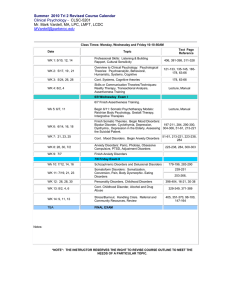
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Tourette syndrome* Comorbid
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
Bipolar Disorder.ppt
... A serious and disabling illness also known as manic-depressive illness. It affects more that 2 million American adults, or about 1 percent of the population age 18 or older. ...
... A serious and disabling illness also known as manic-depressive illness. It affects more that 2 million American adults, or about 1 percent of the population age 18 or older. ...
Chapter 5
... Occasional anxiety is natural response to life events; once the stressful situation is over, so is the anxiety it created ...
... Occasional anxiety is natural response to life events; once the stressful situation is over, so is the anxiety it created ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
... Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
Dissociative Disorders
... emotional distress due to underlying unconscious conflicts, anxiety, and implementation of defense mechanisms ...
... emotional distress due to underlying unconscious conflicts, anxiety, and implementation of defense mechanisms ...
Biomedical Therapies
... Traditional Antianxiety Drugs Best known = benzodiazepine tranquilizers • Examples: Librium, Valium (diazepam), Xanax (alprazolam) • These depressant drugs decrease anxiety disorder symptoms and treat insomnia. • But: can impair memory; interact with alcohol; can cause dependency at higher doses or ...
... Traditional Antianxiety Drugs Best known = benzodiazepine tranquilizers • Examples: Librium, Valium (diazepam), Xanax (alprazolam) • These depressant drugs decrease anxiety disorder symptoms and treat insomnia. • But: can impair memory; interact with alcohol; can cause dependency at higher doses or ...
Bipolar Disorder.pdf
... Bipolar disorder can range from mild transition to a severe condition. It is characterized by an alternating pattern of emotional highs (mania) and lows (depression). Intensity of the signs and symptoms varies. ...
... Bipolar disorder can range from mild transition to a severe condition. It is characterized by an alternating pattern of emotional highs (mania) and lows (depression). Intensity of the signs and symptoms varies. ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... a certain act • Compulsive: Behavior (acting out your obsession) • Causes: inability to resolve guilt, anxiety, insecurity; can be caused by a chemical imbalance ...
... a certain act • Compulsive: Behavior (acting out your obsession) • Causes: inability to resolve guilt, anxiety, insecurity; can be caused by a chemical imbalance ...
Somatoform Disorders and Dissociative Disorders
... which the symptoms take a somatic (bodily) form without apparent physical causes Culture has a big effect on people’s physical complaints Psychological explanations of anxiety and depression are socially less acceptable in China than in Western Culture Chinese appear more willing to report phy ...
... which the symptoms take a somatic (bodily) form without apparent physical causes Culture has a big effect on people’s physical complaints Psychological explanations of anxiety and depression are socially less acceptable in China than in Western Culture Chinese appear more willing to report phy ...
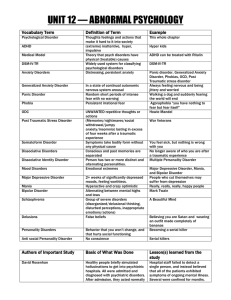
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... In a state of continual autonomic nervous system arousal Random short periods of intense fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience ...
... In a state of continual autonomic nervous system arousal Random short periods of intense fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience ...
Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
... BUT no physiological basis can be found Emotions Physical Symptoms ...
Modules_27-29 - Blue Valley Schools
... (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders • Psychology (science) classify according to symptoms • Why do they do it? (describe the disorder, predict the future course of the disorder, and treat it appropriately) • Use it for research into causes of disorder • 17 categories • Does not li ...
... (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders • Psychology (science) classify according to symptoms • Why do they do it? (describe the disorder, predict the future course of the disorder, and treat it appropriately) • Use it for research into causes of disorder • 17 categories • Does not li ...
