Early risk factors for adult bipolar disorder in
... previous authors have found that the presence of anxiety disorders, especially panic disorder, might be a marker of the early onset of BPD [7,33-35]. Still, the best-established early marker of BPD risk remains family history [14,36,37]. This factor has been widely accepted in clinical practice, des ...
... previous authors have found that the presence of anxiety disorders, especially panic disorder, might be a marker of the early onset of BPD [7,33-35]. Still, the best-established early marker of BPD risk remains family history [14,36,37]. This factor has been widely accepted in clinical practice, des ...
PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2 Current
... » Short term reaction » Symptoms occur between 2 days and 1 month after trauma ...
... » Short term reaction » Symptoms occur between 2 days and 1 month after trauma ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Three features distinguish normal anxiety from pathological anxiety. Pathological anxiety is: 1. Irrational—it is provoked by perceived threats that are exaggerated or nonexistent, and the anxiety response is out of proportion to the actual importance of the ...
... Three features distinguish normal anxiety from pathological anxiety. Pathological anxiety is: 1. Irrational—it is provoked by perceived threats that are exaggerated or nonexistent, and the anxiety response is out of proportion to the actual importance of the ...
Functions - E
... have found that there are physical, social, environmental and psychological causes for mental illness. Physical causes are those which are biological in nature. They can include our individual genetic make-up and the way that this might put us at more or less risk than others. It has also been found ...
... have found that there are physical, social, environmental and psychological causes for mental illness. Physical causes are those which are biological in nature. They can include our individual genetic make-up and the way that this might put us at more or less risk than others. It has also been found ...
Early Onset Conversion Disorder: A Case Report
... she walked normally, that her family would not be allowed to visit her at the beginning of the treatment, and that the amount of time her family was permitted to stay in the hospital would increase in proportion to the level of improvement in her walking. In this way, the secondary gains that T acqu ...
... she walked normally, that her family would not be allowed to visit her at the beginning of the treatment, and that the amount of time her family was permitted to stay in the hospital would increase in proportion to the level of improvement in her walking. In this way, the secondary gains that T acqu ...
White Fat, Brown Fat, Bad Fat, Good Fat
... “So, when I hear a spouse say, ‘My husband has never been a worrier, and now he frets over everything,’ or, ‘He used to be interested in everything and now has no get-up-and-go,’ I have good reason to think Alzheimer’s is involved.” The scenario is common enough that Johns Hopkins scientists, workin ...
... “So, when I hear a spouse say, ‘My husband has never been a worrier, and now he frets over everything,’ or, ‘He used to be interested in everything and now has no get-up-and-go,’ I have good reason to think Alzheimer’s is involved.” The scenario is common enough that Johns Hopkins scientists, workin ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS I-Lecture 10 Anxiety disorder is the most
... It also depends on the quality of worrisome thought. Excessive worriers are more likely than other people to report that the content of their thoughts is negative, that they have less control over the content and direction of their thoughts, and that in comparison to other adults, their worries are ...
... It also depends on the quality of worrisome thought. Excessive worriers are more likely than other people to report that the content of their thoughts is negative, that they have less control over the content and direction of their thoughts, and that in comparison to other adults, their worries are ...
2008 Unit 12 Disorders - TJ
... are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions. (read 49-3, pg 49-5) ...
... are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions. (read 49-3, pg 49-5) ...
Psych_Disorders_12
... was beginning to feel different from his co-workers. He began to realize that he was attracted to one of his customers, a man with whom he had gone to school. When Charles realized this, he became very confused and felt angry with himself for having such feelings. Although he tried to convince himse ...
... was beginning to feel different from his co-workers. He began to realize that he was attracted to one of his customers, a man with whom he had gone to school. When Charles realized this, he became very confused and felt angry with himself for having such feelings. Although he tried to convince himse ...
STRESS AND BRIEF PSYCHOTIC DISORDER
... We had to consider other problems such as psychotic disorder secondary to general condition, delirium and various other disorder, but history, physical examination or laboratory tests ( which were normal) helped us to differentiate. Our major problem was substance – induced psychotic disorder (espec ...
... We had to consider other problems such as psychotic disorder secondary to general condition, delirium and various other disorder, but history, physical examination or laboratory tests ( which were normal) helped us to differentiate. Our major problem was substance – induced psychotic disorder (espec ...
mood disorders - Doral Academy Preparatory
... MOOD DISORDERS (CONT’D) • Causes of mood disorders – Biological factors underlying depression • genetic, neurological, chemical, and physiological components that may predispose or put someone at risk for developing a mood disorder ...
... MOOD DISORDERS (CONT’D) • Causes of mood disorders – Biological factors underlying depression • genetic, neurological, chemical, and physiological components that may predispose or put someone at risk for developing a mood disorder ...
Document
... B. The tics occur many times a day (usually in bouts) nearly every day or intermittently throughout a period of more than 1 year, and during this period there was never a tic-free period of more than 3 consecutive months. C. The onset is before age 18 years. D. The disturbance is not due to the dire ...
... B. The tics occur many times a day (usually in bouts) nearly every day or intermittently throughout a period of more than 1 year, and during this period there was never a tic-free period of more than 3 consecutive months. C. The onset is before age 18 years. D. The disturbance is not due to the dire ...
Memory
... Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. ...
... Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. ...
Dissociative amnesia, Dissociative Fugue, DID
... Psychotherapy is the primary treatment for dissociative disorders. This form of therapy, also known as talk therapy, counseling or psychosocial therapy, involves talking about your disorder and related issues with a mental health provider. Your therapist will work to help you understand the cause of ...
