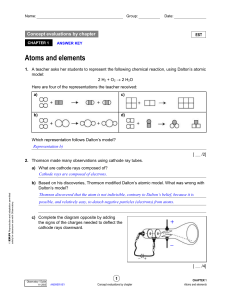
Atomic Theory
... Expected result: particles would pass through Actual result: most passed through, but some were deflected and reflected These results indicated a concentration of positive charge (nucleus), with electrons moving around it at some distance. ...
... Expected result: particles would pass through Actual result: most passed through, but some were deflected and reflected These results indicated a concentration of positive charge (nucleus), with electrons moving around it at some distance. ...
WHAT IS THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... rays. By carefully measuring the effect of the fields, Thomson calculated the ____________________ of the charged particles. 5. Thomson compared his results with other known information and found that his particles were smaller than an atom. He had identified the first subatomic particle: the ______ ...
... rays. By carefully measuring the effect of the fields, Thomson calculated the ____________________ of the charged particles. 5. Thomson compared his results with other known information and found that his particles were smaller than an atom. He had identified the first subatomic particle: the ______ ...
"stuff" that takes up space- is made of tiny particles called atoms
... * Protons are massive (1 amu) and have a positive + charge. Neutrons are massive (1 amu) and have a neutral charge (neither positive nor negative). Electrons are extremely tiny (1/1,837 amu). ...
... * Protons are massive (1 amu) and have a positive + charge. Neutrons are massive (1 amu) and have a neutral charge (neither positive nor negative). Electrons are extremely tiny (1/1,837 amu). ...
The Atom
... Niels Bohr found evidence that electrons in atoms are arranged in energy levels. The lowest energy level is closest to the nucleus and can hold only two electrons. Higher energy levels are farther from the nucleus and can contain more electrons. This simplified model shows a nucleus of protons and ...
... Niels Bohr found evidence that electrons in atoms are arranged in energy levels. The lowest energy level is closest to the nucleus and can hold only two electrons. Higher energy levels are farther from the nucleus and can contain more electrons. This simplified model shows a nucleus of protons and ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... In a particular experiment, 3.50 g samples of each reagent are reacted. The theoretical yield of lithium nitride is _____ g. ...
... In a particular experiment, 3.50 g samples of each reagent are reacted. The theoretical yield of lithium nitride is _____ g. ...
build your own atom - brittany
... Atoms are a combination of protons, neutronsand electrons. The nucleus of an atom appears like the protons and neutrons are all smashed together which creates a spherical center. The electrons orbit around the nucleus. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in that atom. The Periodic ...
... Atoms are a combination of protons, neutronsand electrons. The nucleus of an atom appears like the protons and neutrons are all smashed together which creates a spherical center. The electrons orbit around the nucleus. The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in that atom. The Periodic ...
Unit 1 - Mount St. Mary Catholic High School
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical to other atoms of the same element and different from atoms of other elements. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one ele ...
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical to other atoms of the same element and different from atoms of other elements. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one ele ...
What are Valence Electrons
... • Protons and Neutrons in the nucleus • Surrounded by one or more electrons ...
... • Protons and Neutrons in the nucleus • Surrounded by one or more electrons ...
04 Atom-Review-Worksheet
... an arrangement of elements according to similarities in their properties a vertical column of elements in the periodic table a horizontal row of the periodic table stream of electrons produced at the negative electrode of a tube containing a gas at low pressure the central core of an atom, which is ...
... an arrangement of elements according to similarities in their properties a vertical column of elements in the periodic table a horizontal row of the periodic table stream of electrons produced at the negative electrode of a tube containing a gas at low pressure the central core of an atom, which is ...
Chemistry 2810 Answers to the Second assignment Topic: Atomic
... (0.35)] = 2.85. Thus we expect the forces operating on the valence shell in calcium to be greater than those in potassium, leading to a smaller radius in calcium. (b) Chlorine should be larger than fluorine. We would expect Z* to be very similar, since the two atoms are in the same group of the peri ...
... (0.35)] = 2.85. Thus we expect the forces operating on the valence shell in calcium to be greater than those in potassium, leading to a smaller radius in calcium. (b) Chlorine should be larger than fluorine. We would expect Z* to be very similar, since the two atoms are in the same group of the peri ...
atomic theory presentation final
... electrons move in energy levels but they move so quickly that you can’t be certain where they are… • Heisenburg discovered that electrons move so quickly they form an electron cloud! ...
... electrons move in energy levels but they move so quickly that you can’t be certain where they are… • Heisenburg discovered that electrons move so quickly they form an electron cloud! ...
3—3 Review and Reinforcement
... 6. When an atom loses or gains one or more electrons, it is called an iZ ...
... 6. When an atom loses or gains one or more electrons, it is called an iZ ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
History of the Atom
... • In 1926, he further explained the nature of electrons in an atom by stating that: ...
... • In 1926, he further explained the nature of electrons in an atom by stating that: ...
atom a very small particle that makes up most kinds of matters and
... exists in an electron cloud formation around an atom's nucleus ...
... exists in an electron cloud formation around an atom's nucleus ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... - energy higher the farther the orbits are from the nucleus - the farther the electron is from the nucleus, the less attraction it feels - electrons can jump from one energy level to another, but are not found between levels - they lose or gain a discrete package of energy (quantum of energy) every ...
... - energy higher the farther the orbits are from the nucleus - the farther the electron is from the nucleus, the less attraction it feels - electrons can jump from one energy level to another, but are not found between levels - they lose or gain a discrete package of energy (quantum of energy) every ...
Chemical Reactions PPT
... If an element is more reactive (found higher up in the activity series) than another element, it WILL replace that element. (Higher element will only replace something lower, not lower to higher) Halogen Activity Series (same order as on Periodic Table) ...
... If an element is more reactive (found higher up in the activity series) than another element, it WILL replace that element. (Higher element will only replace something lower, not lower to higher) Halogen Activity Series (same order as on Periodic Table) ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE questions
... Which part of the atom has a POSITIVE charge ? Which part of the atom has a NEGATIVE charge ? This means that the number of PROTONS is equal to the number of ELECTRONS in an atom. How many ELECTRONS are,there in each of the following ATOMS ? Sodium, Lithium, Ba,O, W, the element with an atomic numbe ...
... Which part of the atom has a POSITIVE charge ? Which part of the atom has a NEGATIVE charge ? This means that the number of PROTONS is equal to the number of ELECTRONS in an atom. How many ELECTRONS are,there in each of the following ATOMS ? Sodium, Lithium, Ba,O, W, the element with an atomic numbe ...
Chemical Reactions
... elements) combine and form a compound. (Sometimes these are called combination or addition reactions.) ...
... elements) combine and form a compound. (Sometimes these are called combination or addition reactions.) ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... Review key terms by completing this crossword puzzle, using the following alphabetized list of terms: ...
... Review key terms by completing this crossword puzzle, using the following alphabetized list of terms: ...
10B Atoms and Isotopes
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_corr
... d) Which of these elements are good conductors of electricity? Explain your answer. Sodium and magnesium are good conductors because they are both metals. ...
... d) Which of these elements are good conductors of electricity? Explain your answer. Sodium and magnesium are good conductors because they are both metals. ...
Answer key
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
File
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...