Mental Status Assessment
... Mental status definition: A person’s emotional and cognitive function Mental disorder definition: “A significant behavioral or psychological pattern associated with distress or disability and has a significant risk of pain, disability, or death, or a loss of freedom” (APA, 1994) ...
... Mental status definition: A person’s emotional and cognitive function Mental disorder definition: “A significant behavioral or psychological pattern associated with distress or disability and has a significant risk of pain, disability, or death, or a loss of freedom” (APA, 1994) ...
Bipolar I Disorder
... The specifier with psychotic features is characterized by delusions or hallucinations during the episode. There are two types: mood-congruent and mood-incongruent features. With mood-congruent features, the content of the delusions and hallucinations is consistent with the manic episode of grandi ...
... The specifier with psychotic features is characterized by delusions or hallucinations during the episode. There are two types: mood-congruent and mood-incongruent features. With mood-congruent features, the content of the delusions and hallucinations is consistent with the manic episode of grandi ...
Abnormal Behaviour in Context and an Integrative Approach to
... Abnormal Behaviour in Context and an Integrative Approach to Psychopathology Summary Abnormal Psychology in Historical Context Understanding Psychopathology: - Psychological disorder: A psychological dysfunction within an individual that is associated with distress or impairment in functioning and a ...
... Abnormal Behaviour in Context and an Integrative Approach to Psychopathology Summary Abnormal Psychology in Historical Context Understanding Psychopathology: - Psychological disorder: A psychological dysfunction within an individual that is associated with distress or impairment in functioning and a ...
Abnormal Psychology Modules 48-55
... • "I knew the rituals didn't make sense, and I was deeply ashamed of them, but I couldn't seem to overcome them until I had therapy." • "Getting dressed in the morning was tough, because I had a routine, and if I didn't follow the routine, I'd get anxious and would have to get dressed again. I alway ...
... • "I knew the rituals didn't make sense, and I was deeply ashamed of them, but I couldn't seem to overcome them until I had therapy." • "Getting dressed in the morning was tough, because I had a routine, and if I didn't follow the routine, I'd get anxious and would have to get dressed again. I alway ...
Chapter 4 Reading Guide
... A. Understanding Psychological Disorders Causes 1. In earlier times, what did people think the cause of disorders were? ...
... A. Understanding Psychological Disorders Causes 1. In earlier times, what did people think the cause of disorders were? ...
Somatoform and Sleep Disorders
... characterized • physical symptoms suggesting medical disease but without a demonstrable organic pathological condition or a known pathophysiological mechanism to account for them. • Somatoform disorders are more common ...
... characterized • physical symptoms suggesting medical disease but without a demonstrable organic pathological condition or a known pathophysiological mechanism to account for them. • Somatoform disorders are more common ...
2. Misconceptions about Psychological Disorders
... Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison group Stronger predictors of violence are… 1. Living in impoverished neighborhoods 2. Drug and alcohol abuse ...
... Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison group Stronger predictors of violence are… 1. Living in impoverished neighborhoods 2. Drug and alcohol abuse ...
Diagnosis and Management of Depression
... • Discontinuation reactions usually occur within days of stopping the drug and last for an average of 10 days • If mild: explain to the patient what is happening and continue • If severe: – Increase dose/frequency of drug – Change to longer acting drug – Tail off over a longer period e.g. 3-6 months ...
... • Discontinuation reactions usually occur within days of stopping the drug and last for an average of 10 days • If mild: explain to the patient what is happening and continue • If severe: – Increase dose/frequency of drug – Change to longer acting drug – Tail off over a longer period e.g. 3-6 months ...
What is mental illness?
... There is no universally agreed cut-off point between normal behaviour and behaviour associated with mental illness What is considered abnormal behaviour differs between cultures, social groups etc. ...
... There is no universally agreed cut-off point between normal behaviour and behaviour associated with mental illness What is considered abnormal behaviour differs between cultures, social groups etc. ...
Mental Status PPT
... ASSESSING AFFECT Look for how appropriate the affect is and whether it corresponds to the topic under discussion. A full range of emotional expression is normal. Note any incongruent between affect and topic at hand. Look for lability of affect. Blunted or flat affect is static regardless of topic ...
... ASSESSING AFFECT Look for how appropriate the affect is and whether it corresponds to the topic under discussion. A full range of emotional expression is normal. Note any incongruent between affect and topic at hand. Look for lability of affect. Blunted or flat affect is static regardless of topic ...
ppt_ch11
... Diathesis: What is the person’s vulnerability or predisposition to developing a disorder? Stress: What level of stress is the person experiencing? ...
... Diathesis: What is the person’s vulnerability or predisposition to developing a disorder? Stress: What level of stress is the person experiencing? ...
Personality Disorders Continued
... Common themes include ambivalent & conflicted personality dynamics that underlie presentation. Ambivalence is defined as a lack of certainty over the source of reinforcement in one’s life. Ambivalent individuals = conflicted over whether they should follow what others want them to do or follow ...
