EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially self-damaging (e.g., spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating). Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures, or threats, or self-mutilating behavior. Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood (e.g., intense episodi ...
... Impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially self-damaging (e.g., spending, sex, substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating). Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures, or threats, or self-mutilating behavior. Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood (e.g., intense episodi ...
Axis I comorbidity in bipolar disorder with psychotic features.
... earlier adolescent drug use and later depressive and disruptive disorders in young adulthood, controlling for earlier psychiatric disorders. Strakowsky et a1 (1996) found that patients with bipolar disorder and antecedent alcohol abuse had a later onset of affective illness, arguing that perhaps thi ...
... earlier adolescent drug use and later depressive and disruptive disorders in young adulthood, controlling for earlier psychiatric disorders. Strakowsky et a1 (1996) found that patients with bipolar disorder and antecedent alcohol abuse had a later onset of affective illness, arguing that perhaps thi ...
15 - Chapter 14 - Psychological Disorders
... Comparative Suicide Rates • National Differences: Britain, Italy & Spain’s rates are little more than half that of the US, Canada and Australia. Austria & Finland are double. • Racial Differences: In the US, whites are 2x as likely than blacks. • Gender Differences: Women are more likely to attempt ...
... Comparative Suicide Rates • National Differences: Britain, Italy & Spain’s rates are little more than half that of the US, Canada and Australia. Austria & Finland are double. • Racial Differences: In the US, whites are 2x as likely than blacks. • Gender Differences: Women are more likely to attempt ...
Disorders - Fulton County Schools
... that are not there (hallucinations). Frequently such hallucinations are auditory and lesser visual, somatosensory, olfactory, or gustatory. L. Berthold, Untitled. The Prinzhorn Collection, University of Heidelberg ...
... that are not there (hallucinations). Frequently such hallucinations are auditory and lesser visual, somatosensory, olfactory, or gustatory. L. Berthold, Untitled. The Prinzhorn Collection, University of Heidelberg ...
Bill Sari Mood slides 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... • One of the most common biological abnormalities in patients with major depression is hyperactivity of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis, the stress response system. • Dexamethasone, a synthetic adrenal corticosteroid, normally ...
... • One of the most common biological abnormalities in patients with major depression is hyperactivity of the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis, the stress response system. • Dexamethasone, a synthetic adrenal corticosteroid, normally ...
My Drift
... EATING DISORDERS: Eating disorders are serious, sometimes lifethreatening, conditions that tend to be chronic. Each year, more than five million Americans have an eating disorder. Onset usually occurs in adolescence and tends to predominately affect females. Having an eating disorder is marked by ex ...
... EATING DISORDERS: Eating disorders are serious, sometimes lifethreatening, conditions that tend to be chronic. Each year, more than five million Americans have an eating disorder. Onset usually occurs in adolescence and tends to predominately affect females. Having an eating disorder is marked by ex ...
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
... Generic term – clarify what they mean when taking history and what you mean when proposing treatment. FDA does not recognize this term As relates to treatment of bipolar disorder, ideally treats both depressive and manic episodes as well as prevents recurrence of mood episodes. Since no one compound ...
... Generic term – clarify what they mean when taking history and what you mean when proposing treatment. FDA does not recognize this term As relates to treatment of bipolar disorder, ideally treats both depressive and manic episodes as well as prevents recurrence of mood episodes. Since no one compound ...
ADHD - Pearson - Clinical Assessment
... at work, or during other activities (e.g., overlooks or misses details, work is inaccurate). b. Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play activities (e.g., has difficulty remaining focused during lectures, conversations, or lengthy reading). c. Often does not seem to listen when s ...
... at work, or during other activities (e.g., overlooks or misses details, work is inaccurate). b. Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play activities (e.g., has difficulty remaining focused during lectures, conversations, or lengthy reading). c. Often does not seem to listen when s ...
Somatoform disorders
... A diagnosis of a somatoform disorder implies that psychological factors are a large contributor to the symptoms' onset, severity and duration. ...
... A diagnosis of a somatoform disorder implies that psychological factors are a large contributor to the symptoms' onset, severity and duration. ...
basic disability etiquette tips
... characterized by the occurrence of one or more Manic Episodes (a distinct period during which there is an abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive or irritable mood), or Mixed Episodes (a period of time lasting at least one week in which the criteria are met both for a Manic Episode and a Dep ...
... characterized by the occurrence of one or more Manic Episodes (a distinct period during which there is an abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive or irritable mood), or Mixed Episodes (a period of time lasting at least one week in which the criteria are met both for a Manic Episode and a Dep ...
The Changing Epidemiologyof Depression
... is that proportion of the population with the particular disorder at a given time. Prevalence is usually divided into “point prevalence” (the rate of illness at a given time) or “period prevalence” (the proportion of the population with the disorder within a period of time, usually a month or a year ...
... is that proportion of the population with the particular disorder at a given time. Prevalence is usually divided into “point prevalence” (the rate of illness at a given time) or “period prevalence” (the proportion of the population with the disorder within a period of time, usually a month or a year ...
