Structure of the Atom
... residuum of the strong force that has somewhat different range-properties. The gluon is a member of the family of gauge bosons, which are elementary particles that mediate physical forces. All the bound protons and neutrons in an atom make up a tiny atomic nucleus, and are collectively called nucleo ...
... residuum of the strong force that has somewhat different range-properties. The gluon is a member of the family of gauge bosons, which are elementary particles that mediate physical forces. All the bound protons and neutrons in an atom make up a tiny atomic nucleus, and are collectively called nucleo ...
Class Notes
... The law of conservation of mass (aka: the law of conservation of matter) says that during a chemical reaction or a physical change mass is conserved; mass is neither created nor destroyed. This implies that the atoms that were there in the reactants (before the chemical change) must be there in the ...
... The law of conservation of mass (aka: the law of conservation of matter) says that during a chemical reaction or a physical change mass is conserved; mass is neither created nor destroyed. This implies that the atoms that were there in the reactants (before the chemical change) must be there in the ...
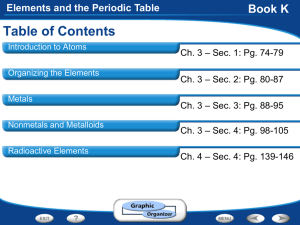
Chapter 4- Elements and the Periodic Table
... formed of small pieces that could not be cut into smaller parts. He used the word atomos, which means "uncuttable;' for these smallest possible pieces. In modern terms, an atom is the smallest particle of an element. The ancient Greeks did not prove the existence of atoms because they did not do exp ...
... formed of small pieces that could not be cut into smaller parts. He used the word atomos, which means "uncuttable;' for these smallest possible pieces. In modern terms, an atom is the smallest particle of an element. The ancient Greeks did not prove the existence of atoms because they did not do exp ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... Naming Covalent Compounds CO CO2 CO32C2O42 Rules for naming covalent compounds: 1) Write the less electronegative element first. 2) Write the root of the more electronegative element with the -ide ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
... Naming Covalent Compounds CO CO2 CO32C2O42 Rules for naming covalent compounds: 1) Write the less electronegative element first. 2) Write the root of the more electronegative element with the -ide ending second. 3) Add prefixes to both indicating the number of atoms of each element ...
Chapter 4 Presentation - Spearfish School District
... 1. The different colors that were created by using different gases showed that atoms of different elements possessed different energies. 2. The cast shadow was thought to be due to the beam of light created by the cathode-ray. However, the experiment made with the spinning paddle-wheel showed that t ...
... 1. The different colors that were created by using different gases showed that atoms of different elements possessed different energies. 2. The cast shadow was thought to be due to the beam of light created by the cathode-ray. However, the experiment made with the spinning paddle-wheel showed that t ...
ATOMS
... In this computer activity you will be creating your own Study Guide. Feel free to complete this lesson at your own pace. Please follow all instructions carefully. Ask your teacher if you need any help. ...
... In this computer activity you will be creating your own Study Guide. Feel free to complete this lesson at your own pace. Please follow all instructions carefully. Ask your teacher if you need any help. ...
iClicker PARTICIPATION Question: Development of the Modern
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Reactions
... both sides of the equations, replace them with a variable to make it easier. – Let X rep SO4 5) When dealing with O2 sometimes you have an odd number on one side. Put a ½ in front of the O2. Then balance and then multiply both sides by 2 6) Double-Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
... both sides of the equations, replace them with a variable to make it easier. – Let X rep SO4 5) When dealing with O2 sometimes you have an odd number on one side. Put a ½ in front of the O2. Then balance and then multiply both sides by 2 6) Double-Check to make sure it is balanced. ...
GLUCOSE - npd117.net
... CHEMICAL ELEMENT is a substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by ordinary means Elements have only ONE kind of atom ...
... CHEMICAL ELEMENT is a substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by ordinary means Elements have only ONE kind of atom ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]
... I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is meant by atomic number and state that all elements are arranged in ...
... I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is meant by atomic number and state that all elements are arranged in ...
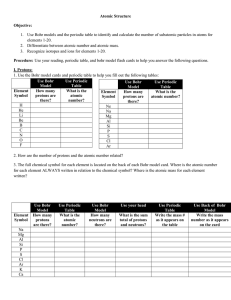
CHEMISTRY 1 CHAPTER II. ATOMIC STRUCTURE 2.1 ATOMIC
... Even though, it wasn´t very well accepted in his time, Democritus was the first to propose that atoms were the basic unit of all matter, it was the smallest indivisible part maintaining the characteristics of the original matter. Many years after John Dalton, took up this theory and support it it wi ...
... Even though, it wasn´t very well accepted in his time, Democritus was the first to propose that atoms were the basic unit of all matter, it was the smallest indivisible part maintaining the characteristics of the original matter. Many years after John Dalton, took up this theory and support it it wi ...
