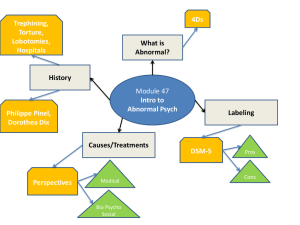
Intro to Abnormal
... DSM-V Definition of Mental Disorder • A mental disorder is a syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes ,underlying mental functio ...
... DSM-V Definition of Mental Disorder • A mental disorder is a syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior that reflects a dysfunction in the psychological, biological, or developmental processes ,underlying mental functio ...
Delirium, amnestic syndrome
... Condition Substance-induced persisting amnestic disorder CRITERIA – development of memory impairment as manifested by impairment in the ability to learn new information or the inability to recall previously learned information – significant impairment in social or occupational functioning due to the ...
... Condition Substance-induced persisting amnestic disorder CRITERIA – development of memory impairment as manifested by impairment in the ability to learn new information or the inability to recall previously learned information – significant impairment in social or occupational functioning due to the ...
Aggression as a Symptom of Mood
... Finally, symptoms can also be masked by psychotropic medications prescribed for other reasons, such as sedation or management of aggression. Research studies and clinical case reports indicate that mood disturbance is associated with an increase in aggressive behaviours in people with developmental ...
... Finally, symptoms can also be masked by psychotropic medications prescribed for other reasons, such as sedation or management of aggression. Research studies and clinical case reports indicate that mood disturbance is associated with an increase in aggressive behaviours in people with developmental ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • DSM will NOT explain the causes or possible cures. • DSM 5 new names mental retardation now intellectual disability • Also new categories hoarding and binge-eating disorder ...
... • DSM will NOT explain the causes or possible cures. • DSM 5 new names mental retardation now intellectual disability • Also new categories hoarding and binge-eating disorder ...
CH 13 study guide
... criteria and the influence of the pharmaceutical industry. They suggest that ordinary human responses to extremely stressful life events are being mistaken for psychological disorder. 16. Schizophrenia affects very few people, but it is the most common psychotic disorder (i.e., a disorder characteri ...
... criteria and the influence of the pharmaceutical industry. They suggest that ordinary human responses to extremely stressful life events are being mistaken for psychological disorder. 16. Schizophrenia affects very few people, but it is the most common psychotic disorder (i.e., a disorder characteri ...
340 h6 mckenna sum16 - Rutgers Psychology
... .We will compare various current theories of the development of behavioral and cognitive disorders as defined by the Diagnostic Statistical Manual V (DSM-V) as well as the efficacy of various treatment modalities including pharmacological interventions. As a result, you will be able to better recogn ...
... .We will compare various current theories of the development of behavioral and cognitive disorders as defined by the Diagnostic Statistical Manual V (DSM-V) as well as the efficacy of various treatment modalities including pharmacological interventions. As a result, you will be able to better recogn ...
May 2015
... social phobia. If left untreated anxiety disorders tend to continue into adulthood and place children at increased risk for other problems, including poor academic performance, depression, and drug dependence. For these reasons understanding the nature of anxiety problems, and how best to treat them ...
... social phobia. If left untreated anxiety disorders tend to continue into adulthood and place children at increased risk for other problems, including poor academic performance, depression, and drug dependence. For these reasons understanding the nature of anxiety problems, and how best to treat them ...
ClassPresentation07
... socially engaging faces. • Greater amygdala activation in autistic group for both ...
... socially engaging faces. • Greater amygdala activation in autistic group for both ...
PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2 Current
... Symptoms similar to PTSD Duration varies » Short term reaction » Symptoms occur between 2 days and 1 month after trauma ...
... Symptoms similar to PTSD Duration varies » Short term reaction » Symptoms occur between 2 days and 1 month after trauma ...
File
... line and violating those rights. It usually begins in childhood or as a teen and continues into their adult lives. Antisocial personality disorder is often referred to as psychopathy or sociopathy in popular culture. However, neither psychopathy nor sociopathy are recognized professional labels used ...
... line and violating those rights. It usually begins in childhood or as a teen and continues into their adult lives. Antisocial personality disorder is often referred to as psychopathy or sociopathy in popular culture. However, neither psychopathy nor sociopathy are recognized professional labels used ...
What is Selective Mutism? - Super Duper Publications
... Selective mutism is a disorder that affects a child’s ability to speak in certain settings. For example, a child may be able to speak with family at home but not with peers at school. Selective mutism is linked to anxiety and may be related to social phobia. It is important to remember that selectiv ...
... Selective mutism is a disorder that affects a child’s ability to speak in certain settings. For example, a child may be able to speak with family at home but not with peers at school. Selective mutism is linked to anxiety and may be related to social phobia. It is important to remember that selectiv ...
