Durand and Barlow Chapter 5: Somatoform and
... Factitious disorder imposed on another’ known previously as Munchausen syndrome by proxy Intentionally produced symptoms in another person ...
... Factitious disorder imposed on another’ known previously as Munchausen syndrome by proxy Intentionally produced symptoms in another person ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
... Studies have shown that it is very difficult to treat because people with it may not even want or think that they need any type of treatment. Long term one on one therapy might work but getting the patient to stick to it is difficult. Treatment for depression & anxiety may be needed to be give ...
What are Mood Disorders?
... Mayo Clinic Staff. Disease and Conditions: Seasonal Affective Disorder, SAD. (2014, September 12). Retrieved February 22, 2016 from URL http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/seasonal-affective-disorder/basics/definition/con20021047 ...
... Mayo Clinic Staff. Disease and Conditions: Seasonal Affective Disorder, SAD. (2014, September 12). Retrieved February 22, 2016 from URL http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/seasonal-affective-disorder/basics/definition/con20021047 ...
Document
... . Consistent with earlier research, these data found a high rate of cooccurring Axis-I psychiatric disorders. While there was substantial overall agreement, there were also many differences - particularly at more detailed levels of diagnosis. This suggests the value of considering both clinical diag ...
... . Consistent with earlier research, these data found a high rate of cooccurring Axis-I psychiatric disorders. While there was substantial overall agreement, there were also many differences - particularly at more detailed levels of diagnosis. This suggests the value of considering both clinical diag ...
mental disorders intro and anxiety
... • describes but does not explain the cause of psychological disorders • critics argue these labels are too arbitrary and misused • labels may cause more harm than good for the individual ...
... • describes but does not explain the cause of psychological disorders • critics argue these labels are too arbitrary and misused • labels may cause more harm than good for the individual ...
Abnormal Psychology - North Cobb High School Class Websites
... depression. • Involves periods of depression and manic episodes. • Manic episodes involve feelings of high energy (but they tend to differ a lot…some get confident and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
... depression. • Involves periods of depression and manic episodes. • Manic episodes involve feelings of high energy (but they tend to differ a lot…some get confident and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
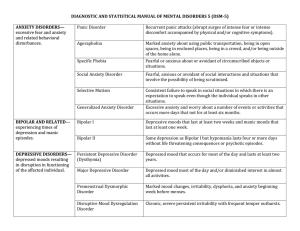
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... Repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate societal norms or rules are violated. Four main groupings: 1) Aggression to people and animals, 2) Destruction of property, 3) Deceitfulness or theft, 4) Serious violation of rules. Can be chil ...
... Repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate societal norms or rules are violated. Four main groupings: 1) Aggression to people and animals, 2) Destruction of property, 3) Deceitfulness or theft, 4) Serious violation of rules. Can be chil ...
A complex case of bipolar disorder responding to combined drug
... among mental illnesses, ranks second only to unipolar depression as a cause of worldwide disability.1 Many patients have a poor outcome, a third suffer chronic symptoms and between 13 and 24 per cent develop rapid cycling disorder, in which four or more episodes occur within a year.2 Several organic ...
... among mental illnesses, ranks second only to unipolar depression as a cause of worldwide disability.1 Many patients have a poor outcome, a third suffer chronic symptoms and between 13 and 24 per cent develop rapid cycling disorder, in which four or more episodes occur within a year.2 Several organic ...
Jagoda Banovic - Dr Andrew Mayers
... Bipolar Disorder is classified into at least two subtypes: Bipolar I type presents as mania† with psychotic features that is often followed by major depression. Bipolar II type presents as depressive episodes or dysthymia (chronic low mood) and brief episodes of hypomania ...
... Bipolar Disorder is classified into at least two subtypes: Bipolar I type presents as mania† with psychotic features that is often followed by major depression. Bipolar II type presents as depressive episodes or dysthymia (chronic low mood) and brief episodes of hypomania ...
Managing “The Why & When”
... – For psychosis as a symptom of dementia, stabilizing behavior may take as long as 12 weeks and may require treatment for at least several months and up to a year – For Schizophrenia, antipsychotic treatment is lifelong although the dose may decrease with age – For Bipolar illness, antipsychotics ar ...
