Supplementary Materials for original manuscript submitted
... water. Its heat of adsorption takes 21.1 kcal/mol without the zero point energy (ZPE) variation. This heat value is in the usual range for the heats of water adsorption at the zeolites with transition metal cations [S12]. The minor shift of the ZPE can be evaluated from the ZPE variation upon adsorp ...
... water. Its heat of adsorption takes 21.1 kcal/mol without the zero point energy (ZPE) variation. This heat value is in the usual range for the heats of water adsorption at the zeolites with transition metal cations [S12]. The minor shift of the ZPE can be evaluated from the ZPE variation upon adsorp ...
File - Ms. Francois` Chemistry Class
... (1) Positive charge is evenly spread throughout its volume (2) Negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) Mass is evenly spread throughout its volume (4) Volume is mainly empty space 2. In Rutherford’s gold foil experiments, some alpha particles were deflected from their original path ...
... (1) Positive charge is evenly spread throughout its volume (2) Negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) Mass is evenly spread throughout its volume (4) Volume is mainly empty space 2. In Rutherford’s gold foil experiments, some alpha particles were deflected from their original path ...
Chem Sheets to Memorize SOLUBILITY CHART
... 7. Which is more electronegative, sulfur or chlorine, and why? 8. Which has a larger atomic radius, potassium or bromine, and why? 9. Which has the smaller ionization energy, nitrogen or phosphorus, and why? 10. Write the noble gas electron configuration for copper. ...
... 7. Which is more electronegative, sulfur or chlorine, and why? 8. Which has a larger atomic radius, potassium or bromine, and why? 9. Which has the smaller ionization energy, nitrogen or phosphorus, and why? 10. Write the noble gas electron configuration for copper. ...
Chem Sheets to Memorize
... 7. Which is more electronegative, sulfur or chlorine, and why? 8. Which has a larger atomic radius, potassium or bromine, and why? 9. Which has the smaller ionization energy, nitrogen or phosphorus, and why? 10. Write the noble gas electron configuration for copper. ...
... 7. Which is more electronegative, sulfur or chlorine, and why? 8. Which has a larger atomic radius, potassium or bromine, and why? 9. Which has the smaller ionization energy, nitrogen or phosphorus, and why? 10. Write the noble gas electron configuration for copper. ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
Chapter 8
... designates an aqueous solution, one that is dissolved in water, placed after the formula. 8. __________ indicates that heat is supplied to the reaction 9. __________ a formula written above or below the yield sign indicates it is used as a catalyst. In this case, platinum. G. What is a skeleton equa ...
... designates an aqueous solution, one that is dissolved in water, placed after the formula. 8. __________ indicates that heat is supplied to the reaction 9. __________ a formula written above or below the yield sign indicates it is used as a catalyst. In this case, platinum. G. What is a skeleton equa ...
2(g)
... 12.4 g of Hydrogen gas reacts with 12.4 g of Oxygen gas to form liquid water. Determine the excess and limiting reagent. Calculate the maximum amount of water that could be produced by reacting these two gases together. ...
... 12.4 g of Hydrogen gas reacts with 12.4 g of Oxygen gas to form liquid water. Determine the excess and limiting reagent. Calculate the maximum amount of water that could be produced by reacting these two gases together. ...
MOTheory
... and –/– combinations both cause growth in the overlap region, i.e., the region along the bond axis, while the +/– and –/+ combinations both cause shrinkage. Since these are identical functions with opposite signs, in the +/– and –/+ cases a nodal plane is formed – this is a plane in space where the ...
... and –/– combinations both cause growth in the overlap region, i.e., the region along the bond axis, while the +/– and –/+ combinations both cause shrinkage. Since these are identical functions with opposite signs, in the +/– and –/+ cases a nodal plane is formed – this is a plane in space where the ...
Chapter 2: Matter Is Made up of Atoms
... the mouse can breathe it and live. Priestley’s gas was oxygen, but because he believed in an older theory of matter called the phlogiston theory, Priestley did not recognize it as an element. Lavoisier repeated Priestley’s experiment and came to the history-making conclusion that air is not a simple ...
... the mouse can breathe it and live. Priestley’s gas was oxygen, but because he believed in an older theory of matter called the phlogiston theory, Priestley did not recognize it as an element. Lavoisier repeated Priestley’s experiment and came to the history-making conclusion that air is not a simple ...
(1/V m C) +
... technique that enhances Raman Scattering by molecules adsorbed on rough metal surfaces or by nanostructures such as plasmonic-magnetic silica nanotubes. The enhancement factor can be as much as 10 10 to 1011 which means the technique may detect single molecules. There are two theories electromagneti ...
... technique that enhances Raman Scattering by molecules adsorbed on rough metal surfaces or by nanostructures such as plasmonic-magnetic silica nanotubes. The enhancement factor can be as much as 10 10 to 1011 which means the technique may detect single molecules. There are two theories electromagneti ...
Unit 4 - cloudfront.net
... G. Metals as Reducing Agents 1. Metal atoms can oxidize to their ionic (cation) form, which makes them reducing agents. Na Na+ ...
... G. Metals as Reducing Agents 1. Metal atoms can oxidize to their ionic (cation) form, which makes them reducing agents. Na Na+ ...
printer-friendly version
... All around us are objects. In school, we see desks, chairs, books, students and teachers. Perhaps you ride to and from school on a school bus that drives over a road paved in asphalt, and you see buildings, clouds, sky, cars and trees on your ride. All of these objects are composed of matter. These ...
