Dissociative Diso
... objects in their visual field, as well as those reporting paralysis of the legs might get up and run somewhere in an emergency and are astounded they were able to do this. -This can account for some who are miraculously “cured” during religious ceremonies. ...
... objects in their visual field, as well as those reporting paralysis of the legs might get up and run somewhere in an emergency and are astounded they were able to do this. -This can account for some who are miraculously “cured” during religious ceremonies. ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Access Copyright (The Canadian Copyright Licensing Agency) is unlawful. Requests for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. The purchaser may make back-up copies ...
... reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Access Copyright (The Canadian Copyright Licensing Agency) is unlawful. Requests for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. The purchaser may make back-up copies ...
Eating_Disordersas_9..
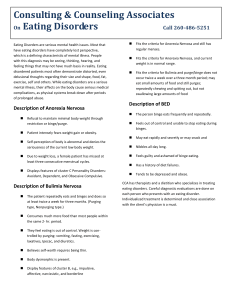
... On Eating Disorders Call 260-486-5251 Eating Disorders are serious mental health issues. Most that have eating disorders have completely lost perspective, which is a defining characteristic of mental illness. People with this diagnosis may be seeing, thinking, hearing, and feeling things that may no ...
... On Eating Disorders Call 260-486-5251 Eating Disorders are serious mental health issues. Most that have eating disorders have completely lost perspective, which is a defining characteristic of mental illness. People with this diagnosis may be seeing, thinking, hearing, and feeling things that may no ...
Recent Burn Injuries Survivors and Families
... 39% of burn survivors had at least one psychiatric disorder in the 12 months after injury, opposed to only 14% of general trauma population (comorbid disorder common as well) Most common (over 10%) Specific Phobia, Generalized anxiety, Major Depression ...
... 39% of burn survivors had at least one psychiatric disorder in the 12 months after injury, opposed to only 14% of general trauma population (comorbid disorder common as well) Most common (over 10%) Specific Phobia, Generalized anxiety, Major Depression ...
Somatoform Disorders
... Somatoform disorders: persons who are overly preoccupied with their health or body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of ...
... Somatoform disorders: persons who are overly preoccupied with their health or body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of ...
BUILDING THE ESSAY DRAFT
... – Combines with a genetic, biological, or other structural/physical factor – When both occur, depression, for example, may result Helps address why some identical events do not produce same outcome in different people ...
... – Combines with a genetic, biological, or other structural/physical factor – When both occur, depression, for example, may result Helps address why some identical events do not produce same outcome in different people ...
A Framework for How Personality Disorders Develop
... aversive lifestyles is accurate, it also overstates the negatives of life of most personality disordered people and certainly overstates the problems of someone with a personality pattern disturbance. In the midst of the struggles faced by people with personality disorders, there are islands of succ ...
... aversive lifestyles is accurate, it also overstates the negatives of life of most personality disordered people and certainly overstates the problems of someone with a personality pattern disturbance. In the midst of the struggles faced by people with personality disorders, there are islands of succ ...
Chapter 16
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
Mental Disorders
... Antisocial Personality Disorder – a personality disorder in which a person’s patterns of behavior are in conflict with society ...
... Antisocial Personality Disorder – a personality disorder in which a person’s patterns of behavior are in conflict with society ...
Somatoform Disorders
... but is not, blind, deaf, paralyzed or insensitive to pain in various parts of the body. – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in only 2% of the population – Usually appears in adole ...
... but is not, blind, deaf, paralyzed or insensitive to pain in various parts of the body. – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in only 2% of the population – Usually appears in adole ...
chapter 15 - Cengage Learning
... 14. Define dissociative disorder. Compare and contrast dissociative fugue and dissociative amnesia. Describe dissociative identity disorder. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 15. State the causes, according to the various theoretical models, of dissociative disorders. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 16 ...
... 14. Define dissociative disorder. Compare and contrast dissociative fugue and dissociative amnesia. Describe dissociative identity disorder. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 15. State the causes, according to the various theoretical models, of dissociative disorders. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 16 ...
Personality disorder
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
AXIS II - DAV College For Girls, Yamunanagar
... Axis III diagnosis, all are reported. If no Axis III disorder is present, then that is indicated by the notation “Axis III: None”. If an Axis III diagnosis is deferred, pending the gathering of additional information then this is indicated by the notation “Axis III-deferred”. AXIS III General Medic ...
... Axis III diagnosis, all are reported. If no Axis III disorder is present, then that is indicated by the notation “Axis III: None”. If an Axis III diagnosis is deferred, pending the gathering of additional information then this is indicated by the notation “Axis III-deferred”. AXIS III General Medic ...
learning objectives chapter 12
... broadcasting, thought blocking, thought withdrawal, and thought insertions. Define hallucinations. (see “Symptoms of Schizophrenia”) 21. Describe the symptoms of the following DSM-IV categories of schizophrenia: paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual. Discuss alternative w ...
... broadcasting, thought blocking, thought withdrawal, and thought insertions. Define hallucinations. (see “Symptoms of Schizophrenia”) 21. Describe the symptoms of the following DSM-IV categories of schizophrenia: paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual. Discuss alternative w ...