Agoraphobia : A fear of going out to public places. Amnesia: A
... situation that presents no realistic danger. Positive symptoms: Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral excesses or peculiarities, such as hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and wild flights of ideas. Preparedness: A species-specific predisposition to be conditioned in certain ways ...
... situation that presents no realistic danger. Positive symptoms: Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral excesses or peculiarities, such as hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and wild flights of ideas. Preparedness: A species-specific predisposition to be conditioned in certain ways ...
appendix d - The George Washington University
... health was prone to change is relatively new. Community surveys have shown that many anxiety disorders are among the most common psychiatric disorders, causing extensive suffering and interference with work and social functioning. According to The Research Unit on Anxiety and Stress Disorders estab ...
... health was prone to change is relatively new. Community surveys have shown that many anxiety disorders are among the most common psychiatric disorders, causing extensive suffering and interference with work and social functioning. According to The Research Unit on Anxiety and Stress Disorders estab ...
Psychology
... – Military, rape victims abused children, rescue workers. – Intense stress is the trigger; symptoms are nightmares, persistent fears, difficulty relating normally with others, troubling memories & flashbacks ...
... – Military, rape victims abused children, rescue workers. – Intense stress is the trigger; symptoms are nightmares, persistent fears, difficulty relating normally with others, troubling memories & flashbacks ...
Racial Disparities in Depression, Anxiety and Schizophrenia
... hallucinations, disorganized thought and behavior) and negative symptoms (apathy, lack of motivation)* Affects approximately 1% of the population Treatment with antipsychotic medications, 1st and 2nd generation, rehabilitation and psychosocial interventions ...
... hallucinations, disorganized thought and behavior) and negative symptoms (apathy, lack of motivation)* Affects approximately 1% of the population Treatment with antipsychotic medications, 1st and 2nd generation, rehabilitation and psychosocial interventions ...
Document
... a condition experienced by high school or university students in response to the challenges of schooling. Symptoms include difficulties in concentrating, remembering, and thinking. Students often state that their brains are “fatigued.” Additional somatic symptoms are usually centered around the head ...
... a condition experienced by high school or university students in response to the challenges of schooling. Symptoms include difficulties in concentrating, remembering, and thinking. Students often state that their brains are “fatigued.” Additional somatic symptoms are usually centered around the head ...
need for the study
... Exceptions to the age limitation were made only if separate analyses for younger children were reported or if individual data from older could be eliminated. Results show that therapy with children was similar in effectiveness to therapy with adults; treated children achieved outcomes about two-thir ...
... Exceptions to the age limitation were made only if separate analyses for younger children were reported or if individual data from older could be eliminated. Results show that therapy with children was similar in effectiveness to therapy with adults; treated children achieved outcomes about two-thir ...
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH PROBLEMS OF FARM PEOPLE DIFFER
... 1.1 percent of Americans develop schizophrenia sometime during their lives. The NIMH has indicated a lifetime prevalence rate of about 3 percent for bipolar disorder and prevalence rates for depression and anxiety disorders in the 11-20 percent range, depending on the study. Schizophrenia tends to r ...
... 1.1 percent of Americans develop schizophrenia sometime during their lives. The NIMH has indicated a lifetime prevalence rate of about 3 percent for bipolar disorder and prevalence rates for depression and anxiety disorders in the 11-20 percent range, depending on the study. Schizophrenia tends to r ...
CHAPTER 14 Psychological Disorders
... & excessive fear that lasts at least 6 months with no focus on particular object or situation (called “free-floating” anxiety) 2. Panic Disorder: sudden, but brief, attacks of intense apprehension (panic attacks) ...
... & excessive fear that lasts at least 6 months with no focus on particular object or situation (called “free-floating” anxiety) 2. Panic Disorder: sudden, but brief, attacks of intense apprehension (panic attacks) ...
"Everybody Hurts" by REM
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in ...
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in ...
Adjustment Disorders
... • 309.4 With Mixed Disturbance of Emotions and Conduct Both emotional symptoms (e.g., depression, anxiety) and disturbance of conduct • 309.9 Unspecified - Maladaptive reactions (e.g., physical complaints or social withdrawal) that is not one of the subtypes. ...
... • 309.4 With Mixed Disturbance of Emotions and Conduct Both emotional symptoms (e.g., depression, anxiety) and disturbance of conduct • 309.9 Unspecified - Maladaptive reactions (e.g., physical complaints or social withdrawal) that is not one of the subtypes. ...
Abnormal Psychology - Solon City Schools
... change in identity, often in response to a traumatic event ...
... change in identity, often in response to a traumatic event ...
Anxiety Disorders and Depression Dr H Grandy
... Panic Disorder with or without agoraphobia • recurring, unexpected panic attacks followed by at least 1 month of worry about additional attacks, implications of the attacks, or a significant change in behavior because of the ...
