Magic Square and isotope worksheet
... 4. The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons 7. Formed the atomic theory model of the atom; English schoolteacher 8. Discovered the nucleus using h ...
... 4. The paths in which electrons circle the nucleus according to the Bohr model 5. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons 7. Formed the atomic theory model of the atom; English schoolteacher 8. Discovered the nucleus using h ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... Atomic number – number of protons and electrons (number at top of box) Atomic mass – number of protons and neutrons added together (number at bottom of box) ...
... Atomic number – number of protons and electrons (number at top of box) Atomic mass – number of protons and neutrons added together (number at bottom of box) ...
Chemistry Final Study Guide
... A __________ is two or more atoms bonded together. Atoms and molecules are always in __________. A __________ __________ cannot be broken down by ordinary physical means. A __________ contains two or more pure substances. A __________ has a fixed volume and a fixed shape. A __________ has a fixed vo ...
... A __________ is two or more atoms bonded together. Atoms and molecules are always in __________. A __________ __________ cannot be broken down by ordinary physical means. A __________ contains two or more pure substances. A __________ has a fixed volume and a fixed shape. A __________ has a fixed vo ...
Notes on Atomic Structure Structure of Atoms Atoms are composed
... The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is neutral. To find the number of neutrons, subtract the number of protons from the mass number. The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. The mass number can be found by rounding the average atomic m ...
... The atomic number also equals the number of electrons whenever the atom is neutral. To find the number of neutrons, subtract the number of protons from the mass number. The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. The mass number can be found by rounding the average atomic m ...
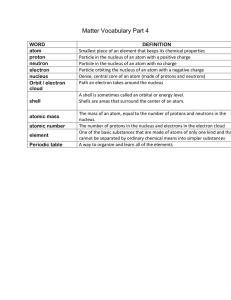
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Identify which of the three subatomic particles (p+, n, e–): is the
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... John Dalton (1803) updates the theory: • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to for ...
... John Dalton (1803) updates the theory: • Matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms. • Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to for ...
Outline Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... • The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8. 10-7. The Periodic Table Formulated by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in ~1869 Periodic law=states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular interv ...
... • The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8. 10-7. The Periodic Table Formulated by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in ~1869 Periodic law=states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular interv ...
Structure of the Atom
... – A rock has a mass of 5 grams. When placed in a graduated cylinder filled to 10mL, the water rises to 12 mL. What is the density of the rock? – A platinum bar measures 5.0 cm long, 4.0 cm wide, and 1.5 cm thick. It has a mass of 700.0 grams. What is the density of the platinum bar? ...
... – A rock has a mass of 5 grams. When placed in a graduated cylinder filled to 10mL, the water rises to 12 mL. What is the density of the rock? – A platinum bar measures 5.0 cm long, 4.0 cm wide, and 1.5 cm thick. It has a mass of 700.0 grams. What is the density of the platinum bar? ...
Friday Flashback Science 8 SC-08 1.1.2 Students will understand
... d. Highly reactive Lord Rutherford found that atoms contain dense central portions called: a. Neutrons b. Electrons c. Nuclei d. Protons The Charged Cloud model describes ________ as being part of a diffused cloud varying densities. a. Atoms b. Protons c. Neutrons d. Electrons The configuration of e ...
... d. Highly reactive Lord Rutherford found that atoms contain dense central portions called: a. Neutrons b. Electrons c. Nuclei d. Protons The Charged Cloud model describes ________ as being part of a diffused cloud varying densities. a. Atoms b. Protons c. Neutrons d. Electrons The configuration of e ...
atomic number - Teacher Pages
... These atoms typically gain or share two atoms in a reaction. The Oxygen we breath is O2 and Ozone = O3. Group 17 is known as the Halogen Family. All but one of these elements in the Halogen Family are nonmetals. A halogen atom has 7 valence electrons and typically gains or shares one electron when i ...
... These atoms typically gain or share two atoms in a reaction. The Oxygen we breath is O2 and Ozone = O3. Group 17 is known as the Halogen Family. All but one of these elements in the Halogen Family are nonmetals. A halogen atom has 7 valence electrons and typically gains or shares one electron when i ...
Chemistry 11 Early Models of the Atom Power Point
... Bohr pictured the hydrogen atom as having discrete energy “levels” which the electron could “inhabit”. In it’s ground state, the electron would be in the lowest level (n=1) When the atom was “excited” the electron could “jump” to a higher level. When the electron came back down, it released energy ...
... Bohr pictured the hydrogen atom as having discrete energy “levels” which the electron could “inhabit”. In it’s ground state, the electron would be in the lowest level (n=1) When the atom was “excited” the electron could “jump” to a higher level. When the electron came back down, it released energy ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every helium atom has two protons in its nucleus. - MASS NUMBER: The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus, Atoms of the same element may have DIFFERENT mass numbers. - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mas ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... This proved that: the atom had a dense but very small positive core the electrons were far away from the nucleus Most of the atom is just EMPTY SPACE! ...
... This proved that: the atom had a dense but very small positive core the electrons were far away from the nucleus Most of the atom is just EMPTY SPACE! ...
CHM 103 Lecture 6 S07
... Electron Configuration Lists the shells containing electrons Written in order of increasing energy Element Shell ...
... Electron Configuration Lists the shells containing electrons Written in order of increasing energy Element Shell ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
Atomic Theory History Presentation
... • 1911 – Rutherford’s Experiment • 1913 – Bohr Model of an atom ...
... • 1911 – Rutherford’s Experiment • 1913 – Bohr Model of an atom ...
Chemistry lecture notes
... Protons and neutrons are held together by an attraction force (strong interaction). An electrostatic ruplsion between protons occurs inside the nucleus The balance of the two forces controls some important features of nuclear stability ...
... Protons and neutrons are held together by an attraction force (strong interaction). An electrostatic ruplsion between protons occurs inside the nucleus The balance of the two forces controls some important features of nuclear stability ...