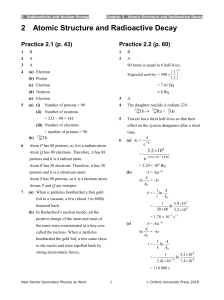
2.1 Introduction
... Some of his followers developed the idea that there were different kinds of atoms, with different properties, and that the properties of the atoms caused ordinary matter to have the properties we all know. These ideas, however, were not accepted by all ancient thinkers. A second group, led by Zeno o ...
... Some of his followers developed the idea that there were different kinds of atoms, with different properties, and that the properties of the atoms caused ordinary matter to have the properties we all know. These ideas, however, were not accepted by all ancient thinkers. A second group, led by Zeno o ...
Examination 3 Multiple Choice Questions
... Provide a basic description of the Rutherford Gold Foil experiment. Your discussion should address the following: i) What was measured? ii) How were the measurements interpreted? iii) Why were the results so "shocking?" -Particles were fired at a thin sheet of Gold foil. The deflection of the parti ...
... Provide a basic description of the Rutherford Gold Foil experiment. Your discussion should address the following: i) What was measured? ii) How were the measurements interpreted? iii) Why were the results so "shocking?" -Particles were fired at a thin sheet of Gold foil. The deflection of the parti ...
Cluster Assembled Metal Encapsulated Thin Nanotubes of Silicon
... Using ab initio total energy calculations will demonstrate how a metal encapsulated silicon cluster SixBey can assemble to form hexagonal nanotube of silicon. ...
... Using ab initio total energy calculations will demonstrate how a metal encapsulated silicon cluster SixBey can assemble to form hexagonal nanotube of silicon. ...
The Bohr Atom The Bohr Atom Electronic Transitions 2.3 Light, Atom
... level and the farther away from the nucleus the electrons are • The number of sublevels in a principal energy level is equal to n – in n = 1, there is one sublevel – in n = 2, there are two sublevels ...
... level and the farther away from the nucleus the electrons are • The number of sublevels in a principal energy level is equal to n – in n = 1, there is one sublevel – in n = 2, there are two sublevels ...
Unit 6 – The Atom Vocabulary
... (1) The energy given off is _________________________ that humans can see. (a) Although the light appears as ________________, it is actually composed of many ___________________ having different __________________ iii) Bright Line Spectra (1) A tool used to ____________________________ into narrow ...
... (1) The energy given off is _________________________ that humans can see. (a) Although the light appears as ________________, it is actually composed of many ___________________ having different __________________ iii) Bright Line Spectra (1) A tool used to ____________________________ into narrow ...
Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review Study Island
... 41. Dr. Grey discovers a new drug that she hypothesizes will increase fat storage in rabbits. She designs an experiment to test her hypothesis. Dr. Grey separates twelve rabbits into two equal groups and measures their body fat individually. She gives one group of rabbits the drug but does not give ...
... 41. Dr. Grey discovers a new drug that she hypothesizes will increase fat storage in rabbits. She designs an experiment to test her hypothesis. Dr. Grey separates twelve rabbits into two equal groups and measures their body fat individually. She gives one group of rabbits the drug but does not give ...
Atoms - Willmar Public Schools
... protons and electrons. Some atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons. For example, some carbon atoms have seven or eight neutrons instead of the usual six. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers. Isotopes of a ...
... protons and electrons. Some atoms of the same element may have different numbers of neutrons. For example, some carbon atoms have seven or eight neutrons instead of the usual six. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers. Isotopes of a ...
Electrons - Irion County ISD
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
chapter 2
... 1. Which atom is bigger, Bi or P? Why? Bi. Atomic radius increases as you do down a group because each row down adds another orbital 2. Name at least one trend among each of the following periodic families: a. Alkali Metals – most reactive metals, react violently with water b. Alkaline Earth Metals ...
... 1. Which atom is bigger, Bi or P? Why? Bi. Atomic radius increases as you do down a group because each row down adds another orbital 2. Name at least one trend among each of the following periodic families: a. Alkali Metals – most reactive metals, react violently with water b. Alkaline Earth Metals ...
The Structure of the Atom - Warren County Public Schools
... Bell Ringer 1. Compare the different views Aristotle and Democritus had about what matter was made of. ...
