2003-XX-XX HOW Live Oaks _ Understory
... plants in their native habitat are well mulched by leaves from surrounding trees so in the home landscape added mulch will help retain moisture. Yaupon stays shrub-like for several years but eventually can grow as tall as oaks, although their multi-trunks remain slender. Both resident and migrant b ...
... plants in their native habitat are well mulched by leaves from surrounding trees so in the home landscape added mulch will help retain moisture. Yaupon stays shrub-like for several years but eventually can grow as tall as oaks, although their multi-trunks remain slender. Both resident and migrant b ...
John W. Nason Garden - The Scott Arboretum of Swarthmore College
... large, new foliage. Keep in mind that not all trees can be treated this way. Pollarded trees in this garden include Robinia pseudoacacia ‘Frisia’, Catalpa bignonioides ‘Aurea’, and Firmiana simplex. This symbol indicates a plant that has received the Gold Medal Plant Award from the Pennsylvania Hort ...
... large, new foliage. Keep in mind that not all trees can be treated this way. Pollarded trees in this garden include Robinia pseudoacacia ‘Frisia’, Catalpa bignonioides ‘Aurea’, and Firmiana simplex. This symbol indicates a plant that has received the Gold Medal Plant Award from the Pennsylvania Hort ...
Chapter 7 Unit Notes - Moore Public Schools
... fruit forms from an ovary and sometimes other parts of the flower and contains one or more seeds generation haploid and diploid stages in the life cycle of a plant mitosis process during which a nucleus and its contents divide ovary structure found at the base of the style that contains ...
... fruit forms from an ovary and sometimes other parts of the flower and contains one or more seeds generation haploid and diploid stages in the life cycle of a plant mitosis process during which a nucleus and its contents divide ovary structure found at the base of the style that contains ...
Passion Flower
... derived from Latin and means passion and flower. The Latin species name incarnata means flesh colored and alludes to part of the flower. Before 1900, the purple variety was partially naturalized and flourishing in coastal areas of Australia. Seeds of the fruit were brought from Australia to Hawaii a ...
... derived from Latin and means passion and flower. The Latin species name incarnata means flesh colored and alludes to part of the flower. Before 1900, the purple variety was partially naturalized and flourishing in coastal areas of Australia. Seeds of the fruit were brought from Australia to Hawaii a ...
Plant Reproduction
... • Plants have a double life cycle with two distinct forms: • Sporophyte: diploid, produce haploid spores by meiosis. • Gametophyte: haploid, produce gametes by mitosis. ...
... • Plants have a double life cycle with two distinct forms: • Sporophyte: diploid, produce haploid spores by meiosis. • Gametophyte: haploid, produce gametes by mitosis. ...
Plant Diversity
... – growth pushes hook above ground – cotyledons are pulled out of ground – turn green and become ...
... – growth pushes hook above ground – cotyledons are pulled out of ground – turn green and become ...
Unit 7 - Plants
... • Plants will die if they dry out from exposure to air and sunlight. o The surfaces of plants are covered with cuticles – waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture. o Tiny holes in the cuticles, called stomata, allow for gas exchange between the plant and the atmosphere. ...
... • Plants will die if they dry out from exposure to air and sunlight. o The surfaces of plants are covered with cuticles – waxy, waterproof layer that helps hold in moisture. o Tiny holes in the cuticles, called stomata, allow for gas exchange between the plant and the atmosphere. ...
PUNCTUREVINE (Tribulus terrestris)
... Green to reddish brown stems (0.3 – 1.5 m long) Normally forms dense mats but may grow upright where there is competition for light. Leaves are 13 mm long, opposite, and divided into 4-8 pairs of oval, 13 mm leaflets Yellow flowers appear from late spring or early summer until frost, opening in the ...
... Green to reddish brown stems (0.3 – 1.5 m long) Normally forms dense mats but may grow upright where there is competition for light. Leaves are 13 mm long, opposite, and divided into 4-8 pairs of oval, 13 mm leaflets Yellow flowers appear from late spring or early summer until frost, opening in the ...
Poinsettias
... period before they will initiate flower buds. Normally, they set flower buds in early October when nights are becoming increasingly longer. If the dark period is interrupted with the light from a window, street light or any other light source, flowering will be markedly delayed or the plant may ...
... period before they will initiate flower buds. Normally, they set flower buds in early October when nights are becoming increasingly longer. If the dark period is interrupted with the light from a window, street light or any other light source, flowering will be markedly delayed or the plant may ...
Review sheet Semester 2 Exam
... Use the genus and then species names in italics with the first letter of the genus capitalized and the species name 3. What are the two kingdoms of bacteria? How do they differ in cell structure from the rest of the living organisms found on Earth? Eubacteria and Archaebacteria; they are both prokar ...
... Use the genus and then species names in italics with the first letter of the genus capitalized and the species name 3. What are the two kingdoms of bacteria? How do they differ in cell structure from the rest of the living organisms found on Earth? Eubacteria and Archaebacteria; they are both prokar ...
Plant Structure - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... Label a diagram of the external parts of a typical flowering plant Shoot, root, stem, leaves, flower, fruit & seed State the function of the root and shoot Identify tap and fibrous root systems Explain the term Meristem and give its location in the stem and root Name and give the function of four zo ...
