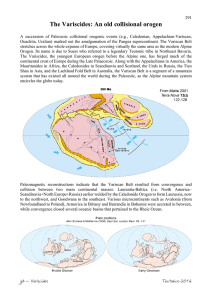
The Variscides
... All sections display large recumbent folds and ductile low-angle thrust sheets which carry high grade rocks over great distances (c. 200 km). Polyphase, syntectonic metamorphism lasted from early high-pressure events (400-380Ma, subduction related?) to a later intermediate to low pressure phase with ...
... All sections display large recumbent folds and ductile low-angle thrust sheets which carry high grade rocks over great distances (c. 200 km). Polyphase, syntectonic metamorphism lasted from early high-pressure events (400-380Ma, subduction related?) to a later intermediate to low pressure phase with ...
Plate Tectonics II - Clark Science Center
... Convection in the asthenosphere and/or lower in the mantle partly drives movement of the plates. In addition, the leading edges of suducting plates are pulled down by gravity, while plates at spreading ridges are pushed apart. ...
... Convection in the asthenosphere and/or lower in the mantle partly drives movement of the plates. In addition, the leading edges of suducting plates are pulled down by gravity, while plates at spreading ridges are pushed apart. ...
Chapter 5: Mountain Belts and Continental Crust At this point in the
... At this point in the course, you should appreciate that mountain building generally occurs at convergent plate boundaries (subduction and collision zones), where compressional stress predominates. As with most topics in geology; however, the details can get somewhat complicated. In this chapter, we’ ...
... At this point in the course, you should appreciate that mountain building generally occurs at convergent plate boundaries (subduction and collision zones), where compressional stress predominates. As with most topics in geology; however, the details can get somewhat complicated. In this chapter, we’ ...
Assessment 3.2 – Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s surface relative to one another is known as a. Tectonic Plates b. Asthenosphere c. Outer Core d. Inner Core 3. Tectonic plates that are not moving directly toward or directly away from each other but rather two tectonic plates grind past each other in a horizontal direction is what type of p ...
... Earth’s surface relative to one another is known as a. Tectonic Plates b. Asthenosphere c. Outer Core d. Inner Core 3. Tectonic plates that are not moving directly toward or directly away from each other but rather two tectonic plates grind past each other in a horizontal direction is what type of p ...
Marine Ecology, Ecosystems, Marine Factors, Seawater Chemistry
... submerged and extending seaward. ...
... submerged and extending seaward. ...
Purpose - Net Start Class
... Expert Information: Metamorphic rocks started out as other types of rock, but have been substantially changed from their original igneous, sedimentary, or earlier metamorphic form. Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to hot, mineral-rich fluids, high heat, high pressure, or more commonly ...
... Expert Information: Metamorphic rocks started out as other types of rock, but have been substantially changed from their original igneous, sedimentary, or earlier metamorphic form. Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to hot, mineral-rich fluids, high heat, high pressure, or more commonly ...
GLS100labF10_FR_fieldtrip
... Appalachians. More recently (last 150,000 years) glaciers flowed across the area scouring and shaping the deeply eroded landscape. The abundant exposed surfaces and are a by-product of glaciation. Assume that the rocks exposed here at Forest River Park are approximately 400 million years old and wer ...
... Appalachians. More recently (last 150,000 years) glaciers flowed across the area scouring and shaping the deeply eroded landscape. The abundant exposed surfaces and are a by-product of glaciation. Assume that the rocks exposed here at Forest River Park are approximately 400 million years old and wer ...
Tectonic jigsaw puzzles File
... oceans. Explain that these are called tectonic plates and the lines are tectonic plate boundaries. 3. Hold up the world globe and discuss the shape of the Earth and New Zealand’s location. 4. Hold up the hardboiled egg and compare it to the globe. Discuss how it is a model of the Earth and compare t ...
... oceans. Explain that these are called tectonic plates and the lines are tectonic plate boundaries. 3. Hold up the world globe and discuss the shape of the Earth and New Zealand’s location. 4. Hold up the hardboiled egg and compare it to the globe. Discuss how it is a model of the Earth and compare t ...
Name: ______ Date: Chapter 8 How Earth Changes Over Time
... o Density measures the amount of mass within a given space, and is compared to ___water_____in the case of minerals. Most rocks are a mixture of ____minerals_____ and can be identified by the minerals they contain. ...
... o Density measures the amount of mass within a given space, and is compared to ___water_____in the case of minerals. Most rocks are a mixture of ____minerals_____ and can be identified by the minerals they contain. ...
earth expansion tectonics
... A set of eleven spherical models, extending from the early Jurassic Period to the present is shown in the next figure. These models have since been extended back in time to the early Archaean Era (about 4,500 million years ago) and one model projected to five million years into the future. ...
