CHAPTER -4 “STRUCTURE OF ATOM” CONCEPT DETAILS Pre
... o The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong , for, an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. o The atoms of same element are similar in all respects , but isotopes of same element have different mass. o Dalton's theory was based on the premise that the atoms of dif ...
... o The indivisibility of an atom was proved wrong , for, an atom can be further subdivided into protons, neutrons and electrons. o The atoms of same element are similar in all respects , but isotopes of same element have different mass. o Dalton's theory was based on the premise that the atoms of dif ...
chemistry_chapter_3
... The first step is to find the mole-to-mole ratio of the elements in the compound If the numbers are both whole numbers, these will be the subscripts of the elements in the formula If the whole numbers are identical, substitute the number 1 Example: C2H2 and C8H8 have an empirical formula of CH ...
... The first step is to find the mole-to-mole ratio of the elements in the compound If the numbers are both whole numbers, these will be the subscripts of the elements in the formula If the whole numbers are identical, substitute the number 1 Example: C2H2 and C8H8 have an empirical formula of CH ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... The videos used for this course were made in the studios at Gulf Coast Community College by Dr. Sandra Etheridge and were designed to meet the needs of students taking chemistry by distance education. The course is referred to on the videos as CHM 1045 which is in accordance with the common course n ...
... The videos used for this course were made in the studios at Gulf Coast Community College by Dr. Sandra Etheridge and were designed to meet the needs of students taking chemistry by distance education. The course is referred to on the videos as CHM 1045 which is in accordance with the common course n ...
Electron Cloud
... matter is made of atoms atoms in an element are identical different elements have different atoms atoms maintain their mass even in a chemical reaction ...
... matter is made of atoms atoms in an element are identical different elements have different atoms atoms maintain their mass even in a chemical reaction ...
Atomic Structure - Kania´s Science Page
... If the atom gives up an electron we say that it has been oxidized (overall charge increases) If the atoms takes in an electron we say that it has been reduced (overall charge decreases) These come from Benjamin Franklin’s names of oxidation and reduction during a chemical reaction. Cation- + ions An ...
... If the atom gives up an electron we say that it has been oxidized (overall charge increases) If the atoms takes in an electron we say that it has been reduced (overall charge decreases) These come from Benjamin Franklin’s names of oxidation and reduction during a chemical reaction. Cation- + ions An ...
Matter and Measurement
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
Atomic mass
... Distinguishing Among Atoms • The atomic number (Z) identifies the atom – protons in the nucleus ...
... Distinguishing Among Atoms • The atomic number (Z) identifies the atom – protons in the nucleus ...
Curriculum Plan
... behavior of solids, liquids, and gases on a molecular level, Describe three different intermolecular forces (IMF): hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces, Recognize that intermolecular forces only affect molecular substances, and recognize IMF as one of four types o ...
... behavior of solids, liquids, and gases on a molecular level, Describe three different intermolecular forces (IMF): hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces, Recognize that intermolecular forces only affect molecular substances, and recognize IMF as one of four types o ...
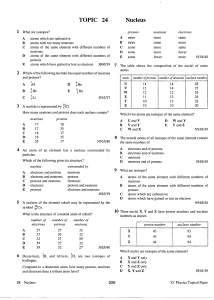
TOPIC 24 Nucleus - jmr physics website
... atoms which are radioactive atoms with too many neutrons atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons atoms of the same element with different numbers of protons atoms which have gained or lost an electron J90/J/39 ...
... atoms which are radioactive atoms with too many neutrons atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons atoms of the same element with different numbers of protons atoms which have gained or lost an electron J90/J/39 ...
Objectives Chapter 4
... Representing Electron Configurations, continued Electron-Configuration Notation • Electron-configuration notation eliminates the lines and arrows of orbital notation. • Instead, the number of electrons in a sublevel is shown by adding a superscript to the sublevel designation. • The helium configura ...
... Representing Electron Configurations, continued Electron-Configuration Notation • Electron-configuration notation eliminates the lines and arrows of orbital notation. • Instead, the number of electrons in a sublevel is shown by adding a superscript to the sublevel designation. • The helium configura ...
9:20 AM
... CH2 is a paramagnetic diradical, with one electron in each of the px and py orbitals of the C. The singlet state, with these electrons paired in one of these nonbonding orbitals, has a significantly higher energy. Bonding orbitals are derived from the 2s of the C atom and the two 1s orbitals of the ...
... CH2 is a paramagnetic diradical, with one electron in each of the px and py orbitals of the C. The singlet state, with these electrons paired in one of these nonbonding orbitals, has a significantly higher energy. Bonding orbitals are derived from the 2s of the C atom and the two 1s orbitals of the ...
AP Syllabus
... Balance equations. Predict products of reactions. Discuss heat content of reactions. 8. Work stoichiometric problems including those involving limiting reagents and percent yield. Also work problems dealing with gases and stoichiometry. 9. Predict periodic trends such as ionization energy, electrone ...
