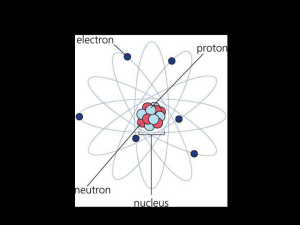
Atomic Structure
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... In the late 1700s solid evidence about the nature of matter, gained through quantitative scientific experiments, accumulated. Such evidence included the finding that during a chemical reaction matter was conserved. In the early 1800s a theory was proposed to explain these experimental facts. In this ...
... In the late 1700s solid evidence about the nature of matter, gained through quantitative scientific experiments, accumulated. Such evidence included the finding that during a chemical reaction matter was conserved. In the early 1800s a theory was proposed to explain these experimental facts. In this ...
8th Grade
... 16. In 1800 another scientist added to the idea of the Greek guy. Who was this man and what was his idea? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. In _______ ...
... 16. In 1800 another scientist added to the idea of the Greek guy. Who was this man and what was his idea? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. In _______ ...
Atomic Theory Booklet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... particles called atoms. An atom is the smallest particle that retains the properties of an element (so a carbon atom would still have the properties of carbon, but if you break the atom down these properties will disappear). This theory, although it sounds simple, is in reality extremely complex. It ...
... particles called atoms. An atom is the smallest particle that retains the properties of an element (so a carbon atom would still have the properties of carbon, but if you break the atom down these properties will disappear). This theory, although it sounds simple, is in reality extremely complex. It ...
The Story Behind Atomic Theory
... equal the ratio of O to C in a large container. In an attempt to explain how and why elements would combine with one another in fixed ratios and sometimes also in multiples of those ratios, Dalton formulated his atomic theory. ...
... equal the ratio of O to C in a large container. In an attempt to explain how and why elements would combine with one another in fixed ratios and sometimes also in multiples of those ratios, Dalton formulated his atomic theory. ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... elements combine in a specific way to create a new material with different properties than elements alone. Na (soft, silver) Cl ( green gas) NaCl – table salt. Done by chemical reaction. Formula – list symbol each element in there. Subscript – tells the number of each ...
... elements combine in a specific way to create a new material with different properties than elements alone. Na (soft, silver) Cl ( green gas) NaCl – table salt. Done by chemical reaction. Formula – list symbol each element in there. Subscript – tells the number of each ...
Lecture 3: Matter: What it is Slide 2: What does it Matter? What is a
... What do we mean by saying that atoms are the fundamental unit of matter? What is the structure of atoms? What are nucleons? What are the electric charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons? If ...
... What do we mean by saying that atoms are the fundamental unit of matter? What is the structure of atoms? What are nucleons? What are the electric charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons? If ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
... p+ and no, but some rare atoms will have only 196. They ALL have 79 p+. Most have 118no, but a few may have 117 no. ...
Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Matter
... something that is too big, too small or too complex to understand otherwise Models can also be used to study events that happen too fast or too slow or would be too dangerous to study otherwise ...
... something that is too big, too small or too complex to understand otherwise Models can also be used to study events that happen too fast or too slow or would be too dangerous to study otherwise ...
HW Problems
... CHE1031 Lecture 2 HW Problems must be solved, or written out, in their entirety with all work shown on engineering graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answer ...
... CHE1031 Lecture 2 HW Problems must be solved, or written out, in their entirety with all work shown on engineering graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answer ...
atoms - Net Start Class
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties ...
Learning session 2: Models of atomic structure
... shell only being able to hold a certain maximum number of electrons at a time, depending on how far it was from the nucleus. This also neatly accounted for why electrons, with a negative charge, were held quite strongly within the atom by the positive charge in the nucleus, but weren't completely su ...
... shell only being able to hold a certain maximum number of electrons at a time, depending on how far it was from the nucleus. This also neatly accounted for why electrons, with a negative charge, were held quite strongly within the atom by the positive charge in the nucleus, but weren't completely su ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... • On the periodic table, atomic radii tend to decrease left to right along a period, so group 1 atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in ...
... • On the periodic table, atomic radii tend to decrease left to right along a period, so group 1 atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in ...
The Evolution of the Atomic Model
... Based on Balmer’s emission line studies of the hydrogen atom and Planck’s work, Bohr proposed… a planetary model in which e- could only occupy certain energy levels. energy levels differed in a step like manner. electrons can occupy different energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy. ...
... Based on Balmer’s emission line studies of the hydrogen atom and Planck’s work, Bohr proposed… a planetary model in which e- could only occupy certain energy levels. energy levels differed in a step like manner. electrons can occupy different energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy. ...
Atomic Physics
... would pass straight through an atom. Rutherford proposed an atom that is open space with positive charge concentrated in a very dense nucleus. Alpha scattering ...
... would pass straight through an atom. Rutherford proposed an atom that is open space with positive charge concentrated in a very dense nucleus. Alpha scattering ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... c) Factors affecting Ionization Energy 1. Distance of outermost electron from the nucleus: Across the period, as atomic number increases, atomic radius decreases. As the distance decreases, the ...
... c) Factors affecting Ionization Energy 1. Distance of outermost electron from the nucleus: Across the period, as atomic number increases, atomic radius decreases. As the distance decreases, the ...
Ch. 2: Biochemistry
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
Atom Review
... When atoms emit alpha, beta or gamma radiation, it is undergoing a radioactive decay. Decay occurs due to instability within the nucleus. As the ratio of protons to neutrons becomes more skewed, the nucleus becomes more unstable. All isotopes with an atomic number greater than 83 are unstabl ...
... When atoms emit alpha, beta or gamma radiation, it is undergoing a radioactive decay. Decay occurs due to instability within the nucleus. As the ratio of protons to neutrons becomes more skewed, the nucleus becomes more unstable. All isotopes with an atomic number greater than 83 are unstabl ...
Physical Science
... D. It is the measure of the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Nitrogen is only a part of what makes up all of the air molecules pushing down on a surface. S.C.8.4.3b DOK1 ...
... D. It is the measure of the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Nitrogen is only a part of what makes up all of the air molecules pushing down on a surface. S.C.8.4.3b DOK1 ...
Name Per ___ Reading Assignment – Chapter 4 pages 100
... 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) __________ charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experiments provided the first evidence for the existence of subatomic particles. _________________ 10. Descri ...
... 8. Thomson concluded that the particles in the glowing beam had a(n) __________ charge because they were attracted to a positive plate. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Thomson’s experiments provided the first evidence for the existence of subatomic particles. _________________ 10. Descri ...
View PDF
... b. collide with other electrons. c. move from higher to lower energy levels. d. collide with the nucleus. ...
... b. collide with other electrons. c. move from higher to lower energy levels. d. collide with the nucleus. ...
Atomic Structure
... • Electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom • Most stable configuration: electrons occupy lowest-energy orbitals (called the ground state) • An atom in an excited state has absorbed enough energy for one electron to move to a higher-energy orbital • Example: Neo ...
... • Electron configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom • Most stable configuration: electrons occupy lowest-energy orbitals (called the ground state) • An atom in an excited state has absorbed enough energy for one electron to move to a higher-energy orbital • Example: Neo ...