14 Disability Categories Under IDEA
... The definitions of the specific disability categories are below. These are federal terms and definitions. 1. Autism A developmental disability significantly affecting verbal and nonverbal communication and social interaction, generally evident before age three, that adversely affects a child’s educa ...
... The definitions of the specific disability categories are below. These are federal terms and definitions. 1. Autism A developmental disability significantly affecting verbal and nonverbal communication and social interaction, generally evident before age three, that adversely affects a child’s educa ...
v-codes relational problems
... based on DSM-IV-TR mood disorder diagnoses. If one or more individuals meet the criteria for an Axis I mood disorder, psychotherapy and medication to address that diagnosis should be primary. Symptoms of anxiety need to be assessed and reviewed based on DSM-IV-TR anxiety diagnoses. If one or more in ...
... based on DSM-IV-TR mood disorder diagnoses. If one or more individuals meet the criteria for an Axis I mood disorder, psychotherapy and medication to address that diagnosis should be primary. Symptoms of anxiety need to be assessed and reviewed based on DSM-IV-TR anxiety diagnoses. If one or more in ...
DSM-IV
... 81.4% with comorbid mood disorder 59% with comorbid unipolar depression 22% with comorbid bipolar depression 38% with comorbid mood disorder made at least one suicide attempt – 28.9%% suicide attempts in pts. with comorbid bipolar disorder ...
... 81.4% with comorbid mood disorder 59% with comorbid unipolar depression 22% with comorbid bipolar depression 38% with comorbid mood disorder made at least one suicide attempt – 28.9%% suicide attempts in pts. with comorbid bipolar disorder ...
psych 2 - Huber Heights City Schools
... 1. Essential features – characteristics that define the disorder 2. Associated features – additional features that are usually present 3. Differential diagnosis – info on how to distinguish the disorder from other disorders with which it might be confused 4. Diagnostic criteria – a list of symptoms, ...
... 1. Essential features – characteristics that define the disorder 2. Associated features – additional features that are usually present 3. Differential diagnosis – info on how to distinguish the disorder from other disorders with which it might be confused 4. Diagnostic criteria – a list of symptoms, ...
POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER
... If it is claimed a medication required to treat Posttraumatic Stress Disorder resulted in whole, or in part, in the clinical onset, or clinical worsening, of a medical condition the following must be established: 1. The individual was receiving the medication at the time of the clinical onset, or cl ...
... If it is claimed a medication required to treat Posttraumatic Stress Disorder resulted in whole, or in part, in the clinical onset, or clinical worsening, of a medical condition the following must be established: 1. The individual was receiving the medication at the time of the clinical onset, or cl ...
Snímek 1
... Difficulty concentrating on reading or watching television. Fear, anxiety or annoying feelings from other people. Restlessness, irritability or quick temperedness. Feeling that something unusual and incomprehensible is about to happen around me. Loss of energy or interests. Decreased capacity to cop ...
... Difficulty concentrating on reading or watching television. Fear, anxiety or annoying feelings from other people. Restlessness, irritability or quick temperedness. Feeling that something unusual and incomprehensible is about to happen around me. Loss of energy or interests. Decreased capacity to cop ...
Management of PICA (Swallowing Behaviors)
... or within the rectal vault. Fecal smearing and eating may result from hemorrhoids, obstipation, constipation, impaction, or other GU problems. Fecal picking or fecal smearing is a serious hygiene problem and these individuals should have meticulous cleansing of hands, face, and careful attention to ...
... or within the rectal vault. Fecal smearing and eating may result from hemorrhoids, obstipation, constipation, impaction, or other GU problems. Fecal picking or fecal smearing is a serious hygiene problem and these individuals should have meticulous cleansing of hands, face, and careful attention to ...
Slide 1
... Self as a form of potency Self developed through a variety of spiritual practices and self restraint The ability to maintain a refined, controlled self is central to normal behavior The powerful self can relate to and interact with the unseen spirit world without being ...
... Self as a form of potency Self developed through a variety of spiritual practices and self restraint The ability to maintain a refined, controlled self is central to normal behavior The powerful self can relate to and interact with the unseen spirit world without being ...
PoSterS - IACAPAP2016
... Adolescents’ Reactions Toward Parental Deployment and Depression: the Moderating Role of Child-Parent Communication Effects of Audience Types on Children’s Drawings of Emotionally Significant Human Figures Concept Analysis of Bodily Integrity in Infants Born Intersex/With Disorders of Sex Developm ...
... Adolescents’ Reactions Toward Parental Deployment and Depression: the Moderating Role of Child-Parent Communication Effects of Audience Types on Children’s Drawings of Emotionally Significant Human Figures Concept Analysis of Bodily Integrity in Infants Born Intersex/With Disorders of Sex Developm ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.