... Balance equations. Predict products of reactions. Discuss heat content of reactions. 8. Work stoichiometric problems including those involving limiting reagents and percent yield. Also work problems dealing with gases and stoichiometry. 9. Predict periodic trends such as ionization energy, electrone ...
chapter
... • A chemical formula is a shorthand expression that describes the chemical composition of a substance • In a simplest formula (empirical formula), subscripts give the smallest ratios for atoms in a compound (e.g. NH2) • A molecular formula gives the actual numbers of each type of atom per molecule ( ...
... • A chemical formula is a shorthand expression that describes the chemical composition of a substance • In a simplest formula (empirical formula), subscripts give the smallest ratios for atoms in a compound (e.g. NH2) • A molecular formula gives the actual numbers of each type of atom per molecule ( ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... 1 Dalton = one twelfth mass of one 12C atom = 1.661x10-27 kg Note: There 6 protons & 6 neutrons in a 12C atom but the mass of a 12C atom is actually less than the combined mass of all of the nucleons individually. Where is this lost mass? It’s released as energy when the nucleons combine (bind ...
... 1 Dalton = one twelfth mass of one 12C atom = 1.661x10-27 kg Note: There 6 protons & 6 neutrons in a 12C atom but the mass of a 12C atom is actually less than the combined mass of all of the nucleons individually. Where is this lost mass? It’s released as energy when the nucleons combine (bind ...
The Origin of Atomic Emission Lines and the Structure of the Atom
... = 1, l = 0, and ms = -½, which differ by the spin of the electron. When we deal with higher atomic numbers, the orbital classification becomes slightly more complicated. For an atomic number greater than 2, the next electron would have to go into an orbital with the principle quantum number n = 2. F ...
... = 1, l = 0, and ms = -½, which differ by the spin of the electron. When we deal with higher atomic numbers, the orbital classification becomes slightly more complicated. For an atomic number greater than 2, the next electron would have to go into an orbital with the principle quantum number n = 2. F ...
4 Structure of The Atom
... 5. J.J. Thomson’s atomic model proposed that electrons are embedded in a positive sphere made from the protons. 6. Rutherford’s atomic model proposed that a very, very small nucleus is present inside the atom and the electrons revolve around it in fixed orbits or shells, much like the planets ...
... 5. J.J. Thomson’s atomic model proposed that electrons are embedded in a positive sphere made from the protons. 6. Rutherford’s atomic model proposed that a very, very small nucleus is present inside the atom and the electrons revolve around it in fixed orbits or shells, much like the planets ...
Glossary: Chemical bonds
... mass units. The terms mass and weight are used interchangeably in this case. The atomic weight given on the periodic table is a weighted average of isotopic masses found in a typical terrestrial sample of the element. Atom. Compare with molecule and ion. An atom is the smallest particle of an elemen ...
... mass units. The terms mass and weight are used interchangeably in this case. The atomic weight given on the periodic table is a weighted average of isotopic masses found in a typical terrestrial sample of the element. Atom. Compare with molecule and ion. An atom is the smallest particle of an elemen ...
Chapter 5
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the mass ...
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the mass ...
Lesson Summary
... course, atoms are too small to actually be seen. Democritus’ idea was disregarded for the next two thousand years, in part, because Democritus did not have evidence to support it. In 1803, the British scientist John Dalton suggested that the idea of atoms could help explain why elements come togethe ...
... course, atoms are too small to actually be seen. Democritus’ idea was disregarded for the next two thousand years, in part, because Democritus did not have evidence to support it. In 1803, the British scientist John Dalton suggested that the idea of atoms could help explain why elements come togethe ...
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Chapter 5 Concepts & Connections Models of
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the mass ...
... • All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differing numbers of neutrons. • The mass number for an isotope is the total number of protons plus neutrons. • The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the mass ...
atomic - Ibiblio
... know something about the history of electricity. Notes 5 Believe it or not, I once read a religious tract that used this paradox as proof of God’s existence. The argument went like this: everyone knows that like charges repel, so it must be God who holds the protons together! Volumes could be writte ...
... know something about the history of electricity. Notes 5 Believe it or not, I once read a religious tract that used this paradox as proof of God’s existence. The argument went like this: everyone knows that like charges repel, so it must be God who holds the protons together! Volumes could be writte ...
physical setting chemistry
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the directions provi ...
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the directions provi ...
BSPH 111 - Refresher Chemistry
... elements in the periodic table is classified according to its atomic number, which is the number of protons in that element's nucleus. Protons have a charge of +1, electrons have a charge of -1, and neutrons have no charge. Neutral atoms have the same number of electrons and protons, but they can ha ...
... elements in the periodic table is classified according to its atomic number, which is the number of protons in that element's nucleus. Protons have a charge of +1, electrons have a charge of -1, and neutrons have no charge. Neutral atoms have the same number of electrons and protons, but they can ha ...