Dalton`s Atomic Theory - timelinevalentinavandconniel
... It was in the early 1800s that John Dalton, an observer of weather and discoverer of color blindness among other things, came up with his atomic theory. Let's set the stage for Dalton's work. Less than twenty years earlier, in the 1780's, Lavoisier ushered in a new chemical era by making careful qua ...
... It was in the early 1800s that John Dalton, an observer of weather and discoverer of color blindness among other things, came up with his atomic theory. Let's set the stage for Dalton's work. Less than twenty years earlier, in the 1780's, Lavoisier ushered in a new chemical era by making careful qua ...
tomic Theory
... No. of valence electrons of a main group atom = Group number (for A groups) Atoms like to either empty or fill their outermost level. Since the outer level contains two s electrons and six p electrons (d & f are always in lower levels), the optimum number of electrons is eight. This is called the oc ...
... No. of valence electrons of a main group atom = Group number (for A groups) Atoms like to either empty or fill their outermost level. Since the outer level contains two s electrons and six p electrons (d & f are always in lower levels), the optimum number of electrons is eight. This is called the oc ...
orbital
... In order to write a complete E config. The order in which the various subshells are filled can be obtained by following a path of increasing atomic number through the table (also taking account of the various subshells along the path) The periodic table can be used to determine the shell in whic ...
... In order to write a complete E config. The order in which the various subshells are filled can be obtained by following a path of increasing atomic number through the table (also taking account of the various subshells along the path) The periodic table can be used to determine the shell in whic ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules
... abbreviation u in the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system. Unfortunately for you, biochemists don’t use IUPAC nomeclature, so they use the term Dalton, (Da) for the atomic mass ratio. Thus you will see the ‘atomic mass’ of C as being: ...
... abbreviation u in the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system. Unfortunately for you, biochemists don’t use IUPAC nomeclature, so they use the term Dalton, (Da) for the atomic mass ratio. Thus you will see the ‘atomic mass’ of C as being: ...
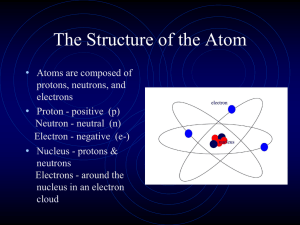
Atomic structure
... location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. • According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
... location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. • According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
KEY Midterm Exam 1 Sept.14, 1999 Chemistry 211 PAGE 1 0f 5
... The inhabitants of a planet "Htrae" in a distant galaxy measure mass in units of "margs", where 1 marg = 4.8648 grams (exactly). Their scale of atomic masses is based on the isotope 3 2S (atomic mass on earth = 31.972 g/mole), so they define one "elom" of 3 2S as the amount of sulfur atoms in exactl ...
... The inhabitants of a planet "Htrae" in a distant galaxy measure mass in units of "margs", where 1 marg = 4.8648 grams (exactly). Their scale of atomic masses is based on the isotope 3 2S (atomic mass on earth = 31.972 g/mole), so they define one "elom" of 3 2S as the amount of sulfur atoms in exactl ...
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
... and carbon binds to four hydrogen atoms. Therefore, valence of these elements is two, three, and four, accordingly. Using this information, we can predict, for example, that a compound formed by oxygen and carbon has a formula CO2 . It is necessary to note, however, that the same element may have di ...
... and carbon binds to four hydrogen atoms. Therefore, valence of these elements is two, three, and four, accordingly. Using this information, we can predict, for example, that a compound formed by oxygen and carbon has a formula CO2 . It is necessary to note, however, that the same element may have di ...
Language of chemistry
... Among these the first three states are found on earth naturally. The plasma state is present in the stars. Plasma state is similar to gaseous state but in which some of the particles are in an ...
... Among these the first three states are found on earth naturally. The plasma state is present in the stars. Plasma state is similar to gaseous state but in which some of the particles are in an ...
All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons but
... • The mass of a proton is about the same as that of a neutron. And the mass of each is about 1,800 times greater than the mass of the electron. • The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the atomic mass unit (amu). • The mass of a proton or a neutron is almost equal to 1 amu. ...
... • The mass of a proton is about the same as that of a neutron. And the mass of each is about 1,800 times greater than the mass of the electron. • The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the atomic mass unit (amu). • The mass of a proton or a neutron is almost equal to 1 amu. ...
Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom
... • The wave function predicts a threedimensional region around the nucleus called the atomic orbital. ...
... • The wave function predicts a threedimensional region around the nucleus called the atomic orbital. ...
All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms
... After completing this topic you should be able to : ...
... After completing this topic you should be able to : ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds containing the major organic functional groups. 46. explain the concept of thermal equilibrium and the chemistry of fire. 47. assign oxidation numbe ...
... 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds containing the major organic functional groups. 46. explain the concept of thermal equilibrium and the chemistry of fire. 47. assign oxidation numbe ...
atoms
... The band indicates various neutron/proton combinations that give rise to nuclei that are either nonradioactive or that are radioactive but decay slowly enough to exist for a measurable time. ...
