Classifying Plants: Plant Types Teacher`s Guide
... Nonvascular, Seedless Plants: Small (usually only 2 cm to 5 cm in height); Green stems; reproduces by spores, threadlike roots; grows in damp areas. ...
... Nonvascular, Seedless Plants: Small (usually only 2 cm to 5 cm in height); Green stems; reproduces by spores, threadlike roots; grows in damp areas. ...
Sexual Life cycles Plant structure and Phylogeny
... cycle stages- gametophyte and sporophyte plants - sporic or diplohaplontic ...
... cycle stages- gametophyte and sporophyte plants - sporic or diplohaplontic ...
Tropical Rainforest
... adaptation which captures the greenish light present at the forest floor. It has striking markings on the upper surface of the leaf. These markings occur naturally; it is not a cultivar. Like the prayer plant (Maranta sp.) the leaves of the peacock plant fold up at night. Panama-Hat Plant ...
... adaptation which captures the greenish light present at the forest floor. It has striking markings on the upper surface of the leaf. These markings occur naturally; it is not a cultivar. Like the prayer plant (Maranta sp.) the leaves of the peacock plant fold up at night. Panama-Hat Plant ...
"Scrunch," "scrunch" went the crunch of dry leaves under my feet
... "Scrunch," "scrunch" went the crunch of dry leaves under my feet. The brown, dead leaves have been a delight for many that love to walk through leaf litter while kicking up fall leaves. For others, the leaves are perhaps part of a fall routine as people rake them from their lawns. For nature, decomp ...
... "Scrunch," "scrunch" went the crunch of dry leaves under my feet. The brown, dead leaves have been a delight for many that love to walk through leaf litter while kicking up fall leaves. For others, the leaves are perhaps part of a fall routine as people rake them from their lawns. For nature, decomp ...
Topic 13 - Southwest High School
... cells for photosynthesis. It is at the top of the leaf, closest to the light. Spongy Mesophyll is the airy space in the middle that allows for the circulation of gases. The Xylem and Phloem are well protected for the the transport of water and sugars. The epidermis is the outside skin that protects ...
... cells for photosynthesis. It is at the top of the leaf, closest to the light. Spongy Mesophyll is the airy space in the middle that allows for the circulation of gases. The Xylem and Phloem are well protected for the the transport of water and sugars. The epidermis is the outside skin that protects ...
gymnosperms
... be the highest evolved plants on earth arising in the Mesozoic (Cretaceous) Age and forming the dominant vegetation today. The group includes crop plants (eg. wheat, rice, maize etc.) that form the basic food supply of the world. They are necessary for human survival in the form of wood for buildin ...
... be the highest evolved plants on earth arising in the Mesozoic (Cretaceous) Age and forming the dominant vegetation today. The group includes crop plants (eg. wheat, rice, maize etc.) that form the basic food supply of the world. They are necessary for human survival in the form of wood for buildin ...
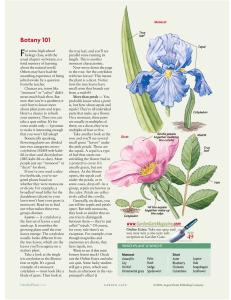
Botany 101 - Garden Gate Magazine
... the sepals. A sepal is a type of leaf that starts out enfolding the flower bud in a protective cover. It’s usually green, but not always. As the bloom opens, the sepals curl under the petals, or in some cases, drop off. As a group, sepals are known as the calyx. Petals are collectively called the co ...
... the sepals. A sepal is a type of leaf that starts out enfolding the flower bud in a protective cover. It’s usually green, but not always. As the bloom opens, the sepals curl under the petals, or in some cases, drop off. As a group, sepals are known as the calyx. Petals are collectively called the co ...
Plant Reproduction - Doral Academy Preparatory
... The life cycle of a fern is very different from the life cycle of many other plants. While many plants grow a mature adult form straight out of the seed, ferns have an intermediate stage, called a gametophyte, which then grows into a mature fern. ...
... The life cycle of a fern is very different from the life cycle of many other plants. While many plants grow a mature adult form straight out of the seed, ferns have an intermediate stage, called a gametophyte, which then grows into a mature fern. ...
Vascular plants
... Most flowering plants are easy to recognize, like roses and tulips. Did you know that grasses, oak trees, and corn are flowering plants? Their flowers are very small and hard to see. ...
... Most flowering plants are easy to recognize, like roses and tulips. Did you know that grasses, oak trees, and corn are flowering plants? Their flowers are very small and hard to see. ...
Classifying Plants: Plant Types Teacher`s Guide
... Nonvascular, Seedless Plants: Small (usually only 2 cm to 5 cm in height); Green stems; reproduces by spores, threadlike roots; grows in damp areas. ...
... Nonvascular, Seedless Plants: Small (usually only 2 cm to 5 cm in height); Green stems; reproduces by spores, threadlike roots; grows in damp areas. ...
The Wild Lilies of Oregon - Scholars` Bank
... this is called dogtooth violet, although it is not a violet at all. It is shown in the lower left hand picture. This plant shows a wide variation of color and size, depending on locality and elevation. Sometimes the leaves are uniformly green and in other cases very decidedly mottled. The yellow for ...
... this is called dogtooth violet, although it is not a violet at all. It is shown in the lower left hand picture. This plant shows a wide variation of color and size, depending on locality and elevation. Sometimes the leaves are uniformly green and in other cases very decidedly mottled. The yellow for ...
