
ATOMIC THEORY Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory
... 1808 based on the following: • Democritus’ atom • Law of conservation of mass • Law of definite proportions • Law of multiple proportions ...
... 1808 based on the following: • Democritus’ atom • Law of conservation of mass • Law of definite proportions • Law of multiple proportions ...
Nuclear pharmacy lecture 1
... ► Each shell is designated by quantum number n, called the principal quantum number. ► Each energy shell is subdivided into subshells or orbitals, which are designated as s, p, d, f, etc. (azimuthal quantum numbers, l). l = 0,1,2……etc. ► The electron will enter the orbital of the lowest energy firs ...
... ► Each shell is designated by quantum number n, called the principal quantum number. ► Each energy shell is subdivided into subshells or orbitals, which are designated as s, p, d, f, etc. (azimuthal quantum numbers, l). l = 0,1,2……etc. ► The electron will enter the orbital of the lowest energy firs ...
Problem Set 4 - Morrisville.org
... Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Read Chapter 25 After having read through chapter 25, respond to these conceptual questions. 47) Define the following terms: a. critical mass d.fusion g.radioisotope b.decay e. half life c. fission f. transmutation 48) Make (or find) a graphical timeline of the developm ...
... Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Read Chapter 25 After having read through chapter 25, respond to these conceptual questions. 47) Define the following terms: a. critical mass d.fusion g.radioisotope b.decay e. half life c. fission f. transmutation 48) Make (or find) a graphical timeline of the developm ...
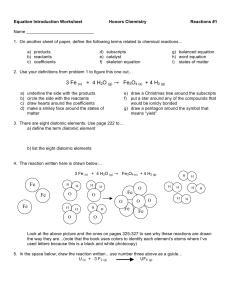
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
Structure of the Atom Cornell Notes (pg
... What is the difference between C-12 and C-14? (p. 177) The mass number of sodium is 23. How many protons and neutrons does it have? (p. 177) What is atomic mass? Using copper isotopes as an example explain why this not always a whole number? ...
... What is the difference between C-12 and C-14? (p. 177) The mass number of sodium is 23. How many protons and neutrons does it have? (p. 177) What is atomic mass? Using copper isotopes as an example explain why this not always a whole number? ...
neutrons
... number due to varying numbers of neutrons Isotopes are usually identified by specifying their mass number. Two methods for specifying isotopes: The mass number is written with a hyphen after the name of the element ex: hydrogen-3 is tritium Show the composition of a nucleus as the isotopes nucle ...
... number due to varying numbers of neutrons Isotopes are usually identified by specifying their mass number. Two methods for specifying isotopes: The mass number is written with a hyphen after the name of the element ex: hydrogen-3 is tritium Show the composition of a nucleus as the isotopes nucle ...
Modern Atomic Theory: Electron Cloud Model
... electrons travel around nucleus in definite paths. Paths were located certain distances from nucleus. Electrons could jump from level to level. ...
... electrons travel around nucleus in definite paths. Paths were located certain distances from nucleus. Electrons could jump from level to level. ...
Measuring and Calculating
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
File
... Like the layers of an onion, as the energy levels extend farther from the nucleus, they get larger in diameter and can hold more electrons. The maximum number each level can hold is shown in figure 18.14. Energy levels can It is important to note that some energy levels can overlap. In fact, each en ...
... Like the layers of an onion, as the energy levels extend farther from the nucleus, they get larger in diameter and can hold more electrons. The maximum number each level can hold is shown in figure 18.14. Energy levels can It is important to note that some energy levels can overlap. In fact, each en ...
Evolution of the Atom - Northwestern University
... is the only force affecting neutrinos (except for gravitation, which is negligible on laboratory scales). The weak interaction enables all lepton and quark particles and antiparticles to interchange energy, mass, electric charge and flavor—effectively to change into each other. It keeps together ele ...
... is the only force affecting neutrinos (except for gravitation, which is negligible on laboratory scales). The weak interaction enables all lepton and quark particles and antiparticles to interchange energy, mass, electric charge and flavor—effectively to change into each other. It keeps together ele ...
Chapter 2 Elements are made up of small particles called atoms. All
... The periodic table is a chart where elements are organized depending on how similar they are. The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns are called groups or families. ...
... The periodic table is a chart where elements are organized depending on how similar they are. The horizontal rows are called periods and the vertical columns are called groups or families. ...
Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element
... of table is an 18 × 7 grid, and elements with the same number of valence electrons are kept together in groups, such as the halogens and the noble gases. There are four distinct rectangular areas or blocks. The f-block is usually not included in the main table, but rather is floated below, as an inl ...
