16 DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOPATHOLOGY LEARNING
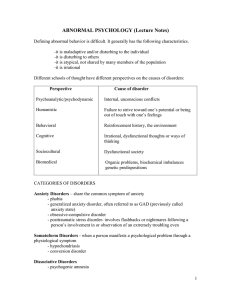
... a. statistical deviance: Does the person's behavior fall outside the normal range of behavior? b. maladaptiveness: Does the person's behavior interfere with personal and social adaptation or pose a danger to self or others? c. personal distress: Does the behavior cause personal anguish or discomfort ...
... a. statistical deviance: Does the person's behavior fall outside the normal range of behavior? b. maladaptiveness: Does the person's behavior interfere with personal and social adaptation or pose a danger to self or others? c. personal distress: Does the behavior cause personal anguish or discomfort ...
Introduction to Psychology
... facial expressions, and body posture. Verbal and nonverbal communication Delay in, or lack of, learning to talk. As many as 40% of people with autism never speak Limited interests in activities or play An unusual focus on pieces or parts on ...
... facial expressions, and body posture. Verbal and nonverbal communication Delay in, or lack of, learning to talk. As many as 40% of people with autism never speak Limited interests in activities or play An unusual focus on pieces or parts on ...
Psychological Disorders
... (PERSON) -- The behavioral model views abnormal behaviors as learned through classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and modeling. (GROUP) -- The sociocultural model emphasizes the importance of social and cultural factors in the frequency, diagnosis, and conception of disorders. ...
... (PERSON) -- The behavioral model views abnormal behaviors as learned through classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and modeling. (GROUP) -- The sociocultural model emphasizes the importance of social and cultural factors in the frequency, diagnosis, and conception of disorders. ...
Personality Disorder
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... *Deviance-Bizarre, unusual behavior *Dysfunction-inability to complete tasks or take responsibility -any behavior that interferes with personal growth ...
... *Deviance-Bizarre, unusual behavior *Dysfunction-inability to complete tasks or take responsibility -any behavior that interferes with personal growth ...
No Slide Title
... • Mood disorders are a class of disorders marked by 44 disturbances of varied kinds that may spill over to physical, perceptual, social, and thought processes. • Major depressive disorder is marked by profound sadness, slowed thought processes, low self-esteem, and loss of interest in previous sourc ...
... • Mood disorders are a class of disorders marked by 44 disturbances of varied kinds that may spill over to physical, perceptual, social, and thought processes. • Major depressive disorder is marked by profound sadness, slowed thought processes, low self-esteem, and loss of interest in previous sourc ...
Disorders Pt. 2
... Somatization disorders are intensely and chronically uncomfortable conditions that indirectly create a high risk of medical complications. They take the form of chronic and recurrent aches, pains, fever, tiredness, and other symptoms of somatic (bodily) illness. In addition, individuals with these d ...
... Somatization disorders are intensely and chronically uncomfortable conditions that indirectly create a high risk of medical complications. They take the form of chronic and recurrent aches, pains, fever, tiredness, and other symptoms of somatic (bodily) illness. In addition, individuals with these d ...
Abnormal Behaviors
... Evolution of the DSM –What is it? 5 AXES – write examples for each 1. Clinical Disorders 2. Intellectual Disabilities & Personality Disorders 3. Medical conditions and physical disorders ...
... Evolution of the DSM –What is it? 5 AXES – write examples for each 1. Clinical Disorders 2. Intellectual Disabilities & Personality Disorders 3. Medical conditions and physical disorders ...
340 h6 mckenna sum16 - Rutgers Psychology
... classrooms stating that the assigned classroom has been reassigned to a different location. Please ignore these notes.. You will receive an email from myself or the psychology department if any changes in classroom assignment are made. Course Objectives This course will introduce you to the fascinat ...
... classrooms stating that the assigned classroom has been reassigned to a different location. Please ignore these notes.. You will receive an email from myself or the psychology department if any changes in classroom assignment are made. Course Objectives This course will introduce you to the fascinat ...
Chapter 6
... Codependence Issues • Codependence is a compulsion to control, take care of, and rescue people by fixing their problems and minimizing their pain ...
... Codependence Issues • Codependence is a compulsion to control, take care of, and rescue people by fixing their problems and minimizing their pain ...
Ch 17 Mental Disorders
... – 1. A type of anxiety disorder in which one cannot relax and is plagued by frequent and overwhelming attacks of anxiety – 2. Sometimes it develops in the person’s psyche, probably developed from years of feeling insecure and helpless. – 3. Often develops because something is physically or chemicall ...
... – 1. A type of anxiety disorder in which one cannot relax and is plagued by frequent and overwhelming attacks of anxiety – 2. Sometimes it develops in the person’s psyche, probably developed from years of feeling insecure and helpless. – 3. Often develops because something is physically or chemicall ...
Lecture Notes
... If depression is the common cold of mental disorders, schizophrenia is the cancer. 1% of population Billions in health care costs Cruelest and most devastating illness Strikes ages 17 - 26 (mostly) some late onset in 30s - 40s 1898 German psychia ...
... If depression is the common cold of mental disorders, schizophrenia is the cancer. 1% of population Billions in health care costs Cruelest and most devastating illness Strikes ages 17 - 26 (mostly) some late onset in 30s - 40s 1898 German psychia ...
Document
... Dissociative Disorders : class of disorders in which people lose contact with portions of consciousness or memory, resulting in the disruption of their sense of identity. Three main types of dissociative disorders: 1 . Dissociative amnesia: sudden loss of memory for important personal informat ...
... Dissociative Disorders : class of disorders in which people lose contact with portions of consciousness or memory, resulting in the disruption of their sense of identity. Three main types of dissociative disorders: 1 . Dissociative amnesia: sudden loss of memory for important personal informat ...