Psychological Disorders
... psychological and socio-cultural factors interact to produce specific psychological disorders. Most common view today. Some disorders occur worldwide (schizophrenia) while others are culture-bound (i.e. “anorexia” & “susto” – fear of black magic in Latin America). ...
... psychological and socio-cultural factors interact to produce specific psychological disorders. Most common view today. Some disorders occur worldwide (schizophrenia) while others are culture-bound (i.e. “anorexia” & “susto” – fear of black magic in Latin America). ...
Psychological Disorders
... psychological and socio-cultural factors interact to produce specific psychological disorders. Most common view today. Some disorders occur worldwide (schizophrenia) while others are culture-bound (i.e. “anorexia” & “susto” – fear of black magic in Latin America). ...
... psychological and socio-cultural factors interact to produce specific psychological disorders. Most common view today. Some disorders occur worldwide (schizophrenia) while others are culture-bound (i.e. “anorexia” & “susto” – fear of black magic in Latin America). ...
Dissociative & Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders
... the future; quite rare in cases of dissociative amnesia. 5) Systemized: memory loss of a particular category of information such as family members or coworkers. ...
... the future; quite rare in cases of dissociative amnesia. 5) Systemized: memory loss of a particular category of information such as family members or coworkers. ...
CH 13 study guide
... agree with the diagnostic categories and criteria in the DSM. There are three principle ideas about what constitutes psychological disorder: the DSM view, the myth of mental illness view, and harmful dysfunction view. 2. The number of people with psychological disorder is not known with certainty, b ...
... agree with the diagnostic categories and criteria in the DSM. There are three principle ideas about what constitutes psychological disorder: the DSM view, the myth of mental illness view, and harmful dysfunction view. 2. The number of people with psychological disorder is not known with certainty, b ...
Psychoanalytic Electronic Publishing: Driven Sexual Behavior in
... studied in large groups of patients with BD up to now. Bipolar disorder is a heterogeneous condition whose symptoms, severity, and comorbidities (e.g., with substance abuse and/or obsessive-compulsive disorder and/or personality disorders) vary. As Miklowitz notes, BD is a highly chronic, disabling, ...
... studied in large groups of patients with BD up to now. Bipolar disorder is a heterogeneous condition whose symptoms, severity, and comorbidities (e.g., with substance abuse and/or obsessive-compulsive disorder and/or personality disorders) vary. As Miklowitz notes, BD is a highly chronic, disabling, ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Lack of empathy, inflated self-appraisal, and superficial charm are features that have been commonly included in traditional conceptions of psychopathy and may be particularly distinguishing of Antisocial Personality Disorder in prison or forensic settings where criminal, delinquent, or aggressive a ...
... Lack of empathy, inflated self-appraisal, and superficial charm are features that have been commonly included in traditional conceptions of psychopathy and may be particularly distinguishing of Antisocial Personality Disorder in prison or forensic settings where criminal, delinquent, or aggressive a ...
Psychological Disorders - Lake Oswego High School
... Unipolar depression Single-episode or recurrent episodes Symptoms must occur for at least 2 weeks Subtypes: Post-partum onset S.A.D. ...
... Unipolar depression Single-episode or recurrent episodes Symptoms must occur for at least 2 weeks Subtypes: Post-partum onset S.A.D. ...
ACT What Is An Emotional or Behavioral Disorder? PACER CENTER
... purge” behaviors, where the person will eat enormous amounts of food, then induce vomiting, abuse laxatives, fast, or follow an austere diet to balance the effects of dramatic overeating. Essential features are binge eating and compensatory methods to prevent weight gain. Bulimia Nervosa symptoms inc ...
... purge” behaviors, where the person will eat enormous amounts of food, then induce vomiting, abuse laxatives, fast, or follow an austere diet to balance the effects of dramatic overeating. Essential features are binge eating and compensatory methods to prevent weight gain. Bulimia Nervosa symptoms inc ...
Ch 12
... 45. What is the Freudian linkage to conversion disorder? 46. Why do the authors say conversion disorder was more common a century ago in Europe and the U. S. than it is today? 47. Discuss hypochondriasis. Where do hypochondriacs often end up going for treatment? 48. What is the common denominator fo ...
... 45. What is the Freudian linkage to conversion disorder? 46. Why do the authors say conversion disorder was more common a century ago in Europe and the U. S. than it is today? 47. Discuss hypochondriasis. Where do hypochondriacs often end up going for treatment? 48. What is the common denominator fo ...
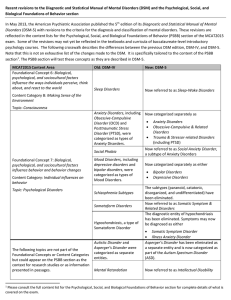
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
Psychiatric Rehabilitation
... Usually occurs during late adolescence to early adulthood. Onset is rare outside of this age range. ...
... Usually occurs during late adolescence to early adulthood. Onset is rare outside of this age range. ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.