... A set of eleven spherical models, extending from the early Jurassic Period to the present is shown in the next figure. These models have since been extended back in time to the early Archaean Era (about 4,500 million years ago) and one model projected to five million years into the future. ...
Geology of Minnesota - A Guide for Teachers
... simple fanns such as bacteria and blue-green algae until ncar the Precambrian-Phanerozoic boundary where more complex fomls such as jellyfish first appear. Some of these organisms arc still living today. Because these fossils have simple morphologies, they can nOI be used to subdivide the Precambria ...
... simple fanns such as bacteria and blue-green algae until ncar the Precambrian-Phanerozoic boundary where more complex fomls such as jellyfish first appear. Some of these organisms arc still living today. Because these fossils have simple morphologies, they can nOI be used to subdivide the Precambria ...
`Rockery 1` - rock game Model different characteristics of rocks
... © Earthlearningidea team. The Earthlearningidea team seeks to produce a teaching idea regularly, at minimal cost, with minimal resources, for teacher educators and teachers of Earth science through school-level geography or science, with an online discussion around every idea in order to develop a g ...
... © Earthlearningidea team. The Earthlearningidea team seeks to produce a teaching idea regularly, at minimal cost, with minimal resources, for teacher educators and teachers of Earth science through school-level geography or science, with an online discussion around every idea in order to develop a g ...
Proterozoic Tectonics: An Indian Perspective
... emplacement of reported ophiolites around 1.85 Ga. Another phase of rifting followed, that is correlated with the break-up of Columbia. This evolved once again into an arc-type environment with addition of new continental crust in the Mesoproterozoic and renewed emplacement of ophiolites. The proces ...
... emplacement of reported ophiolites around 1.85 Ga. Another phase of rifting followed, that is correlated with the break-up of Columbia. This evolved once again into an arc-type environment with addition of new continental crust in the Mesoproterozoic and renewed emplacement of ophiolites. The proces ...
- Catalyst
... -An unconformity is a substantial break or gap in a stratigraphic sequence that marks the absence of part of the rock record -A hiatus is the lapse in time recorded by an unconformity ...
... -An unconformity is a substantial break or gap in a stratigraphic sequence that marks the absence of part of the rock record -A hiatus is the lapse in time recorded by an unconformity ...
(Nyasa) Rift US Scientists Donna J. Shillingt
... (Nyasa) rift that includes characterizing deformation and magmatism in the crust and mantle lithosphere along 2-3 rift segments, quantifying temporal patterns in deformation, and evaluation of the source of magmas. The northern Lake Malawi (Nyasa) region in the East African Rift System is an excelle ...
... (Nyasa) rift that includes characterizing deformation and magmatism in the crust and mantle lithosphere along 2-3 rift segments, quantifying temporal patterns in deformation, and evaluation of the source of magmas. The northern Lake Malawi (Nyasa) region in the East African Rift System is an excelle ...
Drive from UW to Snoqualmie Pass
... ago in a series of about 40 floods that had devastating effects on eastern Washington. For a short time, the floods carried flows greater than all present rivers of the world combined. They cut channels in the loess (wind-deposited glacially-derived sediment) down to the basalt bedrock to form the c ...
... ago in a series of about 40 floods that had devastating effects on eastern Washington. For a short time, the floods carried flows greater than all present rivers of the world combined. They cut channels in the loess (wind-deposited glacially-derived sediment) down to the basalt bedrock to form the c ...
geochemical analysis of beaver river diabase
... SYSTEM • Also known as Keweenawan Rift • Middle Proterozoic in age: ~ 1.1 Ga • Triple- junction rift that extends into Kansas and the lower peninsula of Michigan • Outcrops from the MRS are only seen around the Lake Superior region • Generally composed of flood basalts and intrusions • Source ...
... SYSTEM • Also known as Keweenawan Rift • Middle Proterozoic in age: ~ 1.1 Ga • Triple- junction rift that extends into Kansas and the lower peninsula of Michigan • Outcrops from the MRS are only seen around the Lake Superior region • Generally composed of flood basalts and intrusions • Source ...
Notes: Seafloor Spreading In the early 1900`s, the
... Sonar uses ______________________________to measure ____________________ by measuring the ____________________ it takes for sound waves sent from a ____________________ to bounce off the ____________________ and return. A magnetometer is a device that can ____________________ small changes in __ ...
... Sonar uses ______________________________to measure ____________________ by measuring the ____________________ it takes for sound waves sent from a ____________________ to bounce off the ____________________ and return. A magnetometer is a device that can ____________________ small changes in __ ...
tectonic models for the geological evolution of crust, cratons and
... Abstract The earliest sialic crust was probably destroyed by meteorite impacts, leaving only detrital 4.2-3.9 Ga zircons in later sediments. The oldest rocks are 3.9-3.8 Ga high-grade gneisses commonly associated with lavas and sediments which were transported into the deep crust. They indicate that ...