... – For psychosis as a symptom of dementia, stabilizing behavior may take as long as 12 weeks and may require treatment for at least several months and up to a year – For Schizophrenia, antipsychotic treatment is lifelong although the dose may decrease with age – For Bipolar illness, antipsychotics ar ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
psychotic - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Per DSM-IV – These disorders “are all characterized by having psychotic symptoms as the defining feature…The term psychotic has historically received a number of different definitions, none of which has achieved universal acceptance. The narrowest definition of psychotic is restricted to delusions ...
... • Per DSM-IV – These disorders “are all characterized by having psychotic symptoms as the defining feature…The term psychotic has historically received a number of different definitions, none of which has achieved universal acceptance. The narrowest definition of psychotic is restricted to delusions ...
informativespeechoutline
... A. Using DSM criteria, the mental health professional must identify the criteria including, 1. Your symptoms are not caused by drugs, alcohol, cultural or religious practices, or medical condition. 2. Having recurrent gaps in memory of daily events, traumatic events, personal information, or everyd ...
... A. Using DSM criteria, the mental health professional must identify the criteria including, 1. Your symptoms are not caused by drugs, alcohol, cultural or religious practices, or medical condition. 2. Having recurrent gaps in memory of daily events, traumatic events, personal information, or everyd ...
Mood Disorders - Association for Academic Psychiatry
... • Leads to shorter well periods, increased frequency and severity of illness ...
... • Leads to shorter well periods, increased frequency and severity of illness ...
The puzzling symptom of paranoia - Sri Lanka Journal of Psychiatry
... if the original diagnosis was correct. Case 9 could not be treated immediately as she came seeking help for her son. It is not possible to say that diagnostic errors are more likely in patients presenting with paranoia. Nevertheless, it is worth exploring the possible reasons for diagnostic errors i ...
... if the original diagnosis was correct. Case 9 could not be treated immediately as she came seeking help for her son. It is not possible to say that diagnostic errors are more likely in patients presenting with paranoia. Nevertheless, it is worth exploring the possible reasons for diagnostic errors i ...
Depressive and Bipolar Disorders
... – Can begin suddenly or gradually – Single episode or repeated ...
... – Can begin suddenly or gradually – Single episode or repeated ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
Abnormal Psychology - AP Psychology Community
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
... Catatonic Schizophrenia • Flat effect • Waxy Flexibility • parrot like repeating of another’s speech and movements ...
Schizophrenia
... symptoms: delusions of being controlled by an external force, the belief that thoughts are being inserted into or withdrawn from one's conscious mind, the belief that one's thoughts are being broadcast to other people, hearing hallucinatory voices that comment on one's thoughts ~ see. recent classif ...
... symptoms: delusions of being controlled by an external force, the belief that thoughts are being inserted into or withdrawn from one's conscious mind, the belief that one's thoughts are being broadcast to other people, hearing hallucinatory voices that comment on one's thoughts ~ see. recent classif ...
hi low
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
... Somatization Disorder A. History of many physical complaints beginning before age 30 that result in treatment being sought or significant impairment B. Each of the following criteria must have been met: 1. Four pain symptoms 2. Two gastrointestinal symptoms 3. One sexual or reproductive symptom 4. ...
Psychological Disorders are:
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in most cases cured. • Assumption of the medical model drastically improves conditions in ...
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in most cases cured. • Assumption of the medical model drastically improves conditions in ...
Psychological wellness in religious life
... No one chooses an emotional or psychological disorder. No one joins religious life to be unhappy. Balance in life is an ongoing goal. There are obvious tensions in a life of service between caring for others and caring for self. Our self care is our personal responsibility. ...
... No one chooses an emotional or psychological disorder. No one joins religious life to be unhappy. Balance in life is an ongoing goal. There are obvious tensions in a life of service between caring for others and caring for self. Our self care is our personal responsibility. ...
Schizophrenia - inetTeacher.com
... The first longitudinal MRI study of the teen brain, performed at the National Institute of Mental Health, showed that gray matter increases just before puberty begins. Gray matter is where thought takes place in the brain. The production of gray matter occurs in the area of the frontal lobe and it c ...
... The first longitudinal MRI study of the teen brain, performed at the National Institute of Mental Health, showed that gray matter increases just before puberty begins. Gray matter is where thought takes place in the brain. The production of gray matter occurs in the area of the frontal lobe and it c ...
Dissociative Diso
... This disorder is believed to be ___________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ It is widely agreed that Hypochondriasis is a disorder of cognition or perception with strong ...
... This disorder is believed to be ___________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ It is widely agreed that Hypochondriasis is a disorder of cognition or perception with strong ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.