dsm5 - Index of
... same overeating (and distress about it) at least once per week over a three-month period but without the compensatory behavior. To learn more: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/eating-disorders/symptoms-causes/dxc-20182875 w. Conduct disorders can be childhood-onset type, adolescent-onset ...
... same overeating (and distress about it) at least once per week over a three-month period but without the compensatory behavior. To learn more: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/eating-disorders/symptoms-causes/dxc-20182875 w. Conduct disorders can be childhood-onset type, adolescent-onset ...
What School Teachers Should Know About Bipolar Disorder Jennie
... priate treatment means reduction in undesirable classroom behaviors. Even without diagnosis, if a teacher is suspicious of such a disorder, there are a wide variety of adaptations that can be em ployed to reduce those undesirable behaviors. Therefore, teachers benefit to be well-infonned about thes ...
... priate treatment means reduction in undesirable classroom behaviors. Even without diagnosis, if a teacher is suspicious of such a disorder, there are a wide variety of adaptations that can be em ployed to reduce those undesirable behaviors. Therefore, teachers benefit to be well-infonned about thes ...
Study Guide Final 12-13-2005 - Logan Class of December 2011
... 7. Depersonalization Disorder definition and criteria This is a disorder in which the person feels detached, or like they are having an “out-ofbody” experience. 1. Persistent experience of feeling detached from ones own body or mental processes. 2. Reality testing remains intact. 3. causes significa ...
... 7. Depersonalization Disorder definition and criteria This is a disorder in which the person feels detached, or like they are having an “out-ofbody” experience. 1. Persistent experience of feeling detached from ones own body or mental processes. 2. Reality testing remains intact. 3. causes significa ...
the national institute of mental health guide to bipolar disorder
... Some imaging studies show how the brains of people with bipolar disorder may differ from the brains of healthy people or people with other mental disorders. For example, one study using MRI found that the pattern of brain development in children with bipolar disorder was similar to that in children ...
... Some imaging studies show how the brains of people with bipolar disorder may differ from the brains of healthy people or people with other mental disorders. For example, one study using MRI found that the pattern of brain development in children with bipolar disorder was similar to that in children ...
Anxiety Disorders - Deranged Physiology
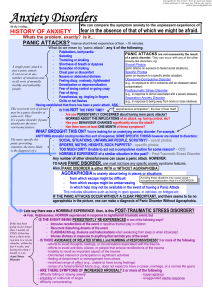
... Avoiding these situations may cause social + - from which escape might be difficult occupational dysfunction; thus it’s a DISORDER - from which escape might be embarrassing - in which help may not be available in the event of having a Panic Attack This includes situations such as being in open space ...
... Avoiding these situations may cause social + - from which escape might be difficult occupational dysfunction; thus it’s a DISORDER - from which escape might be embarrassing - in which help may not be available in the event of having a Panic Attack This includes situations such as being in open space ...
Mood Disorders
... (b) The discovery of truly effective antidepressant medications, which relieved depression by increasing either serotonin or norepinephrine, confirmed the NT role. (i) In terms of NTs, it is likely not one or the other—a complex interaction is at work and other NTs may be involved (c) Biological res ...
... (b) The discovery of truly effective antidepressant medications, which relieved depression by increasing either serotonin or norepinephrine, confirmed the NT role. (i) In terms of NTs, it is likely not one or the other—a complex interaction is at work and other NTs may be involved (c) Biological res ...
Anxiety Disorders - Santa Barbara Therapist
... Marked and persistent fear of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur. May also be hypersensitive to criticism, negative evaluation, or rejection, trouble with assertiveness, low self-esteem and feelings of inferiority, poorer social skills Typical onset in mid-teens, but c ...
... Marked and persistent fear of social or performance situations in which embarrassment may occur. May also be hypersensitive to criticism, negative evaluation, or rejection, trouble with assertiveness, low self-esteem and feelings of inferiority, poorer social skills Typical onset in mid-teens, but c ...
CATALYST PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. (Form: 8-K
... statistically significant change between baseline and week six of treatment (the last point at which subjects were on the maximum dose) for all the tic assessments, and a clinically significant change for all of the assessments in one of the four subjects. This subject was featured as a treatment su ...
... statistically significant change between baseline and week six of treatment (the last point at which subjects were on the maximum dose) for all the tic assessments, and a clinically significant change for all of the assessments in one of the four subjects. This subject was featured as a treatment su ...
The Symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
... Anger and irritability: Traumatic events where a person feels they were treated unfairly can cause them to overreact about small things as well as lose their temper and patience more easily. Mental and physical behavioral changes: Making uncharacteristic choices that affect the well-being of self an ...
... Anger and irritability: Traumatic events where a person feels they were treated unfairly can cause them to overreact about small things as well as lose their temper and patience more easily. Mental and physical behavioral changes: Making uncharacteristic choices that affect the well-being of self an ...
Psychology
... – Military, rape victims abused children, rescue workers. – Intense stress is the trigger; symptoms are nightmares, persistent fears, difficulty relating normally with others, troubling memories & flashbacks ...
