Early Modern Physics
... · Rutherford scattering can either be off a heavier object (nuclei) ---> change in angle but little energy loss --> “multiple scattering” • or off light target (electrons) where can transfer energy but little angular change (energy loss due to ionization, also produces “delta rays” which are just mo ...
... · Rutherford scattering can either be off a heavier object (nuclei) ---> change in angle but little energy loss --> “multiple scattering” • or off light target (electrons) where can transfer energy but little angular change (energy loss due to ionization, also produces “delta rays” which are just mo ...
Quantum Mechanics as Complex Probability Theory
... generally, that P (a; b) = 0 means that b is never observed if a is known to be true. As innocent as it seems, this additional property brings probability theory into the domain of physics and leads to a question: does such a P exist? If we assume that there is no conventional probability P with thi ...
... generally, that P (a; b) = 0 means that b is never observed if a is known to be true. As innocent as it seems, this additional property brings probability theory into the domain of physics and leads to a question: does such a P exist? If we assume that there is no conventional probability P with thi ...
Course Title (1) Brief Course Description Modern Physics involves
... Modern Physics involves the extremes of very small distances and velocities close to the speed of light. These extremes demanded new theories in the early part of the 20th century and yielded the weird and wonderful results of Einstein’s relativity theory and Schrodinger’s equation in quantum mechan ...
... Modern Physics involves the extremes of very small distances and velocities close to the speed of light. These extremes demanded new theories in the early part of the 20th century and yielded the weird and wonderful results of Einstein’s relativity theory and Schrodinger’s equation in quantum mechan ...
Problem-set10 32. Polarization of atomic hydrogen in the vicinity of a
... 34. Variational and perturbation theory for the ground state of helium atom. This is the standard textbook problem so I will just ask you to go over yourself following these steps. (a) Write down the Hamiltonian for the two electrons in the helium atom, neglecting the spin-orbit interaction. (b) Ass ...
... 34. Variational and perturbation theory for the ground state of helium atom. This is the standard textbook problem so I will just ask you to go over yourself following these steps. (a) Write down the Hamiltonian for the two electrons in the helium atom, neglecting the spin-orbit interaction. (b) Ass ...
2. postulates of quantum mechanics 2.1
... Quantum physicists are interested in all kinds of physical systems (photons, conduction electrons in metals and semiconductors, atoms, etc.). State of these rather diverse systems are represented by the same type of functions è STATE FUNCTIONS. First postulate of Quantum mechanics: Every physically- ...
... Quantum physicists are interested in all kinds of physical systems (photons, conduction electrons in metals and semiconductors, atoms, etc.). State of these rather diverse systems are represented by the same type of functions è STATE FUNCTIONS. First postulate of Quantum mechanics: Every physically- ...
Localization, interaction and the modern interpretation(s) of quantum mechanics
... Localization, interaction and the modern interpretation(s) of quantum mechanics In recent years, our continued lack of progress in finding a convincing theory beyond the standard model, one which would unify gravity and quantum physics, has led many physicists to speculate that it may be precisely a ...
... Localization, interaction and the modern interpretation(s) of quantum mechanics In recent years, our continued lack of progress in finding a convincing theory beyond the standard model, one which would unify gravity and quantum physics, has led many physicists to speculate that it may be precisely a ...
Numerical Methods Project: Feynman path integrals in quantum
... Tclassic = 2πω −1 instead, this is done because the FFT used to get the frequency spectre then will be in units of ω/2π, which means that we expect the energy poles at half integer values instead of half integer values divided by two π. As mentioned in the introduction all we have to do is to use fo ...
... Tclassic = 2πω −1 instead, this is done because the FFT used to get the frequency spectre then will be in units of ω/2π, which means that we expect the energy poles at half integer values instead of half integer values divided by two π. As mentioned in the introduction all we have to do is to use fo ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL PHYSICS Molecule Microscopy 1
... Lower Hybrid Oscillating Two-Stream and Modulational Instabilities with Finite Wavelength Pump ...
... Lower Hybrid Oscillating Two-Stream and Modulational Instabilities with Finite Wavelength Pump ...
Lecture 5
... Unitary operations (on 1, 2, or 3 qubits) U1,…,UT; given together with choice of the qubits Applying operation Ui : take the tensor product with the identity on the other qubits, multiply with the current state in the order: 1,...,T One or more fixed qubits are measured in the end (standard basis) ...
