Mood Disorders in Chronic Headache
... depression have odds ratios varying from 2.2 to 4.0. There is about a threefold higher relationship between migraine and bipolar spectrum disorders, with a stronger relationship for migraine with aura than for migraine without aura. There appears to be a bi-directional relationship between migraine ...
... depression have odds ratios varying from 2.2 to 4.0. There is about a threefold higher relationship between migraine and bipolar spectrum disorders, with a stronger relationship for migraine with aura than for migraine without aura. There appears to be a bi-directional relationship between migraine ...
Mental Disorders - Interboro School District
... by serious disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, and behavior. ...
... by serious disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, and behavior. ...
exploring psychology
... These disorders are now rated by severity, rather than by being separated into “abuse” and “dependence.” Gambling disorder is now in this category as a behavioral addiction. Internet gaming disorder has been introduced “for further study.” Note: A number of the changes listed here are simple updates ...
... These disorders are now rated by severity, rather than by being separated into “abuse” and “dependence.” Gambling disorder is now in this category as a behavioral addiction. Internet gaming disorder has been introduced “for further study.” Note: A number of the changes listed here are simple updates ...
presentation
... Serious psychiatric disabilities include major depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and borderline personality disorder. The good news about mental illness is that recovery is possible. Psychiatric disabilities can affect persons of any age, race, religio ...
... Serious psychiatric disabilities include major depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and borderline personality disorder. The good news about mental illness is that recovery is possible. Psychiatric disabilities can affect persons of any age, race, religio ...
Chapter 14: Psychological Disorders
... Describe the symptoms and possible causes of dissociative identity disorder (DID), and explain the controversy surrounding its diagnosis and reports of its prevalence. ...
... Describe the symptoms and possible causes of dissociative identity disorder (DID), and explain the controversy surrounding its diagnosis and reports of its prevalence. ...
Somatic Symptom Disorder - DSM-5
... medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s thoughts, feelings and behaviors about their somatic symptoms are disproportionate or excessive. The new narrative text for SSD notes that some patients with physical conditions such as heart disease or ...
... medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s thoughts, feelings and behaviors about their somatic symptoms are disproportionate or excessive. The new narrative text for SSD notes that some patients with physical conditions such as heart disease or ...
KEY–DSM-5 Major Disorders
... Impairing levels of inattention, disorganization and/or hyperactivityimpulsivity. Multiple motor and one or more vocal tics. Deficits in general mental abilities such as reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning ...
... Impairing levels of inattention, disorganization and/or hyperactivityimpulsivity. Multiple motor and one or more vocal tics. Deficits in general mental abilities such as reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning ...
Cross-Cultural Psychology Psy 420 What is Abnormal? The Cultural
... ____ 1. Bathing only a few times a month. ____ 2. Fearing constantly that the government is after you. ____ 3. Washing thoroughly five or more times a day. ____ 4. Screaming and crying in public situations. ____ 5. Being very upset over the death of a relative for over 2 yrs, wearing dark clothes, a ...
... ____ 1. Bathing only a few times a month. ____ 2. Fearing constantly that the government is after you. ____ 3. Washing thoroughly five or more times a day. ____ 4. Screaming and crying in public situations. ____ 5. Being very upset over the death of a relative for over 2 yrs, wearing dark clothes, a ...
View Full Page PDF - The Royal College of Psychiatrists
... alterations in mood, volition and thought that could occur during an episode of mood disorder. Further, it has the potential to stratify research to identify more homogeneous subgroups of individuals, to develop more personalised treatment. This approach has already proven useful: lurasidone, an aty ...
... alterations in mood, volition and thought that could occur during an episode of mood disorder. Further, it has the potential to stratify research to identify more homogeneous subgroups of individuals, to develop more personalised treatment. This approach has already proven useful: lurasidone, an aty ...
Unit 12 At Home RQ 12
... 9. DSM-IV-TR focuses on clinicians' reports of observable behavior in order to a. facilitate the reliability of diagnoses. b. shorten the time it takes to make a diagnosis. c. avoid invading clients' psychological privacy. d. reduce the need for medical terminology in psychological assessments. e. l ...
... 9. DSM-IV-TR focuses on clinicians' reports of observable behavior in order to a. facilitate the reliability of diagnoses. b. shorten the time it takes to make a diagnosis. c. avoid invading clients' psychological privacy. d. reduce the need for medical terminology in psychological assessments. e. l ...
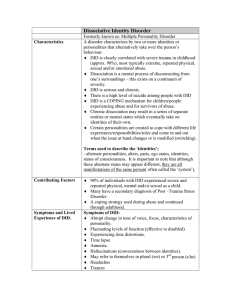
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... ♦ DID is serious and chronic. ♦ There is a high level of suicide among people with DID ♦ DID is a COPING mechanism for children/people experiencing abuse and for survivors of abuse. ♦ Chronic dissociation may result in a series of separate entities or mental states which eventually take on identitie ...
... ♦ DID is serious and chronic. ♦ There is a high level of suicide among people with DID ♦ DID is a COPING mechanism for children/people experiencing abuse and for survivors of abuse. ♦ Chronic dissociation may result in a series of separate entities or mental states which eventually take on identitie ...
Terms in Psychiatry - Northwest Technology Center
... •Describe common mental disorders •Define combining forms used in building words that relate to mental disorders •Identify the meaning of related abbreviations •Name the common tests, procedures, and treatments used in treating mental disorders •Recognize common pharmacological agents used in treati ...