Botany: The Plant Dissection Lab
... Most plants are made up of roots, stems, leaves, which are important for plant growth, and flowers and fruits, which are part of the plant reproductive system We use plants in almost every aspect of our lives, including food, clothing, medicine, and more Plants have different adaptations to help the ...
... Most plants are made up of roots, stems, leaves, which are important for plant growth, and flowers and fruits, which are part of the plant reproductive system We use plants in almost every aspect of our lives, including food, clothing, medicine, and more Plants have different adaptations to help the ...
Wildflower Spot– April 2014 - Gloucester County Virginia
... drought. As needed, pruning can be done in late fall or early spring. Possumhaw viburnum ...
... drought. As needed, pruning can be done in late fall or early spring. Possumhaw viburnum ...
Elaeocarpus sphaericus (Gaertn.) K. Schum
... should be planted in pits at sufficient depth with a distance of 5 m from all sides to avoid falling of large tree by wind due to absence of tap root. Where sufficient land is not available for planting trees, saplings may also be planted along the boundaries, fences or road sides in the gardens or ...
... should be planted in pits at sufficient depth with a distance of 5 m from all sides to avoid falling of large tree by wind due to absence of tap root. Where sufficient land is not available for planting trees, saplings may also be planted along the boundaries, fences or road sides in the gardens or ...
Plant Propagation - MrsLongHorticulture
... • Increase tolerance to heat or cold. • Increase weed ...
... • Increase tolerance to heat or cold. • Increase weed ...
The Biology BitThese notes are just here to give
... When an insect or the wind deposits pollen onto the stigma of a flower, the pollen germinates and grows a pollen tube that, like a root, burrows down through the style and into the ovary. The tube grows through an opening into an ovule, which contains an egg cell, and fertilisation takes place. The ...
... When an insect or the wind deposits pollen onto the stigma of a flower, the pollen germinates and grows a pollen tube that, like a root, burrows down through the style and into the ovary. The tube grows through an opening into an ovule, which contains an egg cell, and fertilisation takes place. The ...
Species at Risk - Prairie Plants at Risk in Southern Alberta
... long silvery hairs. Pink-purple pea-like flowers. Flowers can be seen from late May to early June. Habitat Found in sandy habitats, grassy knolls, and sagebrush plains in the Foothills Fescue Natural Subregion south of Lethbridge. Prefers gravelly soils. ...
... long silvery hairs. Pink-purple pea-like flowers. Flowers can be seen from late May to early June. Habitat Found in sandy habitats, grassy knolls, and sagebrush plains in the Foothills Fescue Natural Subregion south of Lethbridge. Prefers gravelly soils. ...
Chapters 17, 18 and 19
... B. roots and root hairs absorb water and nutrients from the soil C. stomates open to exchange photosynthetic gases and close to limit water loss D. cutin – waxy coating on leaves – prevents water loss from the leaves E. gametangia – protective jacket of cells formed around gametes and zygotes to pre ...
... B. roots and root hairs absorb water and nutrients from the soil C. stomates open to exchange photosynthetic gases and close to limit water loss D. cutin – waxy coating on leaves – prevents water loss from the leaves E. gametangia – protective jacket of cells formed around gametes and zygotes to pre ...
8-28-01
... Cool season grasses have root growth in spring and fall roots decline in summer months Warm season grasses root growth is best in summer months Some grasses keep there roots for extended periods( Kentucky blue grass) others are annual rooting that replace much of there root system( Bermuda and ...
... Cool season grasses have root growth in spring and fall roots decline in summer months Warm season grasses root growth is best in summer months Some grasses keep there roots for extended periods( Kentucky blue grass) others are annual rooting that replace much of there root system( Bermuda and ...
Botany DR
... Fill in each blank with either “seedless plants” or “seed plants” 2. In ________________________, the gametophytes do not live independently of the sporophytes. 3. The gametophytes of ________________________ form within the reproductive structures of the sporophyte. 4. The sperm of ________________ ...
... Fill in each blank with either “seedless plants” or “seed plants” 2. In ________________________, the gametophytes do not live independently of the sporophytes. 3. The gametophytes of ________________________ form within the reproductive structures of the sporophyte. 4. The sperm of ________________ ...
monocot vs. dicot
... ecologically as they provide food and shelter for numerous animals and insects. Gymnosperms prevent soil erosion in forests and are important in the fight against climate change as they help reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. • Some other common uses for gymnosperms are soap, varnish, n ...
... ecologically as they provide food and shelter for numerous animals and insects. Gymnosperms prevent soil erosion in forests and are important in the fight against climate change as they help reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. • Some other common uses for gymnosperms are soap, varnish, n ...
Euphorbia bupleurifolia (SuCa21)
... The tropical plant, the Euphorbia bupleurifolia is easy to care for. It prefers a spot in half shadow and needs little watering. During the growing season it requires a moist soil; on the other hand in the period when there is no growth, the soil must stay dry. The temperature should not drop below ...
... The tropical plant, the Euphorbia bupleurifolia is easy to care for. It prefers a spot in half shadow and needs little watering. During the growing season it requires a moist soil; on the other hand in the period when there is no growth, the soil must stay dry. The temperature should not drop below ...
Hormonal Control in Plants
... prompts that side to grow more, bending the tip towards the light source. ...
... prompts that side to grow more, bending the tip towards the light source. ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.