... All around us are objects. In school, we see desks, chairs, books, students and teachers. Perhaps you ride to and from school on a school bus that drives over a road paved in asphalt, and you see buildings, clouds, sky, cars and trees on your ride. All of these objects are composed of matter. These ...
Lecture 3
... inserting coefficients before the chemical formulas so that the same number of each type of atom is shown on each side of the equation. Chemical equations may be balances “by inspection” or algebraically (Section 2.1, pages 55-57). Inspection is the preferred way for simple reactions. ...
... inserting coefficients before the chemical formulas so that the same number of each type of atom is shown on each side of the equation. Chemical equations may be balances “by inspection” or algebraically (Section 2.1, pages 55-57). Inspection is the preferred way for simple reactions. ...
chapter4
... Explained the nuclear atom. Atom has a dense center of positive charge called the nucleus. Electrons travel around the nucleus in the ...
... Explained the nuclear atom. Atom has a dense center of positive charge called the nucleus. Electrons travel around the nucleus in the ...
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Essential Questions Screencast 1
... 4. What are the main regions of the periodic table? 5. What are the special named groups and where are they located (group #)? Screencast 1-2 Compounds, Mixtures and Classification of Matter 1. How are compounds separated? 2. What are the 2 types of mixtures and what are their differences? 3. How ar ...
... 4. What are the main regions of the periodic table? 5. What are the special named groups and where are they located (group #)? Screencast 1-2 Compounds, Mixtures and Classification of Matter 1. How are compounds separated? 2. What are the 2 types of mixtures and what are their differences? 3. How ar ...
Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced ...
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced ...
Chemistry Answers - Heathcote School and Science College
... a Calculate the maximum theoretical mass of hydrazine that can be made by reacting 340 g of ammonia with an excess of sodium chlorate. ...
... a Calculate the maximum theoretical mass of hydrazine that can be made by reacting 340 g of ammonia with an excess of sodium chlorate. ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... Principal quantum number (n): It determines the main energy level, called shell in which the electron is present. It specifies the location and energy of an electron in any atom. It is a measure of the effective radius of the electron cloud sphere. Azimuthal quantum number (l): It describes the shap ...
... Principal quantum number (n): It determines the main energy level, called shell in which the electron is present. It specifies the location and energy of an electron in any atom. It is a measure of the effective radius of the electron cloud sphere. Azimuthal quantum number (l): It describes the shap ...
EVANS GROUP RESEARCH PROJECT DESCRIPTIONS
... synthesis of unusual hydrocarbon polymers. Since the lanthanide metals have not been heavily investigated in the past, they offer new options for polymer synthesis. Organolanthanide complexes have the added advantage that they can initiate polymerization without an aluminum co-catalyst such as MAO. ...
... synthesis of unusual hydrocarbon polymers. Since the lanthanide metals have not been heavily investigated in the past, they offer new options for polymer synthesis. Organolanthanide complexes have the added advantage that they can initiate polymerization without an aluminum co-catalyst such as MAO. ...
Principles of Technology
... e. On the basis of his experiments, Rutherford drew the conclusion that according to calculations using Coulomb’s law, the interaction of alpha particles with a very small, massive nucleus would result in it following a hyberbolic path and produce the observed angular pattern of scattering. Rutherfo ...
... e. On the basis of his experiments, Rutherford drew the conclusion that according to calculations using Coulomb’s law, the interaction of alpha particles with a very small, massive nucleus would result in it following a hyberbolic path and produce the observed angular pattern of scattering. Rutherfo ...
HC CH 4 sec 1
... If you grind a piece of copper into dust, each speck of red dust would still have the properties of copper. • If you could continue to make the dust particles smaller, you would eventually come upon a particle that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. • This ...
... If you grind a piece of copper into dust, each speck of red dust would still have the properties of copper. • If you could continue to make the dust particles smaller, you would eventually come upon a particle that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. • This ...
Chapter 5 ppt
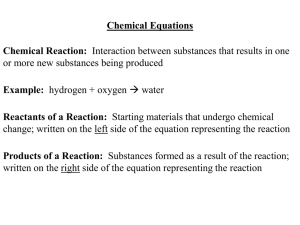
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
... change; written on the left side of the equation representing the reaction Products of a Reaction: Substances formed as a result of the reaction; written on the right side of the equation representing the reaction ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... • It can make stable bonds with itself • It can make multiple bonds to C, N, O • The C-H bond is nonpolar, but bonds to other elements (N, O, halogens) are polar This is why life is based on the chemistry of carbon ...
... • It can make stable bonds with itself • It can make multiple bonds to C, N, O • The C-H bond is nonpolar, but bonds to other elements (N, O, halogens) are polar This is why life is based on the chemistry of carbon ...
Grade 8 th Science Curriculum Scope and Sequence
... compare the properties of compounds with those of the elements from which they are made. Provide evidence to support the fact that the idea of atoms explains conservation of matter. a. Use appropriate tools to measure temperature (thermometer), mass (balance), length (meter stick), volume (graduated ...
... compare the properties of compounds with those of the elements from which they are made. Provide evidence to support the fact that the idea of atoms explains conservation of matter. a. Use appropriate tools to measure temperature (thermometer), mass (balance), length (meter stick), volume (graduated ...