... of table is an 18 × 7 grid, and elements with the same number of valence electrons are kept together in groups, such as the halogens and the noble gases. There are four distinct rectangular areas or blocks. The f-block is usually not included in the main table, but rather is floated below, as an inl ...
chapter 4, arrangement of electrons in atoms
... According to the above equation, the minimum energy corresponds to a minimum frequency. If a photon’s frequency is below the minimum, then the electron remains bound to the metal surface. And, electrons in different metals are bound more or less tightly, so different metals require different minimum ...
... According to the above equation, the minimum energy corresponds to a minimum frequency. If a photon’s frequency is below the minimum, then the electron remains bound to the metal surface. And, electrons in different metals are bound more or less tightly, so different metals require different minimum ...
Notes - Zion Central Middle School
... Atoms are made up of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons and electrons. o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom. o Electrons occupy orbitals or electron clouds that surround the nucleus. Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms and have an electric charge of +1. Neutrons are found in ...
... Atoms are made up of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons and electrons. o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom. o Electrons occupy orbitals or electron clouds that surround the nucleus. Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms and have an electric charge of +1. Neutrons are found in ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 4
... lines of specific wavelengths. This is called Atomic Emission Spectrum or the Line Spectrum. This is a discontinuous spectrum. Every element has its own characteristic emission spectrum, which is used to identify the element. Hence, it is called the atomic finger print. When radiations pass through ...
... lines of specific wavelengths. This is called Atomic Emission Spectrum or the Line Spectrum. This is a discontinuous spectrum. Every element has its own characteristic emission spectrum, which is used to identify the element. Hence, it is called the atomic finger print. When radiations pass through ...
File first semester final study guide key
... 1. John Dalton’s atomic theory states that, “atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.” The underlined portion of this statement is incorrect. Why? Because of the presence of ions and isotopes. ...
... 1. John Dalton’s atomic theory states that, “atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.” The underlined portion of this statement is incorrect. Why? Because of the presence of ions and isotopes. ...
Prerequisite Knowledge for Chemistry
... Compounds are represented by chemical formulas consisting of element symbols and subscripts. For instance, water’s chemical formula is H2O. The “H” stands for hydrogen and the “O” stands for oxygen. The subscripts come after the element to which they refer. Subscripts state the number of atoms of th ...
... Compounds are represented by chemical formulas consisting of element symbols and subscripts. For instance, water’s chemical formula is H2O. The “H” stands for hydrogen and the “O” stands for oxygen. The subscripts come after the element to which they refer. Subscripts state the number of atoms of th ...
e - Humble ISD
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
... He fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. He found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit and bounced back. ...
Atomic Structure-PRACTICE TEST
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element (atomic number) TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRU ...
Structure of the Atom - Models
... Models – Tools for Scientists Models are used to represent things that are difficult to visualize / see, or picture in the mind. Models must accurately represent all information known about what is being modeled. ...
... Models – Tools for Scientists Models are used to represent things that are difficult to visualize / see, or picture in the mind. Models must accurately represent all information known about what is being modeled. ...
Ch2ov1
... Î All matter is composed of atoms. Ù All atoms of an element have the same mass (atomic weight). Ú All atoms of different elements have different masses (i.e., different atomic weights). Û Atoms are indestructible and indivisible. Ò Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. Ó ...
... Î All matter is composed of atoms. Ù All atoms of an element have the same mass (atomic weight). Ú All atoms of different elements have different masses (i.e., different atomic weights). Û Atoms are indestructible and indivisible. Ò Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. Ó ...
1 Dalton`s Atomic Theory THE NATURE OF ATOMS (p.44)
... Groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) of periodic table are named after orbitals that are partially filled: e.g. S is in group VI (six valence electrons) [Ne] 3s2 3p4 and period 3 (valence electrons are in n = 3 shell) e.g. Ca is in group II (two valence electrons) [Ar] 4s2 and per ...
... Groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) of periodic table are named after orbitals that are partially filled: e.g. S is in group VI (six valence electrons) [Ne] 3s2 3p4 and period 3 (valence electrons are in n = 3 shell) e.g. Ca is in group II (two valence electrons) [Ar] 4s2 and per ...
Atomic Structure
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...
... Atomic Mass. Step 1: Write out the mass number and % abundance as a multiplication problem with a ...










![Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001197267_1-624cb7c7c4dbdb26b0769567aa77b6ad-300x300.png)











