Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders, Dissociative and Somatoform
... reaction to trauma, characterized by symptoms of dissociation, re-experiencing avoidance, and increases anxiety or arousal. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)characterized by persistent, maladaptive disruptions in the integration of memory, consciousness, or identity. ...
... reaction to trauma, characterized by symptoms of dissociation, re-experiencing avoidance, and increases anxiety or arousal. Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)characterized by persistent, maladaptive disruptions in the integration of memory, consciousness, or identity. ...
Chapter 13 Notes (Part 2)
... psychical illness that is largely caused by physiological factors such as stress and anxiety EX: tension headaches Caused by muscle contractions brought on by stress Headache is real but considered psychosomatic because stress and anxiety (psychological factors) play an important role in causi ...
... psychical illness that is largely caused by physiological factors such as stress and anxiety EX: tension headaches Caused by muscle contractions brought on by stress Headache is real but considered psychosomatic because stress and anxiety (psychological factors) play an important role in causi ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... 8. Often has difficulty waiting one's turn. 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
... 8. Often has difficulty waiting one's turn. 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
... C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Bipolar disorder- Manic Episode (dopamine levels are high) a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state euphoria- great elation and sense of wellbeing heightened or exaggerated self-esteem increased motor activity increased goal-directed activity reduced need for sle ...
... Bipolar disorder- Manic Episode (dopamine levels are high) a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state euphoria- great elation and sense of wellbeing heightened or exaggerated self-esteem increased motor activity increased goal-directed activity reduced need for sle ...
Developmental Psychopathology
... in the brains of depressed individuals • However, SSRIs do not appear to be as effective with children as with adults • Some research suggested that SSRIs may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior among child and adolescent users, causing the U.S. government to issue a warning to that ...
... in the brains of depressed individuals • However, SSRIs do not appear to be as effective with children as with adults • Some research suggested that SSRIs may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior among child and adolescent users, causing the U.S. government to issue a warning to that ...
Navigating the Kraepelinian Vortex2
... Disorders as “reactions” Disorders were nonspecific Definitions were nonspecific Descriptions were paragraphs of ...
... Disorders as “reactions” Disorders were nonspecific Definitions were nonspecific Descriptions were paragraphs of ...
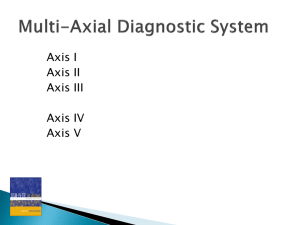
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders * 5th
... II – Stable, enduring problems III – Medical conditions (related) IV – Psychosocial problems V – rating of adaptive functioning ...
... II – Stable, enduring problems III – Medical conditions (related) IV – Psychosocial problems V – rating of adaptive functioning ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik
... • behavior is considered abnormal if it ________________________________ from _________________________________________________, values, or norms – Maladaptive behavior approach – MOST USEFUL DEF. • Behavior may be considered ______________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
... • behavior is considered abnormal if it ________________________________ from _________________________________________________, values, or norms – Maladaptive behavior approach – MOST USEFUL DEF. • Behavior may be considered ______________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
ABC Studentships
... [9] Rochelle, K.S.H. & Talcott, J. (2006). Impaired balance in developmental dyslexia: a meta-analysis of the contending evidence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 77, 1159-1166 Neural and behavioural correlates of Developmental coordination disorder. Principal Investigators: Kim Rochelle ...
... [9] Rochelle, K.S.H. & Talcott, J. (2006). Impaired balance in developmental dyslexia: a meta-analysis of the contending evidence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 77, 1159-1166 Neural and behavioural correlates of Developmental coordination disorder. Principal Investigators: Kim Rochelle ...
Psychology 11
... 1. What are dissociative disorders? 2. Differentiate between the following: a) dissociative amnesia; b) dissociative fugue; and c) dissociative identity disorder (DID). 3. Why is the diagnosis of a dissociative identity disorder so controversial? 4. What are somatoform disorders? Give some examples. ...
