adulthood. Obsessions-uncontrollable thoughts or impulses occur repeatedly Compulsions-performed behaviors or r ...
Anxiety Disorders
... » Onset often adolescence » Diagnosed as either generalized or specific 33% also diagnosed with Avoidant Personality Disorder » Overlap in genetic vulnerability for both disorders ...
... » Onset often adolescence » Diagnosed as either generalized or specific 33% also diagnosed with Avoidant Personality Disorder » Overlap in genetic vulnerability for both disorders ...
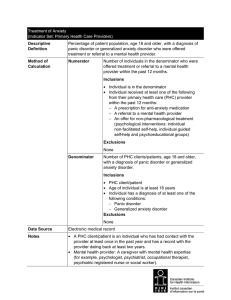
Treatment of Anxiety
... Indicator Rationale Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health disorders, but because of their chronic and disabling nature their prevalence is often underestimated.1–4 Evidence suggests that between 10% and 29% of Canadians will experience an anxiety disorder during their lifetime.5 ...
... Indicator Rationale Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health disorders, but because of their chronic and disabling nature their prevalence is often underestimated.1–4 Evidence suggests that between 10% and 29% of Canadians will experience an anxiety disorder during their lifetime.5 ...
Personality disorder
... emphasize habits of thinking and ways of interpreting events. Depressed people believe their situation is permanent, uncontrollable. Rumination Brooding about negative aspects of one’s life Cognitive therapy is often effective in treating depression ...
... emphasize habits of thinking and ways of interpreting events. Depressed people believe their situation is permanent, uncontrollable. Rumination Brooding about negative aspects of one’s life Cognitive therapy is often effective in treating depression ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Two main theoretical models of treatment – Medical Model • Diseases, including psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and controlled or cured (in most cases). • May include need for hospitalization. – Bio-psycho-social Model (perspective) • All behavior, incl ...
... • Two main theoretical models of treatment – Medical Model • Diseases, including psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and controlled or cured (in most cases). • May include need for hospitalization. – Bio-psycho-social Model (perspective) • All behavior, incl ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Physical Problems occur for psychological reasons. 1. Conversion Disorder: a rare disorder in which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no psychological basis can be found ...
... Physical Problems occur for psychological reasons. 1. Conversion Disorder: a rare disorder in which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no psychological basis can be found ...
File - Pharmacology (HOME)
... o Hypocortisolism: depression, motivation problems o Hypercortisolism: OCD, panic disorders, atrophy of the hippocampus Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Panic Disorder o GAD’s prominent feature: frequent, uncontrollable worrying which can manifest as physical symptoms Restlessness, irritabil ...
... o Hypocortisolism: depression, motivation problems o Hypercortisolism: OCD, panic disorders, atrophy of the hippocampus Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Panic Disorder o GAD’s prominent feature: frequent, uncontrollable worrying which can manifest as physical symptoms Restlessness, irritabil ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders and Stress
... difficulty breathing. Heart rate can accelerate up to 180 beats per minute and can last from a few minutes to an hour. Victims may believe they are going crazy or having a heart attack. –This collection of symptoms is called a Panic Attack ...
... difficulty breathing. Heart rate can accelerate up to 180 beats per minute and can last from a few minutes to an hour. Victims may believe they are going crazy or having a heart attack. –This collection of symptoms is called a Panic Attack ...
What is Anxiety?
... Anxiety disorders are typically overwhelming by nature and occur over a long time scale. Children may develop anxiety disorders for a whole host of reasons. Such disorders may include: Separation anxiety: Separation anxiety refers to the feelings of stress or worry induced when a child is away from ...
... Anxiety disorders are typically overwhelming by nature and occur over a long time scale. Children may develop anxiety disorders for a whole host of reasons. Such disorders may include: Separation anxiety: Separation anxiety refers to the feelings of stress or worry induced when a child is away from ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Characterized by general feelings of dread and foreboding and heightened states of bodily arousal that are not triggered by any specific object, situation, or activity. “Worrying about Worrying” Emotional distress caused by worrying about everyday, minor things, and about unlikely future events ...
... Characterized by general feelings of dread and foreboding and heightened states of bodily arousal that are not triggered by any specific object, situation, or activity. “Worrying about Worrying” Emotional distress caused by worrying about everyday, minor things, and about unlikely future events ...
Anxiety Disorders - Austin Community College
... stumbling while dancing, choking while eating Specific phobia: fear of a specific object or situation; animals, heigth, flying ...
... stumbling while dancing, choking while eating Specific phobia: fear of a specific object or situation; animals, heigth, flying ...
Depression and Mental Disorders PP
... intense worry, fears, or anxiety most days for at least six months Phobia: anxiety that is related to a specific situation or object ...
... intense worry, fears, or anxiety most days for at least six months Phobia: anxiety that is related to a specific situation or object ...
Panic disorder

Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring panic attacks, causing a series of intense episodes of extreme anxiety during panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral changes lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks (DSM-IVR).Panic disorder is not the same as agoraphobia (fear of public places), although many afflicted with panic disorder also suffer from agoraphobia. Panic attacks cannot be predicted, therefore an individual may become stressed, anxious or worried wondering when the next panic attack will occur. Panic disorder may be differentiated as a medical condition. The DSM-IV-TR describes panic disorder and anxiety differently. Whereas anxiety is preceded by chronic stressors which build to reactions of moderate intensity that can last for days, weeks or months, panic attacks are acute events triggered by a sudden, out-of-the-blue cause: duration is short and symptoms are more intense. Panic attacks can occur in children, as well as adults. Panic in young people may be particularly distressing because children tend to have less insight about what is happening, and parents are also likely to experience distress when attacks occur.Screening tools like Patient Health Questionnaire can be used to detect possible cases of the disorder, and suggest the need for a formal diagnostic assessment.Panic disorder is a potentially disabling disorder, but can be controlled and successfully treated. Because of the intense symptoms that accompany panic disorder, it may be mistaken for a life-threatening physical illness such as a heart attack. This misconception often aggravates or triggers future attacks (some are called ""anticipatory attacks""). People frequently go to hospital emergency rooms on experiencing a panic attack, and extensive medical tests may be performed to rule out other conditions, thus creating further anxiety. There are three types of panic attacks: unexpected, situationally bounded, and situationally predisposed.