PS 2.3
... 2. Show pictures of everyday objects. Ask students what elements go into the make-up of each object. Choose some objects that are have elements in their make up that are not obvious. E1 3. Introduce the essential questions: What are the sub-atomic particles? How do subatomic particles affect the pro ...
... 2. Show pictures of everyday objects. Ask students what elements go into the make-up of each object. Choose some objects that are have elements in their make up that are not obvious. E1 3. Introduce the essential questions: What are the sub-atomic particles? How do subatomic particles affect the pro ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... "Describe and justify the criteria used to place metals into an order of activity based on their ease of reaction with oxygen, water and dilute acids". "Perform a first hand investigation and/or process information from secondary sources to determine the metal activity series". I would recommend tha ...
... "Describe and justify the criteria used to place metals into an order of activity based on their ease of reaction with oxygen, water and dilute acids". "Perform a first hand investigation and/or process information from secondary sources to determine the metal activity series". I would recommend tha ...
Chapter 03
... ►Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in each atom of an element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. ►Atoms are neutral overall and have no net charge because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electrons a ...
... ►Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in each atom of an element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. ►Atoms are neutral overall and have no net charge because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electrons a ...
Ancient and Modern Atomic Theory PPT
... 1. Determine the number of rings, or energy levels. (Look at the period, or row, number.) 2. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3. Determine the number of valence electrons. (Look at the group, or column, number.) 4. Draw the correct number of rings. 5. Draw the correct number ...
... 1. Determine the number of rings, or energy levels. (Look at the period, or row, number.) 2. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3. Determine the number of valence electrons. (Look at the group, or column, number.) 4. Draw the correct number of rings. 5. Draw the correct number ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... change to Dalton’s atomic theory is that atoms are divisible into subatomic particles: ...
... change to Dalton’s atomic theory is that atoms are divisible into subatomic particles: ...
Name - shssci
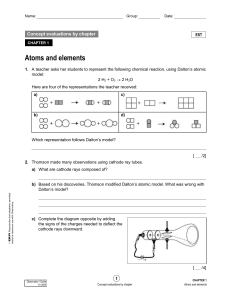
... 13. (2 points) Tell me 2 parts of Dalton’s atomic theory that are still relevant today? All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numbered ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separat ...
... 13. (2 points) Tell me 2 parts of Dalton’s atomic theory that are still relevant today? All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numbered ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separat ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... (a) first to propose that matter is composed of atoms (b) identified matter as being composed of either elements or compounds (c) showed that mass is conserved during chemical reactions (d) proposed that compounds always contain the same proportion of elements by mass (e) showed that matter composed ...
... (a) first to propose that matter is composed of atoms (b) identified matter as being composed of either elements or compounds (c) showed that mass is conserved during chemical reactions (d) proposed that compounds always contain the same proportion of elements by mass (e) showed that matter composed ...
atoms.
... • In 1803, Dalton proposed that elements consist of individual particles called atoms. • His atomic theory of matter contains four hypotheses: 1. All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and fundamental chemical properties. 3. A chemical ...
... • In 1803, Dalton proposed that elements consist of individual particles called atoms. • His atomic theory of matter contains four hypotheses: 1. All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and fundamental chemical properties. 3. A chemical ...
Chapter 8 and 10: Structure of the Atom
... 4. What specific information did Thompson include in his model of the atom that was different from Dalton? 5. Describe Millikan’s oil-drop experiment, the observations he made and the inductive reasoning he used to further the developing model of the atom. 6. Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experime ...
... 4. What specific information did Thompson include in his model of the atom that was different from Dalton? 5. Describe Millikan’s oil-drop experiment, the observations he made and the inductive reasoning he used to further the developing model of the atom. 6. Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experime ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Review WS
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit, which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller part ...
... Our model of the atom continues to evolve as new discoveries are made. The first atomic model that was based on scientific experiments came from John Dalton. He believed that each element had a smallest subunit, which he called the atom. He believed the atom could not be subdivided into smaller part ...
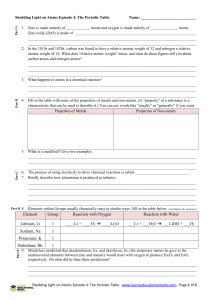
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or " ...
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or " ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
... is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manufactured in China. China therefore has a certain economic interest in Tibet. Mining the resource is r ...
... is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manufactured in China. China therefore has a certain economic interest in Tibet. Mining the resource is r ...
Unit 1 – Atomic Structure
... 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleu ...
... 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleu ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... A balanced chemical equation shows the correct number of each atom Balancing ensures that the number of each atom is the same on both sides of the reaction arrow Always use the smallest whole number ratio 4K(s) + O2 (g) 2K2O(s) ...
... A balanced chemical equation shows the correct number of each atom Balancing ensures that the number of each atom is the same on both sides of the reaction arrow Always use the smallest whole number ratio 4K(s) + O2 (g) 2K2O(s) ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
Chapter 14 ~ Atoms
... number of protons in its nucleus. Every atom of the same element has the same number of protons. For example, every carbon atom has six protons. Therefore, it has the atomic number 6. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. For example, every carbon atom has six protons, but e ...
... number of protons in its nucleus. Every atom of the same element has the same number of protons. For example, every carbon atom has six protons. Therefore, it has the atomic number 6. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. For example, every carbon atom has six protons, but e ...
Electronic Structure
... atomic radius. The bonding atomic radius- radius of the atom when it is bonded to another atom- is shorter than the nonbonding atomic radius. Think of an atom as a sphere. Atomic size tends to decrease as one goes from left to right per period on the periodic table. The bonding radii across period 2 ...
... atomic radius. The bonding atomic radius- radius of the atom when it is bonded to another atom- is shorter than the nonbonding atomic radius. Think of an atom as a sphere. Atomic size tends to decrease as one goes from left to right per period on the periodic table. The bonding radii across period 2 ...
Atomic Structure
... The mass number of this isotope of lithium is 7. Notice that 7 is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons. If you remove the protons (atomic number), the neutrons are left. ...
... The mass number of this isotope of lithium is 7. Notice that 7 is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons. If you remove the protons (atomic number), the neutrons are left. ...
1 - WordPress.com
... Which form of radiation has the lowest energy (ex. can be stopped by paper)? Alpha Which form has the highest energy (ex. will pass through several feet of concrete)? Gamma ...
... Which form of radiation has the lowest energy (ex. can be stopped by paper)? Alpha Which form has the highest energy (ex. will pass through several feet of concrete)? Gamma ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Part 2
... The word isotopes is from the Greek words for “equal place”. ...
... The word isotopes is from the Greek words for “equal place”. ...
Subatomic Particles
... Robert Millikan, an American scientist, experimentally determined the charge of an electron to be -1.6 x 10-19 coulomb. using the data of Thomson and Millikan, it was possible to calculate the actual mass of the electron. It was found to be 9.1 x 10-28 g = 1/1837 the mass of 1 H atom. Thomson ...
... Robert Millikan, an American scientist, experimentally determined the charge of an electron to be -1.6 x 10-19 coulomb. using the data of Thomson and Millikan, it was possible to calculate the actual mass of the electron. It was found to be 9.1 x 10-28 g = 1/1837 the mass of 1 H atom. Thomson ...