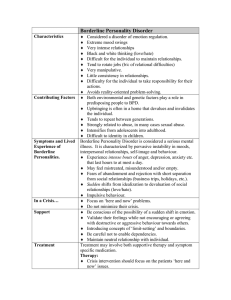
Borderline Personality Disorder
... ♦ Be careful not to enable dependencies. ♦ Maintain neutral relationship with individual. Treatment may involve both supportive therapy and symptom specific medication. Therapy: ♦ Crisis intervention should focus on the patients ‘here and now’ issues. ...
... ♦ Be careful not to enable dependencies. ♦ Maintain neutral relationship with individual. Treatment may involve both supportive therapy and symptom specific medication. Therapy: ♦ Crisis intervention should focus on the patients ‘here and now’ issues. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Two main theoretical models of treatment – Medical Model • Diseases, including psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and controlled or cured (in most cases). • May include need for hospitalization. – Bio-psycho-social Model (perspective) • All behavior, incl ...
... • Two main theoretical models of treatment – Medical Model • Diseases, including psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and controlled or cured (in most cases). • May include need for hospitalization. – Bio-psycho-social Model (perspective) • All behavior, incl ...
Key terms - Ms. Paras
... Reading Guide Due: Thursday, March 2nd Exam (combined with Abnormal Behavior): Wednesday, March 8th This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on variou ...
... Reading Guide Due: Thursday, March 2nd Exam (combined with Abnormal Behavior): Wednesday, March 8th This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on variou ...
psych mod 22 terms
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV-Test Revision (DSM-IVTR): a uniform system for assessing specific symptoms and matching them to almost 300 different mental disorders Labeling: identifying and naming differences among individuals, the label, which places individuals into spec ...
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV-Test Revision (DSM-IVTR): a uniform system for assessing specific symptoms and matching them to almost 300 different mental disorders Labeling: identifying and naming differences among individuals, the label, which places individuals into spec ...
Psychological Disorders When is behavior likely to be labeled as
... Which therapeutic approach is more interested in removing specific troubling symptoms than with providing special insights? What is systematic desensitization? Describe. What is behavior modification? What is the focus of cognitive therapy? What is the role of the therapist working from the cogniti ...
... Which therapeutic approach is more interested in removing specific troubling symptoms than with providing special insights? What is systematic desensitization? Describe. What is behavior modification? What is the focus of cognitive therapy? What is the role of the therapist working from the cogniti ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... No Well Established Treatments Address the Trauma Remove Sources of Secondary Gain Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
... No Well Established Treatments Address the Trauma Remove Sources of Secondary Gain Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
Anxiety Disorders - Northwest ISD Moodle
... for more than 1 month & are associated with functional impairment about 50% of cases remit within 6 months ...
... for more than 1 month & are associated with functional impairment about 50% of cases remit within 6 months ...
Motor neurons
... GABA and Glutumate • Consist of amino acids – GABA - produces only inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (PSP) – Glutamate – widely distributed in the brain, only has excitatory effects ...
... GABA and Glutumate • Consist of amino acids – GABA - produces only inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (PSP) – Glutamate – widely distributed in the brain, only has excitatory effects ...
PSY 111 Practice Quiz Psychological Disorders Answers will be
... (6) Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. The medical model suggests that disorders can be cured like a disease. This idea is tied to the discovery of underlying biological causes for many disorders and the description of symptoms for the disorders. ...
... (6) Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. The medical model suggests that disorders can be cured like a disease. This idea is tied to the discovery of underlying biological causes for many disorders and the description of symptoms for the disorders. ...
Mental Disorder Notes File
... A person becomes disconnected from their former identity. A) Schizophrenia: severe disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, behavior. Mind is separated from reality. Ex: irrational fears not based in reality B) Multiple Personality Disorder: switching between two or more separate personalities. Un ...
... A person becomes disconnected from their former identity. A) Schizophrenia: severe disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, behavior. Mind is separated from reality. Ex: irrational fears not based in reality B) Multiple Personality Disorder: switching between two or more separate personalities. Un ...
Mental Disorders and Addictive Behavior
... real or imagined fears occur so often they prevent a person from enjoying life. • Phobias are an example. ...
... real or imagined fears occur so often they prevent a person from enjoying life. • Phobias are an example. ...