Depressive disorders include disruptive mood
... between biology, genetics, environment, and personality. In simpler terms, someone is born with a susceptibility to major depressive disorder or dysthymia and the disease develops because that individual is exposed to specific risk factors. Genetics and Biology Major depressive disorder and dysthymi ...
... between biology, genetics, environment, and personality. In simpler terms, someone is born with a susceptibility to major depressive disorder or dysthymia and the disease develops because that individual is exposed to specific risk factors. Genetics and Biology Major depressive disorder and dysthymi ...
Interpersonal Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) for Bipolar Disorder
... theory suggests that individuals with bipolar disorder have a predisposition to circadian rhythm and sleep/wake cycle abnormalities that may account, in part, for bipolar symptoms. This model defines a social zeitgeber as a personal relationship, social demand, or life task that entrains biological ...
... theory suggests that individuals with bipolar disorder have a predisposition to circadian rhythm and sleep/wake cycle abnormalities that may account, in part, for bipolar symptoms. This model defines a social zeitgeber as a personal relationship, social demand, or life task that entrains biological ...
PPA-Fall2012-short1
... •Clinicians should follow the general rule of recording as many diagnoses as are necessary to cover the clinical picture. ...
... •Clinicians should follow the general rule of recording as many diagnoses as are necessary to cover the clinical picture. ...
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
... these ‘thinking styles’ are particularly pronounced for people whose moods are extreme enough to attract a diagnosis of bipolar disorder. n There is evidence that some people with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder show these more extreme thinking styles even at times when they are not experiencing ver ...
... these ‘thinking styles’ are particularly pronounced for people whose moods are extreme enough to attract a diagnosis of bipolar disorder. n There is evidence that some people with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder show these more extreme thinking styles even at times when they are not experiencing ver ...
Name Removed ENGL 101, Sect. 0202 Prof. Thomas Geary August
... poison are the same people who are supposed to be giving them support and care. By prescribing antipsychotic medication to children, doctors are unnecessarily putting our children at risk for serious harm and even death. The use of antipsychotic medication in children is unethical due to their harmf ...
... poison are the same people who are supposed to be giving them support and care. By prescribing antipsychotic medication to children, doctors are unnecessarily putting our children at risk for serious harm and even death. The use of antipsychotic medication in children is unethical due to their harmf ...
... THIS ARTICLE SUMMARIZES some of the more recent research and clinical findings on the diagnosis, etiology, and preferred treatment approaches for treating antisocial, histrionic, borderline, and narcissistic personality disorders—the Cluster B Personality Disorders of the Diagnostic and Statistical ...
Understanding Bipolar Disorder - British Psychological Society
... However, not all mental health professionals accept the idea that these experiences are caused by an underlying illness. There is increasing evidence that it may be more helpful to conceptualise these problems as being on a continuum: we are all subject to mood variation, but within this, people ran ...
... However, not all mental health professionals accept the idea that these experiences are caused by an underlying illness. There is increasing evidence that it may be more helpful to conceptualise these problems as being on a continuum: we are all subject to mood variation, but within this, people ran ...
Managing Student-Athletes` Mental Health Issues
... death of a family member, break-up of a significant relationship). When these situational factors become intense or an individual feels out of control with his or her life, depression may follow. • Depression also can occur without any specific precipitant (trigger). Some depressions are believed to ...
... death of a family member, break-up of a significant relationship). When these situational factors become intense or an individual feels out of control with his or her life, depression may follow. • Depression also can occur without any specific precipitant (trigger). Some depressions are believed to ...
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The
... checking and symmetry/ordering factors, but that the contamination/cleaning and hoarding factors also hold relevance. To date, no published report exists that examines the relationship between miscellaneous symptoms and symptom dimensions in pediatric patients. Thus, the goal of the present study wa ...
... checking and symmetry/ordering factors, but that the contamination/cleaning and hoarding factors also hold relevance. To date, no published report exists that examines the relationship between miscellaneous symptoms and symptom dimensions in pediatric patients. Thus, the goal of the present study wa ...
Anxiety - CBE Home
... play a role in causing anxiety. However, the home, the neighbourhood, and other settings can contribute. ...
... play a role in causing anxiety. However, the home, the neighbourhood, and other settings can contribute. ...
The Paroxysmal Disorders - Pacific Neuropsychiatric Institute
... Seizures. A controversial condition, Paroxysmal Startle Disorder, one major manifestation of this Paroxysmal Somatoform Disorder is postulated not only to exist, but argued to demonstrate an important biological mechanism for Paroxysmal Somatoform Disorder. Finally, a new name is suggested, namely P ...
... Seizures. A controversial condition, Paroxysmal Startle Disorder, one major manifestation of this Paroxysmal Somatoform Disorder is postulated not only to exist, but argued to demonstrate an important biological mechanism for Paroxysmal Somatoform Disorder. Finally, a new name is suggested, namely P ...
... hyperactivity disorder. In June 2008, we revised the “Medications” section of this document to include the American Heart Association’s (AHA) recommendations for screening children who may be vulnerable to sudden cardiac death. In September 2008, Magellan revised this section again to include a join ...
Do dissociative disorders exist in Northern Ireland?: Blind
... disorder, 3 dissociative amnesia; 2 depersonalisation disorder and dissociative amnesia, and 5 DDNOS. Three individuals classified as DDNOS had strong self-report indications of DID but no switching between dissociative identities was observed during assessment. The assessing psychiatrist and clinic ...