... 1. What are dissociative disorders? 2. Differentiate between the following: a) dissociative amnesia; b) dissociative fugue; and c) dissociative identity disorder (DID). 3. Why is the diagnosis of a dissociative identity disorder so controversial? 4. What are somatoform disorders? Give some examples. ...
Disruptive, Impulse Control, and Conduct Disorders
... control, and conduct disorders is new to DSM-5. It combines disorders that were previously included among disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence (that is, oppositional defiant disorder; conduct disorder; other specified and unspecified disruptive, impulse-control, an ...
... control, and conduct disorders is new to DSM-5. It combines disorders that were previously included among disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence (that is, oppositional defiant disorder; conduct disorder; other specified and unspecified disruptive, impulse-control, an ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... 31. The DSM-IV diagnosis of mental retardation requires both low intellectual functioning and a. Poor social skills b. poor adaptive skills c. poor achievement skills d. inability to hold a job 32. The category of “pervasive developmental disorder” includes which of the following disorders? a. Learn ...
... 31. The DSM-IV diagnosis of mental retardation requires both low intellectual functioning and a. Poor social skills b. poor adaptive skills c. poor achievement skills d. inability to hold a job 32. The category of “pervasive developmental disorder” includes which of the following disorders? a. Learn ...
Friday, October 29
... (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
... (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
Document
... • Importance of Initial and Ongoing Assessments • Variability of the person’s presentation • Understanding what the presenting symptoms and/or Challenging Behaviors (CB) means to the person • Understanding the complex needs of the individual (most cases individual’s Dual Diagnoses are involved in th ...
... • Importance of Initial and Ongoing Assessments • Variability of the person’s presentation • Understanding what the presenting symptoms and/or Challenging Behaviors (CB) means to the person • Understanding the complex needs of the individual (most cases individual’s Dual Diagnoses are involved in th ...
Chapter 7: Self & Moral Development
... overly dependent on others for support • Often co-morbid with depressive disorders or may be influential in the later development of depression ...
... overly dependent on others for support • Often co-morbid with depressive disorders or may be influential in the later development of depression ...
STRESS AND POST-TRAUMATIC DISORDERS IN
... Medium to large effect sizes: • Peri-trauma fear • Perceived life threat • Low social support • Social withdrawal • Psychiatric comorbidity • Poor family functioning • Use of distraction and thought suppression ...
... Medium to large effect sizes: • Peri-trauma fear • Perceived life threat • Low social support • Social withdrawal • Psychiatric comorbidity • Poor family functioning • Use of distraction and thought suppression ...
WHAT DOES FASD LOOK LIKE?
... to generalize (They may understand that they’re not to run into the street in front of their house, but can’t apply that lesson instinctively to other ...
... to generalize (They may understand that they’re not to run into the street in front of their house, but can’t apply that lesson instinctively to other ...
Asperger Syndrome - Brian J. Murphy`s Blog Portfolio
... Asperger syndrome (AS) is a pervasive developmental disorder, also known as High Functioning Autism. It is classified as an Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) characterized by impairment in language and communication skills, along with repetitive or restrictive patterns of behavior and thought. “The sim ...
... Asperger syndrome (AS) is a pervasive developmental disorder, also known as High Functioning Autism. It is classified as an Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) characterized by impairment in language and communication skills, along with repetitive or restrictive patterns of behavior and thought. “The sim ...
DSM-IV-TR in Action Powerpoint
... Acculturation Problem: exposure to living in a new culture Aging Associated Cognitive Decline: normal aging causes stress or impairment ...
... Acculturation Problem: exposure to living in a new culture Aging Associated Cognitive Decline: normal aging causes stress or impairment ...
Autism And Mirror Neurons
... Dapretto, M, MS Davies, JH Pfeifer, AA Scott, M Sigman, SY Bookheimer & M Iacoboni. “Understanding emotions in others: mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders.” Nature Neuroscience 9 (2006): 28-30..15 May 2007
Dupont S, ...
... Dapretto, M, MS Davies, JH Pfeifer, AA Scott, M Sigman, SY Bookheimer & M Iacoboni. “Understanding emotions in others: mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders.” Nature Neuroscience 9 (2006): 28-30.