The Atom
... - have different numbers of electrons - may have the same number of electrons in the outer energy levels - the electrons in the outer energy levels determine the chemical properties of the element Different elements with the same number of electrons in the outer energy levels have similar chemical p ...
... - have different numbers of electrons - may have the same number of electrons in the outer energy levels - the electrons in the outer energy levels determine the chemical properties of the element Different elements with the same number of electrons in the outer energy levels have similar chemical p ...
Multiple Choice - EDU360ScienceMethods
... The vertical rows are called periods. The elements that share a period have the same number of atomic orbitals. The elements that are within the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer atomic orbitals. All the elements within a same family have the same properties. It is organize ...
... The vertical rows are called periods. The elements that share a period have the same number of atomic orbitals. The elements that are within the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer atomic orbitals. All the elements within a same family have the same properties. It is organize ...
The Periodic Table
... nucleus to the valence shell of an atom. • Increases down a group. • Decreases going right in a period. ...
... nucleus to the valence shell of an atom. • Increases down a group. • Decreases going right in a period. ...
Class Notes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed ...
what is inside an atom? - FSU High Energy Physics
... (“RAISIN CAKE MODEL”): J.J. Thomson (1897): discovery of electron; electron = charged particle, much less massive (2000 times) than lightest known ion; appeared to come out of matter - part of atoms? Thomson's atom model: atom = sphere of positive charge ...
... (“RAISIN CAKE MODEL”): J.J. Thomson (1897): discovery of electron; electron = charged particle, much less massive (2000 times) than lightest known ion; appeared to come out of matter - part of atoms? Thomson's atom model: atom = sphere of positive charge ...
Unit 2 Atomic Structure Study Guide
... 17.What is a cation? Which particles does it have more of: electrons or protons? Average Atomic Mass 1. How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an element? 2. Example: The Carbon atom has three isotopes: Carbon12 at 98.2%, Carbon-13 at 1.2%, and Carbon-14 at 0.6%. What is the average atomic ...
... 17.What is a cation? Which particles does it have more of: electrons or protons? Average Atomic Mass 1. How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an element? 2. Example: The Carbon atom has three isotopes: Carbon12 at 98.2%, Carbon-13 at 1.2%, and Carbon-14 at 0.6%. What is the average atomic ...
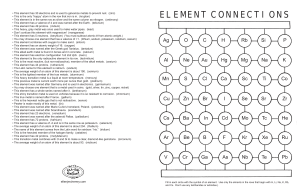
element connections
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
Electrons
... For example: Na (Sodium), has originally 11 electrons but when an electron is lost it becomes a positive ion. Na+ ...
... For example: Na (Sodium), has originally 11 electrons but when an electron is lost it becomes a positive ion. Na+ ...
I. Atoms are the smallest forms
... Group 2 loses two electrons to become +2 ions Group 18 do not form ions at all Group 17 gain an electron to become negative ions Group 16 can gain 2 electrons to become -2 ions Groups 3 to 12 all form positive ions but the charge can ...
... Group 2 loses two electrons to become +2 ions Group 18 do not form ions at all Group 17 gain an electron to become negative ions Group 16 can gain 2 electrons to become -2 ions Groups 3 to 12 all form positive ions but the charge can ...
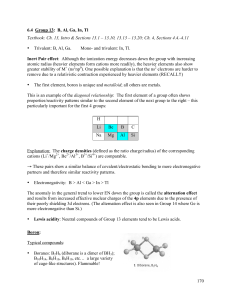
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
... 1. a. Magnesium, chromium and sodium are all metals, hence, they react with oxygen to form basic oxides b. Chromium, as it is a transition metal. Metals have high density and coloured compounds are formed by transition metals. c. Bromine - the formula is Br2, that is, two atoms of bromine. d. Bromin ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... diagonal staircase line that runs from boron (B) to astatine (At). • Hydrogen, though a nonmetal, is on the left side of the periodic table. • The state of matter at which nonmetals are at room temperature, vary from element to element. ...
... diagonal staircase line that runs from boron (B) to astatine (At). • Hydrogen, though a nonmetal, is on the left side of the periodic table. • The state of matter at which nonmetals are at room temperature, vary from element to element. ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... 31. Which substance would have London dispersion forces as the main type of intermolecular forces of attraction? a. H2O b. F2 d. HCl d. NaCl 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipol ...
... 31. Which substance would have London dispersion forces as the main type of intermolecular forces of attraction? a. H2O b. F2 d. HCl d. NaCl 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipol ...
Energy Atoms and Elements Practice Problems
... B) An electron has a negative charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. C) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 2 amu. D) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. ...
... B) An electron has a negative charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. C) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 2 amu. D) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. ...
Electron Arrangement
... Atomic Number • Moseley, in an experiment called the X-ray tube experiment, determined that each element has a different and unique number of protons. • The number of protons is referred to as the element’s atomic number. • The atomic number can be used to identify the element. • Atomic Number = # ...
... Atomic Number • Moseley, in an experiment called the X-ray tube experiment, determined that each element has a different and unique number of protons. • The number of protons is referred to as the element’s atomic number. • The atomic number can be used to identify the element. • Atomic Number = # ...
Guided Notes - Fordson High School
... • Extremely well respected and influential philosopher. • He did ________ believe that anything was empty, and that atoms could not exist because they had ___________ space. John Dalton (1766 – 1844) • Revised _____________________________ ideas. • Created Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Matter is made up ...
... • Extremely well respected and influential philosopher. • He did ________ believe that anything was empty, and that atoms could not exist because they had ___________ space. John Dalton (1766 – 1844) • Revised _____________________________ ideas. • Created Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Matter is made up ...
ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Evolution of Atomic Theory
... Positively charged particles, called protons, are contained in the nucleus. Electrons (negatively charged particles) “orbit” around the nucleus throughout the atom. Later experiments also confirmed that all atoms except hydrogen must contain one or more neutral (non-charged) particles called neutron ...
... Positively charged particles, called protons, are contained in the nucleus. Electrons (negatively charged particles) “orbit” around the nucleus throughout the atom. Later experiments also confirmed that all atoms except hydrogen must contain one or more neutral (non-charged) particles called neutron ...
rev8thgrade - PAMS
... neutral atom • Atomic mass is the average mass of all the isotopes of an element • Neutrons can be determined by subtracting the atomic mass from the atomic number. ...
... neutral atom • Atomic mass is the average mass of all the isotopes of an element • Neutrons can be determined by subtracting the atomic mass from the atomic number. ...
Dalton, Plum Pudding, and Rutherford`s Atomic Theories (Models) 9
... • Alpha particles (small, positive particles) were aimed at a thin piece of metal (gold) foil. ...
... • Alpha particles (small, positive particles) were aimed at a thin piece of metal (gold) foil. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... called the nucleus. Calculations showed that the nucleus must contain most of the mass of the atom and must be very small compared to the volume occupied by the atom. The positively charged particle present in the nucleus was called a proton. The nucleus of the hydrogen atom carries one positive cha ...
... called the nucleus. Calculations showed that the nucleus must contain most of the mass of the atom and must be very small compared to the volume occupied by the atom. The positively charged particle present in the nucleus was called a proton. The nucleus of the hydrogen atom carries one positive cha ...
Group IV Elements
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their ...
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their ...
1.2 Basic Atomic Theory Electrical structure of matter
... Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass) Compounds form when elements combine ...
... Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in chemical reactions (law of conservation of mass) Compounds form when elements combine ...