... disorder, 3 dissociative amnesia; 2 depersonalisation disorder and dissociative amnesia, and 5 DDNOS. Three individuals classified as DDNOS had strong self-report indications of DID but no switching between dissociative identities was observed during assessment. The assessing psychiatrist and clinic ...
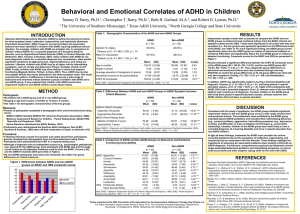
N - The University of Southern Mississippi
... for three symptom areas: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity (American Psychiatric Association, 2000). However, several correlates and associated features have been identified in children with ADHD requiring additional clinical attention. For example, children with ADHD are at higher risk, i ...
... for three symptom areas: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity (American Psychiatric Association, 2000). However, several correlates and associated features have been identified in children with ADHD requiring additional clinical attention. For example, children with ADHD are at higher risk, i ...
the nature of central auditory processing disorder
... An additional definition of CAPD was proposed by the British Society of Audiology (BSA, 2011). In this definition, CAPD is purported to represent a more general cognitive and/or developmental disorder rather than a bottom-up, auditory deficit per se. Much of this definition is derived from the findi ...
... An additional definition of CAPD was proposed by the British Society of Audiology (BSA, 2011). In this definition, CAPD is purported to represent a more general cognitive and/or developmental disorder rather than a bottom-up, auditory deficit per se. Much of this definition is derived from the findi ...
Co-occurring Disorders Treatment Workbook
... Services grant #5 UD1 TI12662-02. The opinions contained in this publication are those of the grantee and do not necessarily reflect those of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. As permitted by the Copyright Act, this workbook, in part or in full, may, in any form or by an ...
... Services grant #5 UD1 TI12662-02. The opinions contained in this publication are those of the grantee and do not necessarily reflect those of the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. As permitted by the Copyright Act, this workbook, in part or in full, may, in any form or by an ...
suicidal-behavior in-adolescents
... • Prevalence of comorbid substance abuse in bipolar I and bipolar II disorder is as high as 61% and 48% respectively • This is greater than the prevalence of substance abuse seen with any other psychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia, panic disorder, dysthymia and unipolar depression • Comor ...
... • Prevalence of comorbid substance abuse in bipolar I and bipolar II disorder is as high as 61% and 48% respectively • This is greater than the prevalence of substance abuse seen with any other psychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia, panic disorder, dysthymia and unipolar depression • Comor ...
Mental Disorders as Causal Systems: A Network Approach to
... do some symptoms tend to occur together? Answers often involve formulation of diagnostic constructs designed to impose order on the complexity of psychological suffering. There are two common ways to formulate the relation between indicators and constructs (Schmittmann et al., 2013). The first is t ...
... do some symptoms tend to occur together? Answers often involve formulation of diagnostic constructs designed to impose order on the complexity of psychological suffering. There are two common ways to formulate the relation between indicators and constructs (Schmittmann et al., 2013). The first is t ...
2. Intermediate CIT - TCOLE Course #3841
... mental illness demonstrated by disturbances in one’s emotional reactions and feelings. B. Severe depression and bipolar ...
... mental illness demonstrated by disturbances in one’s emotional reactions and feelings. B. Severe depression and bipolar ...
International consensus clinical practice statements for the treatment
... should be undertaken for all new PWE, and for all PWE attending epilepsy review with their primary care, secondary, or tertiary care physicians on an annual basis. Even though there was overall agreement in the consensus group on this statement, concerns were raised about resource challenges, availa ...
... should be undertaken for all new PWE, and for all PWE attending epilepsy review with their primary care, secondary, or tertiary care physicians on an annual basis. Even though there was overall agreement in the consensus group on this statement, concerns were raised about resource challenges, availa ...
Psychosis Uncommonly and Inconsistently Precedes Violence
... you thinking before those things were taking place?” and “Were you hearing voices just before this happened?” When interviewers rated patients’ answers to either question as indicating yes (presence of delusions or hallucinations), we classified the violent incident as “psychosis-preceded” (otherwis ...
... you thinking before those things were taking place?” and “Were you hearing voices just before this happened?” When interviewers rated patients’ answers to either question as indicating yes (presence of delusions or hallucinations), we classified the violent incident as “psychosis-preceded” (otherwis ...
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Louise Burkhart Jaime Hamm
... history of trauma. He or she will likely also use psychological assessment tools to confirm the diagnosis and involve an appropriately trained specialist • Although it may be tempting to diagnosis yourself, the diagnosis should be made by a mental health professional. This usually involves a a forma ...
... history of trauma. He or she will likely also use psychological assessment tools to confirm the diagnosis and involve an appropriately trained specialist • Although it may be tempting to diagnosis yourself, the diagnosis should be made by a mental health professional. This usually involves a a forma ...
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
... history of trauma. He or she will likely also use psychological assessment tools to confirm the diagnosis and involve an appropriately trained specialist • Although it may be tempting to diagnosis yourself, the diagnosis should be made by a mental health professional. This usually involves a a forma ...
... history of trauma. He or she will likely also use psychological assessment tools to confirm the diagnosis and involve an appropriately trained specialist • Although it may be tempting to diagnosis yourself, the diagnosis should be made by a mental health professional. This usually involves a a forma ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.