PowerPoint Presentation - The Atom: Chp 12 sect 2
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
... the same, • although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. • Some isotopes are radioactivemeaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, • perhaps another element half-life: time required for half of the atoms of an element to decay into stable form. ...
Abstract
... where SMOW is standard mean ocean water that is used as a standard material for oxygen isotope ratios. Isotope ratios change during physico-chemical and nuclear reactions. In the physico-chemical reactions, mass differences between isotopes are responsible for changing isotope ratios, because heavie ...
... where SMOW is standard mean ocean water that is used as a standard material for oxygen isotope ratios. Isotope ratios change during physico-chemical and nuclear reactions. In the physico-chemical reactions, mass differences between isotopes are responsible for changing isotope ratios, because heavie ...
Safety - Wando High School
... 1. What makes a covalent bond? What makes an ionic bond? 2. What happens with the electrons in an ionic and covalent bond? 3. Why do atoms bond? 4. In a chemical formula what do the symbols and numbers represent? 5. What is a molecule? Is CO2 a molecule? Is NaCl a molecule? 6. What is an elements ox ...
... 1. What makes a covalent bond? What makes an ionic bond? 2. What happens with the electrons in an ionic and covalent bond? 3. Why do atoms bond? 4. In a chemical formula what do the symbols and numbers represent? 5. What is a molecule? Is CO2 a molecule? Is NaCl a molecule? 6. What is an elements ox ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... theory has been revised since then – now electrons are believed to be found in orbitals around the nucleus, called the quantum theory. Atomic Structure Terms: ...
... theory has been revised since then – now electrons are believed to be found in orbitals around the nucleus, called the quantum theory. Atomic Structure Terms: ...
Ground state electron arrangement
... Bohr proposed that when energy is added to a hydrogen atom, its ___________________________moves to a higher-energy orbit ...
... Bohr proposed that when energy is added to a hydrogen atom, its ___________________________moves to a higher-energy orbit ...
History of Atomic Theory
... that showed electrons orbiting the nucleus in distinct energy levels, much the way the planets orbit the sun. This model explained the atomic emission spectrum for hydrogen but it did not explain the emission spectra for other elements. ...
... that showed electrons orbiting the nucleus in distinct energy levels, much the way the planets orbit the sun. This model explained the atomic emission spectrum for hydrogen but it did not explain the emission spectra for other elements. ...
Atoms
... Discovered the nucleus of an atom and named the positive particles in the nucleus “protons”. Concluded that electrons are scattered in empty space around the nucleus. ...
... Discovered the nucleus of an atom and named the positive particles in the nucleus “protons”. Concluded that electrons are scattered in empty space around the nucleus. ...
AtomicStructure_Peri..
... - the energy of an atom occurs in discrete levels - accounts for wave and particle nature of matter and energy - exact location of an electron is impossible to know ...
... - the energy of an atom occurs in discrete levels - accounts for wave and particle nature of matter and energy - exact location of an electron is impossible to know ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... • The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is the mass number. • The mass of a subatomic particle is too small to be expressed easily in grams, so a special unit called the atomic mass unit (amu) is used. • Protons and neutrons each have an atomic mass close to 1 amu. • Electrons hav ...
... • The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is the mass number. • The mass of a subatomic particle is too small to be expressed easily in grams, so a special unit called the atomic mass unit (amu) is used. • Protons and neutrons each have an atomic mass close to 1 amu. • Electrons hav ...
Chapter 1
... B. Now for Some Neutrons C. Building Bigger Atoms D. Protons and Atomic Number *Notes-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom give the element its _____________________. (also the number of electrons) ...
... B. Now for Some Neutrons C. Building Bigger Atoms D. Protons and Atomic Number *Notes-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom give the element its _____________________. (also the number of electrons) ...
Slide 1
... - a given compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass ...
... - a given compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Atoms
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons when chemically bonded. • Same trend as ionization energy. – In general, it increases across a row. Why? – increasing attraction as the number of protons in the nucleus increases (stronger magnet) – it decreases going down a group. Why? – Outer shell e ...
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons when chemically bonded. • Same trend as ionization energy. – In general, it increases across a row. Why? – increasing attraction as the number of protons in the nucleus increases (stronger magnet) – it decreases going down a group. Why? – Outer shell e ...
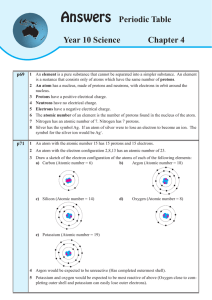
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
... 1 Briefly describe the chemical properties of group 17 - the halogens. The group 17 halogens are reactive and dangerous (Chlorine was used as a poisonous gas during World War I). The halogens react with metals to form salts. The halogens become less reactive the further down the group. 2 Briefly ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
What does an atom look like?
... What does an atom look like? Date Event / Scientist 400 B.C. Democritus (Pg. 67) ...
... What does an atom look like? Date Event / Scientist 400 B.C. Democritus (Pg. 67) ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? Ions 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? Isotope 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? Different element (proton determines the IDENTIY of element) 9. How many protons, ...
... 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? Ions 7. What do we call atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons? Isotope 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? Different element (proton determines the IDENTIY of element) 9. How many protons, ...
Particular particle knowledge
... In any atom, the atomic mass is .............................................................. ...
... In any atom, the atomic mass is .............................................................. ...
Democritus John Dalton Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson Dimitri
... that were yet to be discovered. Later versions refined & expanded the table. ...
... that were yet to be discovered. Later versions refined & expanded the table. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... 17. The number of protons in an atom is the ___________________ number. All atoms of the same element have the _____________________ number of protons. Atoms of ________________________ elements have ______________________ numbers of protons. 18. The ___________________ ________________________ of a ...
... 17. The number of protons in an atom is the ___________________ number. All atoms of the same element have the _____________________ number of protons. Atoms of ________________________ elements have ______________________ numbers of protons. 18. The ___________________ ________________________ of a ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...