... Bell Ringer 1. Compare the different views Aristotle and Democritus had about what matter was made of. ...
Atomic Theory - Northwest ISD Moodle
... able to predict the density, atomic mass, melting or boiling points and formulas of compounds for several “missing” elements. ...
... able to predict the density, atomic mass, melting or boiling points and formulas of compounds for several “missing” elements. ...
Chemical Equations
... Examine the chemical equation to see if there are the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the arrow. If not, place coefficients in front of each formula to make them equal. Re-inventory each time a coefficient is added. When counting the atoms of each element, the coefficient gets dist ...
... Examine the chemical equation to see if there are the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the arrow. If not, place coefficients in front of each formula to make them equal. Re-inventory each time a coefficient is added. When counting the atoms of each element, the coefficient gets dist ...
V Ch 2
... (Correct presentation of equation.) (1A) (b) Radon in the body decays to emit radiation which has strong ionizing power. (1A) Also, the decay product polonium is a radioactive solid which will stay inside the body and undergo further radioactive decay. ...
... (Correct presentation of equation.) (1A) (b) Radon in the body decays to emit radiation which has strong ionizing power. (1A) Also, the decay product polonium is a radioactive solid which will stay inside the body and undergo further radioactive decay. ...
Document
... (iii) The basic oxides react with the impurities in the iron and form a slag. What information in the diagram suggests that the slag is less dense than the molten iron? ...
... (iii) The basic oxides react with the impurities in the iron and form a slag. What information in the diagram suggests that the slag is less dense than the molten iron? ...
Electronegativity - Sierra Vista Chemistry
... 2. The number of unshielded protons The greater the number of protons in a nucleus, the greater the attraction to the electrons in the covalent bond, resulting in higher electronegativity. However, full energy levels of electrons shield the electrons in the bond from the increased attraction of the ...
... 2. The number of unshielded protons The greater the number of protons in a nucleus, the greater the attraction to the electrons in the covalent bond, resulting in higher electronegativity. However, full energy levels of electrons shield the electrons in the bond from the increased attraction of the ...
nuclear physics - Effingham County Schools
... The larger the nucleus the greater the electric force. The distances become too large for the strong force to hold the nucleons together. The balance of force favors electric force. Transmutation: Occasionally parts of the nucleus are repelled out with great force and speed. When part of the nucleus ...
... The larger the nucleus the greater the electric force. The distances become too large for the strong force to hold the nucleons together. The balance of force favors electric force. Transmutation: Occasionally parts of the nucleus are repelled out with great force and speed. When part of the nucleus ...
Electronegativity
... 2. The number of unshielded protons The greater the number of protons in a nucleus, the greater the attraction to the electrons in the covalent bond, resulting in higher electronegativity. However, full energy levels of electrons shield the electrons in the bond from the increased attraction of the ...
... 2. The number of unshielded protons The greater the number of protons in a nucleus, the greater the attraction to the electrons in the covalent bond, resulting in higher electronegativity. However, full energy levels of electrons shield the electrons in the bond from the increased attraction of the ...
electrons and the structure of atoms
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
Chapter 3
... D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 35. Atoms of the same element with different mas ...
... D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 35. Atoms of the same element with different mas ...
Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Element
... On the basis of periodic trends, determine which element in each pair has the higher first ionization energy (if possible). a. Al or S b. As or Sb (antimony) c. N or Si ...
... On the basis of periodic trends, determine which element in each pair has the higher first ionization energy (if possible). a. Al or S b. As or Sb (antimony) c. N or Si ...
Electrons - TeacherWeb
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
Electrons - Chemistry Geek
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
... Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle • Remember d and f orbitals require LARGE amounts of energy • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the pu ...
APS Practice Final 2011
... ____ 91. On a velocity-time graph, a line with a negative slope indicates that the object is a. speeding up. c. not moving. b. slowing down. d. traveling at a constant speed. ____ 92. When the velocity of an object changes, it is acted upon by a(n) a. force. c. momentum. b. inertia. d. deceleration. ...
... ____ 91. On a velocity-time graph, a line with a negative slope indicates that the object is a. speeding up. c. not moving. b. slowing down. d. traveling at a constant speed. ____ 92. When the velocity of an object changes, it is acted upon by a(n) a. force. c. momentum. b. inertia. d. deceleration. ...