... •Describe common mental disorders •Define combining forms used in building words that relate to mental disorders •Identify the meaning of related abbreviations •Name the common tests, procedures, and treatments used in treating mental disorders •Recognize common pharmacological agents used in treati ...
47.272 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY Fall 2014 Quiz 5 For each
... a. the ease with which people can fake a medical illness b. the placebo effect c. how hypnosis can be used to induce unusual bodily sensations and reactions d. the difficulty distinguishing between dementia and some form of depressive disorder among the elderly e. faith-healing 2. Which of the follo ...
... a. the ease with which people can fake a medical illness b. the placebo effect c. how hypnosis can be used to induce unusual bodily sensations and reactions d. the difficulty distinguishing between dementia and some form of depressive disorder among the elderly e. faith-healing 2. Which of the follo ...
Psyche means mind/soul, "osis“ means abnormal condition or
... Besides, there are scientifically laid down guidelines and diagnostic criteria for arriving at a diagnosis, like the International Classification of Diseases and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders ( V) which help a psychiatrist in making the right diagnosis. ...
... Besides, there are scientifically laid down guidelines and diagnostic criteria for arriving at a diagnosis, like the International Classification of Diseases and the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders ( V) which help a psychiatrist in making the right diagnosis. ...
Perspectives ppt. - Ms. Engel @ South
... can be interpreted in many ways. – It is difficult to create a classification system for mental illness that is reliable and valid. • Reliability -- the degree to which psychologists agree that a disorder is present • Validity -- the degree to which a person’s symptoms are correctly classified • The ...
... can be interpreted in many ways. – It is difficult to create a classification system for mental illness that is reliable and valid. • Reliability -- the degree to which psychologists agree that a disorder is present • Validity -- the degree to which a person’s symptoms are correctly classified • The ...
Schizophrenia Disorder Diagnostic Tool
... most common. The hallucinations are experienced while the individual is awake. Auditory hallucinations are perceived as coming from an external source distinct from the individual’s own thoughts. *(only one symptom is required if hallucinations consist of a voice keeping up a running commentary on t ...
... most common. The hallucinations are experienced while the individual is awake. Auditory hallucinations are perceived as coming from an external source distinct from the individual’s own thoughts. *(only one symptom is required if hallucinations consist of a voice keeping up a running commentary on t ...
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Tourette syndrome* Comorbid
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
Presentation - ACT for Youth
... Severe changes in mood Inflated self-esteem Great energy increase Increased talking Distractibility Increased goal-directed activity or physical agitation Disregard of risk Decreased appetite May be delusional ...
... Severe changes in mood Inflated self-esteem Great energy increase Increased talking Distractibility Increased goal-directed activity or physical agitation Disregard of risk Decreased appetite May be delusional ...
Issues relating to the validity and reliability of the classification of
... The DSM and the ICD are the two main diagnostic classification systems. Issues with reliability might arise as the two systems differ slightly in their criteria and because no physical cause can be measured so diagnosis places emphasis on report symptoms and the interpretation of the symptoms by the ...
... The DSM and the ICD are the two main diagnostic classification systems. Issues with reliability might arise as the two systems differ slightly in their criteria and because no physical cause can be measured so diagnosis places emphasis on report symptoms and the interpretation of the symptoms by the ...
Hypochondria: hypochondriasis
... At first they should meet every 4 week. The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be caref ...
... At first they should meet every 4 week. The patient is help to interpret the symptoms properly rather than focusing on the intensity of the pain or where he’s felling it. If the patient is administer medication it must be limited and the time the PA will spend with him too. The PA must be caref ...
Terms in Psychiatry - Northwest Technology Center
... •Describe common mental disorders. •Define combining forms used in building words that relate to mental disorders. •Identify the meaning of related abbreviations. •Name the common tests, procedures, and treatments used in treating mental disorders. •Recognize common pharmacological agents used in tr ...
... •Describe common mental disorders. •Define combining forms used in building words that relate to mental disorders. •Identify the meaning of related abbreviations. •Name the common tests, procedures, and treatments used in treating mental disorders. •Recognize common pharmacological agents used in tr ...
Friday, October 29
... Norepinephrine’s & Serotonin’s role in depression (people suffering from depression tend to have low levels of both of these neurotransmitters) ...
... Norepinephrine’s & Serotonin’s role in depression (people suffering from depression tend to have low levels of both of these neurotransmitters) ...
Slide 1
... - low grade depression with less severe symptoms - chronic – longer than 2 years - able to function Cyclothymic Disorder -low grade bipolar – less severe mood swings I lied – a fifth mood disorder – Seasonal Affective Disorder – SAD - related to seasonal conditions - depression symptoms ...
... - low grade depression with less severe symptoms - chronic – longer than 2 years - able to function Cyclothymic Disorder -low grade bipolar – less severe mood swings I lied – a fifth mood disorder – Seasonal Affective Disorder – SAD - related to seasonal conditions - depression symptoms ...
Tips for Living - Understanding Mood Disorders
... Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person experiences symptoms of mania, he or she has feelings of extreme irritability, inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, poor judgment, and the urge to engage in extremely risky ...
... Some people with depression also experience mania, and the combination of the two is known as bipolar disorder. When a person experiences symptoms of mania, he or she has feelings of extreme irritability, inflated self-esteem, racing thoughts, poor judgment, and the urge to engage in extremely risky ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.