... Abstract The earliest sialic crust was probably destroyed by meteorite impacts, leaving only detrital 4.2-3.9 Ga zircons in later sediments. The oldest rocks are 3.9-3.8 Ga high-grade gneisses commonly associated with lavas and sediments which were transported into the deep crust. They indicate that ...
Geological Terranes of Indian Continent
... The arcuate Himalaya province, forming the wide northern fringe of the Indian continent, is a product of docking of India with Asia—which happened sometime in the time interval 65–55 Ma. In the north, its frontier is defined by the zone of Asia-India welding characterized by squeezed up, strongly de ...
... The arcuate Himalaya province, forming the wide northern fringe of the Indian continent, is a product of docking of India with Asia—which happened sometime in the time interval 65–55 Ma. In the north, its frontier is defined by the zone of Asia-India welding characterized by squeezed up, strongly de ...
HistGanderbelt
... These rocks were tightly folded and subjected to low-pressure amphibolite-facies metamorphism in the Late Silurian.This phase of deformation and metamorphism was followed by the development of a variety of structures consistent with a period of dextral transpression in Middle Devonian – Early Carbon ...
... These rocks were tightly folded and subjected to low-pressure amphibolite-facies metamorphism in the Late Silurian.This phase of deformation and metamorphism was followed by the development of a variety of structures consistent with a period of dextral transpression in Middle Devonian – Early Carbon ...
Precambrian geology and the Bible: a harmony
... the date of 4.4 Ga. Analysis suggested that the early Earth, instead of being a boiling ocean of magma, was cool enough to have water, continents and exhibited conditions that could have supported life. This also challenges common views of an early Earth with intense meteorite bombardment, and an or ...
... the date of 4.4 Ga. Analysis suggested that the early Earth, instead of being a boiling ocean of magma, was cool enough to have water, continents and exhibited conditions that could have supported life. This also challenges common views of an early Earth with intense meteorite bombardment, and an or ...
Define and Differentiate Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Submitted
... activity that form in complex fault systems along the suture zone. Earthquake patterns in subduction zones are more complex. As the oceanic crust begins to descend, it begins to break into blocks because of tension stress. Shallow earthquakes in the upper part of the subduction zone are a result of ...
... activity that form in complex fault systems along the suture zone. Earthquake patterns in subduction zones are more complex. As the oceanic crust begins to descend, it begins to break into blocks because of tension stress. Shallow earthquakes in the upper part of the subduction zone are a result of ...
Great Lakes tectonic zone
The Great Lakes tectonic zone is bounded by South Dakota at its tip and heads northeast to south of Duluth, Minnesota, then heads east through northern Wisconsin, Marquette, Michigan, and then trends more northeasterly to skim the northern-most shores of lakes Michigan and Huron before ending in the Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, area.During the Late Archean Era the Algoman orogeny added landmass to the Superior province by volcanic activity and continental collision along a boundary that stretches from present-day South Dakota, U.S., into the Lake Huron region near Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.This crustal boundary is the Great Lakes tectonic zone. It is 1,400 km (870 mi) long, and separates the older Archean gneissic terrane to the south from younger Late Archean greenstone-granite terrane to the north.The zone is characterized by active compression during the Algoman orogeny (about 2,700 million years ago), a pulling-apart (extensional) tectonics (2,450 to 2,100 million years ago), a second compression during the Penokean orogeny (1,900 to 1,850 million years ago), a second extension during Middle Proterozoic time (1,600 million years ago) and minor reactivation during Phanerozoic time (the past 500 million years).Collision began along the Great Lakes tectonic zone (GLTZ) with the Algoman mountain-building event and continued for tens of millions of years. During the formation of the GLTZ, the gneissic Minnesota River Valley subprovince was thrust up onto the Superior province's edge as it consumed the Superior province's oceanic crust. Fragmentation of the Kenorland supercontinent began 2,450 million years ago and was completed by 2,100 million years ago. The Wyoming province is the continental landmass that is hypothesized to have rifted away from the southern Superior province portion of Kenorland, before moving rapidly west and docking with the Laurentia supercontinent 1,850 to 1,715 million years ago. Sedimentation from the GLTZ-rifting environment continued into the Penokean orogeny, which is the next major tectonic event in the Great Lakes region. Several earthquakes have been documented in Minnesota, Michigan's Upper Peninsula and Sudbury in the last 120 years along the GLTZ.