... Panic Disorder with or without agoraphobia • recurring, unexpected panic attacks followed by at least 1 month of worry about additional attacks, implications of the attacks, or a significant change in behavior because of the ...
Lecture Notes
... of mind or cognitive functioning" and praecox meaning "early". He wanted to distinguish this kind of dementia from that studied by his friend Alois Alzheimer who did so much work in studying dementia in the elderly. Kraepelin originally identified it as a discrete mental illness and helped define th ...
... of mind or cognitive functioning" and praecox meaning "early". He wanted to distinguish this kind of dementia from that studied by his friend Alois Alzheimer who did so much work in studying dementia in the elderly. Kraepelin originally identified it as a discrete mental illness and helped define th ...
Mental Illness for Individuals with IDD
... communication. Individuals with IDD are very receptive and can “read” what you want them to do/say. *Help build self-esteem and confidence by working on adaptive skills *If you use figures of speech, make sure you provide a ...
... communication. Individuals with IDD are very receptive and can “read” what you want them to do/say. *Help build self-esteem and confidence by working on adaptive skills *If you use figures of speech, make sure you provide a ...
Chapter 43 Student Assignment Mental Health Problems Matching
... 1. _____ Often, anxiety occurs when needs are not met. 2. _____ A stressor can be emotional, physical, social, or economic. 3. _____ Coping mechanisms are always unhealthy. 4. _____ Panic is the highest level of anxiety. 5. _____ Mood disorders involve hallucinations and paranoia. 6. _____ Drug abus ...
... 1. _____ Often, anxiety occurs when needs are not met. 2. _____ A stressor can be emotional, physical, social, or economic. 3. _____ Coping mechanisms are always unhealthy. 4. _____ Panic is the highest level of anxiety. 5. _____ Mood disorders involve hallucinations and paranoia. 6. _____ Drug abus ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
... B. Some hyperactive, impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment were present before 7 years of age. C. Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school/work and at home). D. There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in so ...
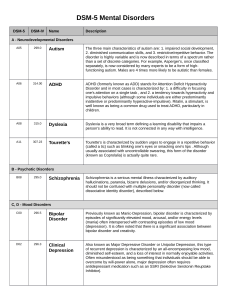
DSM V Mental Disorders
... Formerly known as hysteria (a common 19th century diagnosis made exclusively in women), conversion disorder occurs when patients suffer apparently neurological symptoms -- such as numbness, paralysis, or fits -but without a neurological cause. The term originates in Freud's belief that, in such case ...
... Formerly known as hysteria (a common 19th century diagnosis made exclusively in women), conversion disorder occurs when patients suffer apparently neurological symptoms -- such as numbness, paralysis, or fits -but without a neurological cause. The term originates in Freud's belief that, in such case ...
Depression
... supernatural forces. Ancient human skulls have been found with large holes in them, a process that has become known as trepanning. The accepted theory is that it was an attempt to let evil spirits out. We cannot be certain of this, but we do know that again and again human kind has returned to the i ...
... supernatural forces. Ancient human skulls have been found with large holes in them, a process that has become known as trepanning. The accepted theory is that it was an attempt to let evil spirits out. We cannot be certain of this, but we do know that again and again human kind has returned to the i ...
Module 13.5 Schizophrenia Lecture Outline
... 1. Person suffers loss of physical function, such as loss of limb movement without physical cause 2. Patient may appear indifferent to the loss of functioning 3. Many cases turn out to be undiagnosed medical conditions C. Hypochondriasis LB 13.9 1. Preoccupation with idea that there is something ter ...
... 1. Person suffers loss of physical function, such as loss of limb movement without physical cause 2. Patient may appear indifferent to the loss of functioning 3. Many cases turn out to be undiagnosed medical conditions C. Hypochondriasis LB 13.9 1. Preoccupation with idea that there is something ter ...
Pathways to psychosis: A comparison of the
... 1999; Schothorst et al., 2006). Over the past decade, the focus of attention in schizophrenia research has been widened to also include the prodromal phase. Projects are being set up all over the world to identify and offer treatment to prodromal individuals in the hope of preventing or delaying psy ...
... 1999; Schothorst et al., 2006). Over the past decade, the focus of attention in schizophrenia research has been widened to also include the prodromal phase. Projects are being set up all over the world to identify and offer treatment to prodromal individuals in the hope of preventing or delaying psy ...
Learners with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... phobia experience separation anxiety and cannot easily contemplate being parted from their main care giver, ...
... phobia experience separation anxiety and cannot easily contemplate being parted from their main care giver, ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... may reduce anxiety b. May run in families, genetic c. Most people with the disorder know that their thoughts and actions are irrational, but they feel unable to stop them ...
... may reduce anxiety b. May run in families, genetic c. Most people with the disorder know that their thoughts and actions are irrational, but they feel unable to stop them ...