... The band indicates various neutron/proton combinations that give rise to nuclei that are either nonradioactive or that are radioactive but decay slowly enough to exist for a measurable time. ...
In-Class Exam - Fayetteville State University
... Fayetteville State University Department of Natural Sciences CHEM 140, Summer I 2005 Friday, June 17, 2005 In-Class Exam Note: Answer 33 questions only. Leave three questions of your choice unmarked. Mark your answers on SCANTRON provided. Each correct answer is worth 3 points. ...
... Fayetteville State University Department of Natural Sciences CHEM 140, Summer I 2005 Friday, June 17, 2005 In-Class Exam Note: Answer 33 questions only. Leave three questions of your choice unmarked. Mark your answers on SCANTRON provided. Each correct answer is worth 3 points. ...
Protons and Electrons
... atoms. Typically, atoms are stable when they have a full valence energy shell. This is referred to as the octet rule. Atoms with eight electrons in the valence shell are the most stable. This is true for most atoms except hydrogen and helium. These two elements have a full valence shell with two ele ...
... atoms. Typically, atoms are stable when they have a full valence energy shell. This is referred to as the octet rule. Atoms with eight electrons in the valence shell are the most stable. This is true for most atoms except hydrogen and helium. These two elements have a full valence shell with two ele ...
Ch. 4 Statement of Evidence Atoms + Notes Outline
... 9. If an atoms nucleus was the size of a grape, how much would the mass in its nucleus at least have to be? (pg.89) 10. What makes atoms different from each other? (pg 90) 11. What are isotopes? Give an example of one. (pg. 91. ...
... 9. If an atoms nucleus was the size of a grape, how much would the mass in its nucleus at least have to be? (pg.89) 10. What makes atoms different from each other? (pg 90) 11. What are isotopes? Give an example of one. (pg. 91. ...
Year 10 Chemistry File
... Its electron arrangement is 2,6 which means it has six electrons in its outer shell. To become stable, oxygen could lose all 6 electrons but it is easier for it to gain two electrons instead to fill its outer shell. i.e. The O atom gains two electrons to form an oxide ion. oxygen atom: 8 protons (+) ...
... Its electron arrangement is 2,6 which means it has six electrons in its outer shell. To become stable, oxygen could lose all 6 electrons but it is easier for it to gain two electrons instead to fill its outer shell. i.e. The O atom gains two electrons to form an oxide ion. oxygen atom: 8 protons (+) ...
History of the Atom White Board Presentation
... Experimental Evidence: cathode ray tube experiment where particles smaller than atoms are shown to have negative charge (electrons) with a small mass to charge ratio Model: Plum Pudding Model: ...
... Experimental Evidence: cathode ray tube experiment where particles smaller than atoms are shown to have negative charge (electrons) with a small mass to charge ratio Model: Plum Pudding Model: ...
History of the Atom Notes Key
... Experimental Evidence: cathode ray tube experiment where particles smaller than atoms are shown to have negative charge (electrons) with a small mass to charge ratio Model: Plum Pudding Model: ...
... Experimental Evidence: cathode ray tube experiment where particles smaller than atoms are shown to have negative charge (electrons) with a small mass to charge ratio Model: Plum Pudding Model: ...
Make a large atom with p:95, n:146, e:95 - TSDCurriculum
... 5. READ: This simulation only lets you to build atoms that exist in nature or have been made by scientists. If you can’t build it, it can't be made in the real world. Scientists use the word isotope to distinguish between atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... 5. READ: This simulation only lets you to build atoms that exist in nature or have been made by scientists. If you can’t build it, it can't be made in the real world. Scientists use the word isotope to distinguish between atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
Ionic Bond - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • The outer most electron shell in any atom is called the valence shell • The electrons in the valence shell are called Valence Electrons • By looking at the number of valence electrons an element has we can predict its reactivity. • THE OCTET RULE: Atoms will try to lose, gain or share electrons to ...
... • The outer most electron shell in any atom is called the valence shell • The electrons in the valence shell are called Valence Electrons • By looking at the number of valence electrons an element has we can predict its reactivity. • THE OCTET RULE: Atoms will try to lose, gain or share electrons to ...
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number of
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
Unit 7 Notes - Mahtomedi High School
... • In 1912 Bohr joined Rutherford. He realized that Rutherford's model wasn't quite right. The orbiting electrons should give off energy and eventually spiral down into the nucleus, making the atom collapse. Or the electrons could be knocked out of position if a charged particle passed by. • Boh ...
... • In 1912 Bohr joined Rutherford. He realized that Rutherford's model wasn't quite right. The orbiting electrons should give off energy and eventually spiral down into the nucleus, making the atom collapse. Or the electrons could be knocked out of position if a charged particle passed by. • Boh ...
Catalyst (4 min) - Schurz High School
... Why do atoms have a neutral charge overall even though they are made of charged particles? #protons = # electrons Protons (+) and electrons (-) have opposite charges The charges cancel out! ...
... Why do atoms have a neutral charge overall even though they are made of charged particles? #protons = # electrons Protons (+) and electrons (-) have opposite charges The charges cancel out! ...