Understanding the Atom - Verona Public Schools
... types of quarks: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom. • Protons are made of two up quarks and one down quark. ...
... types of quarks: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom. • Protons are made of two up quarks and one down quark. ...
AP Chapter Five Outline
... the oxidizing agent. The substance that is oxidized causes the other species to be reduced and is called the reducing agent. ...
... the oxidizing agent. The substance that is oxidized causes the other species to be reduced and is called the reducing agent. ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
- ISIS neutron source
... This American physicist shared the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1994 with Bertram N. Brockhouse for 'pioneering contributions to the development of neutron scattering techniques for studies of condensed matter' – specifically for his 'development of the neutron diffraction technique'. Shull's first su ...
... This American physicist shared the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1994 with Bertram N. Brockhouse for 'pioneering contributions to the development of neutron scattering techniques for studies of condensed matter' – specifically for his 'development of the neutron diffraction technique'. Shull's first su ...
File
... 2. Masses of all elements are determined in comparison to the carbon 12 12 atom ( C), the most common isotope of carbon 3. Comparisons are made using a mass spectrometer B. Atomic Mass (Average atomic mass, atomic weight) 1. Atomic masses are the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an ele ...
... 2. Masses of all elements are determined in comparison to the carbon 12 12 atom ( C), the most common isotope of carbon 3. Comparisons are made using a mass spectrometer B. Atomic Mass (Average atomic mass, atomic weight) 1. Atomic masses are the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an ele ...
Chemistry-5th-Edition-Brady-Solution-Manual
... Strontium and calcium are in the same Group of the periodic table, so they are expected to have similar chemical properties. Strontium should therefore form compounds that are similar to those of calcium, including the sorts of compounds found in bone. ...
... Strontium and calcium are in the same Group of the periodic table, so they are expected to have similar chemical properties. Strontium should therefore form compounds that are similar to those of calcium, including the sorts of compounds found in bone. ...
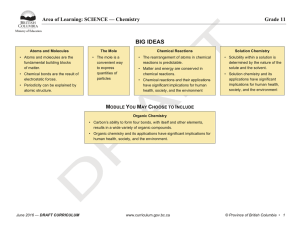
BIG IDEAS - BC Curriculum - Province of British Columbia
... • Formulate physical or mental theoretical models to describe a phenomenon • Communicate scientific ideas, information, and perhaps a suggested course of action, for a specific purpose and audience, constructing evidence-based arguments and using appropriate scientific language, conventions, and rep ...
... • Formulate physical or mental theoretical models to describe a phenomenon • Communicate scientific ideas, information, and perhaps a suggested course of action, for a specific purpose and audience, constructing evidence-based arguments and using appropriate scientific language, conventions, and rep ...
Chapter 7: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... integer whose value must be between - l and + l. mℓ specifies the direction of the orbital. Think of a specific orbital (or specific wave function ψ) as the house for an electron. The house is characterized by an address (three quantum numbers: n, ℓ and mℓ). n defines the city (shell) where ...
... integer whose value must be between - l and + l. mℓ specifies the direction of the orbital. Think of a specific orbital (or specific wave function ψ) as the house for an electron. The house is characterized by an address (three quantum numbers: n, ℓ and mℓ). n defines the city (shell) where ...
(p. 522)
... C.Hydrogen molecules and atoms occupy holes within the crystal structure of the metal. D.These substances are useful catalysts. E.These hydrides are stabilized by hydrogen bonding forces. 8. Xenon forms several compounds with oxygen and fluorine. It is the most reactive non-radioactive noble gas bec ...
... C.Hydrogen molecules and atoms occupy holes within the crystal structure of the metal. D.These substances are useful catalysts. E.These hydrides are stabilized by hydrogen bonding forces. 8. Xenon forms several compounds with oxygen and fluorine. It is the most reactive non-radioactive noble gas bec ...
Democritus (460
... levels (orbits) without ever existing in an in-between state. Thus when an atom absorbs or gives off energy (as in light or heat), the electron jumps to higher or lower orbits. Bohr's theory that electrons existed in set orbits around the nucleus was the key to the periodic repetition of properties ...
... levels (orbits) without ever existing in an in-between state. Thus when an atom absorbs or gives off energy (as in light or heat), the electron jumps to higher or lower orbits. Bohr's theory that electrons existed in set orbits around the nucleus was the key to the periodic repetition of properties ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... a. How do these values compare to the mass numbers as they appear on the back of the Bohr model for each element? b. Why are the atomic masses for each element represented as decimals instead of whole numbers (Hint: use your reading to help you with this)? 6. Using your chart, write an equation for ...
... a. How do these values compare to the mass numbers as they appear on the back of the Bohr model for each element? b. Why are the atomic masses for each element represented as decimals instead of whole numbers (Hint: use your reading to help you with this)? 6. Using your chart, write an equation for ...









![02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000821172_1-5bf1afd152b32026d524139a10b8292f-300x300.png)