... Unitary operations (on 1, 2, or 3 qubits) U1,…,UT; given together with choice of the qubits Applying operation Ui : take the tensor product with the identity on the other qubits, multiply with the current state in the order: 1,...,T One or more fixed qubits are measured in the end (standard basis) ...
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II, Spring 2014 Course
... The first one-third to one-half of the course will cover strong and weak nonequilibrium statistical physics. The second part will cover the modern theory of scaling in equilibrium statistical physics (the “renormalization group”), applied to understand continuous phase transitions. At the end of the ...
... The first one-third to one-half of the course will cover strong and weak nonequilibrium statistical physics. The second part will cover the modern theory of scaling in equilibrium statistical physics (the “renormalization group”), applied to understand continuous phase transitions. At the end of the ...
ptt-file - Parmenides Foundation
... The Newtonian potential DRIVES the particle. The QP ORGANISES the FORM of the trajectories. The QP carries INFORMATION about the particle’s ENVIRONMENT. e.g., in TWO-SLIT experiment QP depends on:(a) slit-widths, distance apart, shape, etc. (b) Momentum of particle. QP carries Information about the ...
... The Newtonian potential DRIVES the particle. The QP ORGANISES the FORM of the trajectories. The QP carries INFORMATION about the particle’s ENVIRONMENT. e.g., in TWO-SLIT experiment QP depends on:(a) slit-widths, distance apart, shape, etc. (b) Momentum of particle. QP carries Information about the ...
Quantum Mechanics from Classical Statistics
... point wise multiplication of classical observables on the level of classical states classical correlation depends on probability distribution for the atom and its environment not available on level of probabilistic observables definition depends on details of classical observables , while many diffe ...
... point wise multiplication of classical observables on the level of classical states classical correlation depends on probability distribution for the atom and its environment not available on level of probabilistic observables definition depends on details of classical observables , while many diffe ...
quantum mechanics from classical statistics
... point wise multiplication of classical observables on the level of classical states classical correlation depends on probability distribution for the atom and its environment not available on level of probabilistic observables definition depends on details of classical observables , while many diffe ...
... point wise multiplication of classical observables on the level of classical states classical correlation depends on probability distribution for the atom and its environment not available on level of probabilistic observables definition depends on details of classical observables , while many diffe ...
Physics 432: Electricity and Magnetism
... • You will get your first serious introduction to the field concepts that are used almost universally in more advanced theory. • You will learn and apply the mathematical methods of vector calculus, which is the natural mathematical language needed to describe fields. In addition, E&M provides a cri ...
... • You will get your first serious introduction to the field concepts that are used almost universally in more advanced theory. • You will learn and apply the mathematical methods of vector calculus, which is the natural mathematical language needed to describe fields. In addition, E&M provides a cri ...
Instructions for Preparing Abstracts for MS+S2004
... Superconducting circuit containing Josephson junctions is one of the promising candidates as a quantum bit (qubit) which is an essential ingredient for quantum computation [1]. A three-junction flux qubit [2] is one of such candidates. On the basis of fundamental qubit operations [3,4], the cavity Q ...
... Superconducting circuit containing Josephson junctions is one of the promising candidates as a quantum bit (qubit) which is an essential ingredient for quantum computation [1]. A three-junction flux qubit [2] is one of such candidates. On the basis of fundamental qubit operations [3,4], the cavity Q ...
Atom: Program 3 - Educational Resource Guide
... existing equations of the atom. They bent and twisted them into all sorts of new weird and wonderful shapes. Then, guided by his unshakable belief that nature's laws must be beautiful, Dirac honed in one equation, an entirely new description of what goes on inside the atom. Dirac knew it was right ...
... existing equations of the atom. They bent and twisted them into all sorts of new weird and wonderful shapes. Then, guided by his unshakable belief that nature's laws must be beautiful, Dirac honed in one equation, an entirely new description of what goes on inside the atom. Dirac knew it was right ...
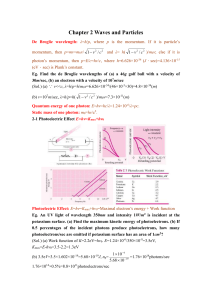
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
... Photoelectric Effect: E=hν=Kmax+hν0=Maximal electron’s energy + Work function Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, ho ...
... Photoelectric Effect: E=hν=Kmax+hν0=Maximal electron’s energy + Work function Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, ho ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.