... – Military, rape victims abused children, rescue workers. – Intense stress is the trigger; symptoms are nightmares, persistent fears, difficulty relating normally with others, troubling memories & flashbacks ...
Abnormal Psychology - Henry County Schools
... speech and hallucinations) Due to: substance intoxication, substance withdrawal, medication induced, due to medical condition, other) Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders (previously characterized as “dementia”): a usually progressive condition marked by deteriorated cognitive functioning often w ...
... speech and hallucinations) Due to: substance intoxication, substance withdrawal, medication induced, due to medical condition, other) Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders (previously characterized as “dementia”): a usually progressive condition marked by deteriorated cognitive functioning often w ...
Psychological Disorders
... • slow development/history of social inadequacy • rapid development/reaction to particular life stress (Richardson, 1999) ...
... • slow development/history of social inadequacy • rapid development/reaction to particular life stress (Richardson, 1999) ...
Chapter Preview
... Mental health workers label behavior as psychologically disordered when there is a significant dysfunction in a person’s thoughts, feelings, or behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) provides an authoritative classification scheme. Whether we use a medical m ...
... Mental health workers label behavior as psychologically disordered when there is a significant dysfunction in a person’s thoughts, feelings, or behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV-TR) provides an authoritative classification scheme. Whether we use a medical m ...
Document
... - previous history of trauma - genetic predispositions © 2011 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... - previous history of trauma - genetic predispositions © 2011 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES To demonstrate mastery of this chapter
... To demonstrate mastery of this chapter, the student should be able to: OBJECTIVE 12.1 — Indicate the magnitude of mental health problems in the U.S. and Canada; define psychopathology; describe the following ways of viewing normality: a. subjective discomfort, b. statistical abnormality, c. social n ...
... To demonstrate mastery of this chapter, the student should be able to: OBJECTIVE 12.1 — Indicate the magnitude of mental health problems in the U.S. and Canada; define psychopathology; describe the following ways of viewing normality: a. subjective discomfort, b. statistical abnormality, c. social n ...
CSD 5980 DIAGNOSING AND TREATMENT PLANNING Dr
... 3. Consider first, the patient's history of other disorders, since they may be related. If a woman with longstanding Alcohol Dependence becomes depressed, this may indicate that she has Alcohol-Induced Mood Disorder with Depressive Features, rather than two independent disorders. 4. Use family histo ...
... 3. Consider first, the patient's history of other disorders, since they may be related. If a woman with longstanding Alcohol Dependence becomes depressed, this may indicate that she has Alcohol-Induced Mood Disorder with Depressive Features, rather than two independent disorders. 4. Use family histo ...
Presenter - New Mexico Counseling Association
... or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history • Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech • Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior • Highly restricted, fixate ...
... or activities, as manifested by at least two of the following, currently or by history • Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech • Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior • Highly restricted, fixate ...
Chapter 3
... Fears focused on various internal bodily functions Introreceptive Conditioning (bodily sensations become associated with panic attacks and then acquire the capacity to invoke panic) ...
... Fears focused on various internal bodily functions Introreceptive Conditioning (bodily sensations become associated with panic attacks and then acquire the capacity to invoke panic) ...
Chpt.14 & 15 Psychological Disorders & Treatment
... a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state, excessive excitement, silliness, poor judgment, abrasive, rapid flight of ideas b) Major depression Lethargic, sleepy, social withdrawal, irritability ...
... a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state, excessive excitement, silliness, poor judgment, abrasive, rapid flight of ideas b) Major depression Lethargic, sleepy, social withdrawal, irritability ...
16.Abnormal PsychologyDSM5
... speech and hallucinations) Due to: substance intoxication, substance withdrawal, medication induced, due to medical condition, other) Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders (previously characterized as “dementia”): a usually progressive condition marked by deteriorated cognitive functioning often w ...
... speech and hallucinations) Due to: substance intoxication, substance withdrawal, medication induced, due to medical condition, other) Major and Mild Neurocognitive Disorders (previously characterized as “dementia”): a usually progressive condition marked by deteriorated cognitive functioning often w ...
DSM 5: TOP 10 Changes Justin K. Hughes, MA, LPC, NCC
... “The primary criterion for any diagnostic revisions should be strictly scientific evidence. However, there are sometimes differences of opinion among scientific experts. At present, most psychiatric disorders lack validated diagnostic biomarkers, and although considerable advances are being made in ...
... “The primary criterion for any diagnostic revisions should be strictly scientific evidence. However, there are sometimes differences of opinion among scientific experts. At present, most psychiatric disorders lack validated diagnostic biomarkers, and although considerable advances are being made in ...
355 A
... Each student will give an in-class presentation and lead a discussion on a disorder or important construct in psychopathology for approximately 60 minutes (45 minutes of lecture and 15 minutes of seminar discussion). The presenting student should prepare a Power Point presentation and several questi ...
... Each student will give an in-class presentation and lead a discussion on a disorder or important construct in psychopathology for approximately 60 minutes (45 minutes of lecture and 15 minutes of seminar discussion). The presenting student should prepare a Power Point presentation and several questi ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.