... Psychotherapy is the primary treatment for dissociative disorders. This form of therapy, also known as talk therapy, counseling or psychosocial therapy, involves talking about your disorder and related issues with a mental health provider. Your therapist will work to help you understand the cause of ...
69/2009 - Repatriation Medical Authority
... or amount of the substance used or the duration of use; or there is other evidence suggesting the existence of an independent nonsubstance-induced anxiety disorder (e.g., a history of recurrent non-substance-related episodes). D. ...
... or amount of the substance used or the duration of use; or there is other evidence suggesting the existence of an independent nonsubstance-induced anxiety disorder (e.g., a history of recurrent non-substance-related episodes). D. ...
Psychiatric Terminology
... c. Cyclothymic disorder i. Mild form of bipolar disorders ii. Characterized by at least 2 years of hypomania and numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes w ...
... c. Cyclothymic disorder i. Mild form of bipolar disorders ii. Characterized by at least 2 years of hypomania and numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes w ...
Anxiety Disorders
... negative emotions and images » Allows avoidance of more disturbing emotions –e.g., distress of previous trauma » Avoidance prevents extinction of underlying anxiety » Individuals with GAD less able to identify their own negative feelings (Mennin et al., ...
... negative emotions and images » Allows avoidance of more disturbing emotions –e.g., distress of previous trauma » Avoidance prevents extinction of underlying anxiety » Individuals with GAD less able to identify their own negative feelings (Mennin et al., ...
Manic-Depressive Illness and Creativity
... to rhyme and use other sound associations, such as alliteration, far more often than do unaffected individuals. They also use idiosyncratic words nearly three times as often as do control subjects. Moreover, in specific drills, they can list synonyms or form other word associations much more rapidly ...
... to rhyme and use other sound associations, such as alliteration, far more often than do unaffected individuals. They also use idiosyncratic words nearly three times as often as do control subjects. Moreover, in specific drills, they can list synonyms or form other word associations much more rapidly ...
Mood Disorders in Children and Adolescents Caleb W. Lack, PhD
... mania, as well as high rates of mania among children diagnosed with ADHD. According to the DSM-IV-TR, there are two types of bipolar disorders. Although both require a history of major depressive episodes, Bipolar I is defined by the presence of manic or mixed episodes, whereas Bipolar II has hypoma ...
... mania, as well as high rates of mania among children diagnosed with ADHD. According to the DSM-IV-TR, there are two types of bipolar disorders. Although both require a history of major depressive episodes, Bipolar I is defined by the presence of manic or mixed episodes, whereas Bipolar II has hypoma ...
- Bepress
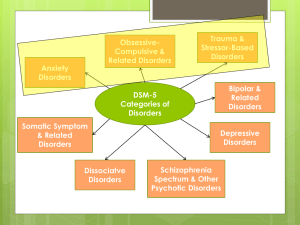
... • Non-Substance-Related Disorders – Gambling Disorder • “Pathological Gambling” in DSM-IV was renamed “Gambling Disorder” and moved from the Impulse Control Disorders chapter to the chapter in DSM-5 called Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders. • Internet Gaming Disorder is included in Chapter ...
... • Non-Substance-Related Disorders – Gambling Disorder • “Pathological Gambling” in DSM-IV was renamed “Gambling Disorder” and moved from the Impulse Control Disorders chapter to the chapter in DSM-5 called Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders. • Internet Gaming Disorder is included in Chapter ...
14 CHAPTER Psychological Disorders Chapter Preview Mental
... to depression, the tendency for most major depressive episodes to self-terminate, the link between stressful events and the onset of depression, and the disorder’s increasing rate and earlier age of onset. The biological perspective emphasizes the importance of genetic, neural, and biochemical influ ...
... to depression, the tendency for most major depressive episodes to self-terminate, the link between stressful events and the onset of depression, and the disorder’s increasing rate and earlier age of onset. The biological perspective emphasizes the importance of genetic, neural, and biochemical influ ...
NCLEX PREPARATION PROGRAM MODULE 7
... The spouse of a client who is experiencing a fugue state asks the nurse if the spouse will be able to remember what happened during the time of fugue. What is the nurse’s best response? A. “Your spouse will probably have no memory for events during the fugue.” B. “Your spouse will be able to tell y ...
... The spouse of a client who is experiencing a fugue state asks the nurse if the spouse will be able to remember what happened during the time of fugue. What is the nurse’s best response? A. “Your spouse will probably have no memory for events during the fugue.” B. “Your spouse will be able to tell y ...
File
... defined as a pattern of behaviors or psychological symptoms that cause significant personal distress and/or impairs the ability to function in one or more important areas of life. ...
... defined as a pattern of behaviors or psychological symptoms that cause significant personal distress and/or impairs the ability to function in one or more important areas of life. ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... Somatoform Disorders • Psychological factors produce physical symptoms in the Somatoform Disorders: – Hypochondriasis is a preoccupation with having a disease – Body dysmorphic disorder involves a preoccupation with an imagined physical defect – Conversion disorder involves a change in sensory/moto ...
... Somatoform Disorders • Psychological factors produce physical symptoms in the Somatoform Disorders: – Hypochondriasis is a preoccupation with having a disease – Body dysmorphic disorder involves a preoccupation with an imagined physical defect – Conversion disorder involves a change in sensory/moto ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.