... Label a diagram of the external parts of a typical flowering plant Shoot, root, stem, leaves, flower, fruit & seed State the function of the root and shoot Identify tap and fibrous root systems Explain the term Meristem and give its location in the stem and root Name and give the function of four zo ...
AP Biology Exam Review
... of legume family; converts N into soluble form for plant use; bacteria get food and shelter ...
... of legume family; converts N into soluble form for plant use; bacteria get food and shelter ...
winners - State Botanical Garden of Georgia
... Chinese Pistache grows two to three feet per year. It has a reputation of looking lanky when young, but gets more and more attractive with age, eventually spreading much wider than it is tall. It is tolerant of many soil types, but not boggy soil. Chinese Pistache is tough enough to be used in urban ...
... Chinese Pistache grows two to three feet per year. It has a reputation of looking lanky when young, but gets more and more attractive with age, eventually spreading much wider than it is tall. It is tolerant of many soil types, but not boggy soil. Chinese Pistache is tough enough to be used in urban ...
Plant notes
... Naked seeds: not enclosed in fruits Wind pollination (NEEDS A LOT) Seeds, vascular tissue No flowers Often needles thick with cuticle and small in size to limit transpiration. ...
... Naked seeds: not enclosed in fruits Wind pollination (NEEDS A LOT) Seeds, vascular tissue No flowers Often needles thick with cuticle and small in size to limit transpiration. ...
Chapter 8: The Parts of a Plant and Their Functions
... ThePartsof a PlantandTheirFunctions- 67 cocoa and figs, also have on their stems a third kind of bud that can give shoots that will carry flowers and produce fruit on the side of the stem. At or near the nodes of the stems of some plants are often seen small root eyes from which adventitious roots ...
... ThePartsof a PlantandTheirFunctions- 67 cocoa and figs, also have on their stems a third kind of bud that can give shoots that will carry flowers and produce fruit on the side of the stem. At or near the nodes of the stems of some plants are often seen small root eyes from which adventitious roots ...
Lecture 11
... ◦ In day light or red light, phytochrome red (Pr) is converted to phytochrome far red (Pfr). The conversion actually only requires a brief exposure to white or red light. ◦ In the dark, Pfr is slowly converted back to Pr. A long night means that there is a long time for the conversion. ◦ Under short ...
... ◦ In day light or red light, phytochrome red (Pr) is converted to phytochrome far red (Pfr). The conversion actually only requires a brief exposure to white or red light. ◦ In the dark, Pfr is slowly converted back to Pr. A long night means that there is a long time for the conversion. ◦ Under short ...
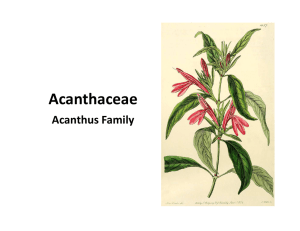
Acanthaceae (PDF file)
... occasionally violet, dotted with purple, 2lipped; upper lip notched or 2-lobed, turned backward; lower lip deeply 3lobed, occasionally turned under; flowers few, in cluster at tip of long stalk from leaf axils ...
... occasionally violet, dotted with purple, 2lipped; upper lip notched or 2-lobed, turned backward; lower lip deeply 3lobed, occasionally turned under; flowers few, in cluster at tip of long stalk from leaf axils ...
Lecture 6
... seeds showed red flowers as compared to the control seeds treated with their own DNA. Some genetic analysis was done to show that new anthocyanin synthesis loci were present. These results were never confirmed or repeated. In a case study of Arabidopsis (1971) experiments suggested that exogenous DN ...
... seeds showed red flowers as compared to the control seeds treated with their own DNA. Some genetic analysis was done to show that new anthocyanin synthesis loci were present. These results were never confirmed or repeated. In a case study of Arabidopsis (1971) experiments suggested that exogenous DN ...
Plant Structure and Function
... leaves is used up, they dry up and drop off. More leaves grow from buds on the stem as the plant grows taller. The new leaves can trap energy from sunlight and make sugar. Plants use the energy in the sugar to grow. ...
... leaves is used up, they dry up and drop off. More leaves grow from buds on the stem as the plant grows taller. The new leaves can trap energy from sunlight and make sugar. Plants use the energy in the sugar to grow. ...
Plant - CCCScienceDepartment
... leaves is used up, they dry up and drop off. More leaves grow from buds on the stem as the plant grows taller. The new leaves can trap energy from sunlight and make sugar. Plants use the energy in the sugar to grow. ...
... leaves is used up, they dry up and drop off. More leaves grow from buds on the stem as the plant grows taller. The new leaves can trap energy from sunlight and make sugar. Plants use the energy in the sugar to grow. ...
Gymnosperms Gymnosperms are non-flowering plants that do not
... This division includes palm-like gymnosperms, not to mention the surviving order Cycadales< and other extinct orders. The cycads are slow growing palm-like plants. These plants also have another characteristic feature that the leaves of these plants are borne together on the top of the trunk. The se ...
... This division includes palm-like gymnosperms, not to mention the surviving order Cycadales< and other extinct orders. The cycads are slow growing palm-like plants. These plants also have another characteristic feature that the leaves of these plants are borne together on the top of the trunk. The se ...
The first seedless vascular plants ______.
... adaptations to land make it possible for fertilization to occur without water ...
... adaptations to land make it possible for fertilization to occur without water ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.