... Common themes include ambivalent & conflicted personality dynamics that underlie presentation. Ambivalence is defined as a lack of certainty over the source of reinforcement in one’s life. Ambivalent individuals = conflicted over whether they should follow what others want them to do or follow ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Psychological Disorders
... mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. ...
... mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. ...
Psychological Disorders
... ability to identify familiar objects. The conditions in this category usually result from a medical condition, substance abuse, or adverse reactions to medication or poisonous substances ...
... ability to identify familiar objects. The conditions in this category usually result from a medical condition, substance abuse, or adverse reactions to medication or poisonous substances ...
Binge-eating Disorder - University of Alberta
... The problem of abnormal behavior is personally relevant and emotionally charged, but in this course we will explore the problem from an objective and scientific point of view. Although we must be dispassionate in our study of the problem, it is important that we keep in mind the importance and the i ...
... The problem of abnormal behavior is personally relevant and emotionally charged, but in this course we will explore the problem from an objective and scientific point of view. Although we must be dispassionate in our study of the problem, it is important that we keep in mind the importance and the i ...
Pediatric Mood Disorders: From Neurobiology to Clinical Practice
... • Children can be suicidal. These ideations can quickly develop into plans and actions. • Children with mania have the same urges that adults do, they also become hypersexual, grandiose, obsessive and desire to spend money. • Children, like adults, require medication to stabilize their mood. Therapy ...
... • Children can be suicidal. These ideations can quickly develop into plans and actions. • Children with mania have the same urges that adults do, they also become hypersexual, grandiose, obsessive and desire to spend money. • Children, like adults, require medication to stabilize their mood. Therapy ...
What are the diagnostic criteria for PTSD?
... People cope with these things in different ways. When exposed to trauma, some people1,2 will develop Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, a potentially disabling affliction involving feelings of helplessness, fear and dread that result in avoidance and isolation. The lifetime prevalence in the general pop ...
... People cope with these things in different ways. When exposed to trauma, some people1,2 will develop Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, a potentially disabling affliction involving feelings of helplessness, fear and dread that result in avoidance and isolation. The lifetime prevalence in the general pop ...
Mood Disorders
... emotionally numb, especially with people they were once close to. They may experience sleep problems, feel detached or numb, or be easily startled. ...
... emotionally numb, especially with people they were once close to. They may experience sleep problems, feel detached or numb, or be easily startled. ...
Psychological Disorders
... may have more to do with social ills or failures of _________________ than with problems within the individual. Socioculltural theorists believe that the stress of coping with poverty and social disadvantage can eventually take its toll on mental health. The Biopsychosocial Model argue that most f ...
... may have more to do with social ills or failures of _________________ than with problems within the individual. Socioculltural theorists believe that the stress of coping with poverty and social disadvantage can eventually take its toll on mental health. The Biopsychosocial Model argue that most f ...
Class 8: Mental Illness and Diagnosis
... 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning at the higher or lower end of the 10-point range. For example, consider an individual who hears voices that do not influence his behavior (e.g., someone with long standing Schiz ...
... 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning at the higher or lower end of the 10-point range. For example, consider an individual who hears voices that do not influence his behavior (e.g., someone with long standing Schiz ...
a severe mood disorder characterized by major
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
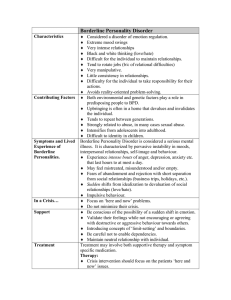
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
... Difficulty for the individual to take responsibility for their actions. ♦ Avoids reality-oriented problem-solving. ♦ Both environmental and genetic factors play a role in predisposing people to BPD. ♦ Upbringing is often in a home that devalues and invalidates the individual. ♦ Tends to repeat betwe ...
Spectrum disorder
A spectrum disorder is a mental disorder that includes a range of linked conditions, sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case, a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be ""not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups"". The spectrum may represent a range of severity, comprising relatively ""severe"" mental disorders through to relatively ""mild and nonclinical deficits"".In some cases, a spectrum approach joins together conditions that were previously considered separately. A notable example of this trend is the autism spectrum, where conditions on this spectrum may now all be referred to as autism spectrum disorders. In other cases, what was treated as a single disorder comes to be seen (or seen once again) as comprising a range of types, a notable example being the bipolar spectrum. A spectrum approach may also expand the type or the severity of issues which are included, which may lessen the gap with other diagnoses or with what is considered ""normal"". Proponents of this approach argue that it is in line with evidence of gradations in the type or severity of symptoms in the general population, and helps reduce the stigma associated with a diagnosis. Critics, however, argue that it can take attention and resources away from the most serious conditions associated with the most disability, or on the other hand could unduly medicalize problems which are simply challenges people face in life.