* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
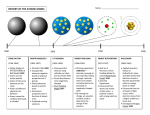
ATOMIC THEORY History of the Atom http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=njGz69B_pUg& feature=related John Dalton http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wsYDL6EjV4k Suggested that elements were made up of atoms. A given compound always contains the same combination of atoms. Prepared the first table of atomic masses. Law of Multiple Proportions: When 2 elements form a series of compounds (i.e., CO and CO2), the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. (See Sample Exercise 2.1, p.45) Amadeo Avogadro Avogadro’s Hypothesis: at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of particles. J.J. Thomson http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_SY7qBrVxsU &feature=related Cathode-ray tubes (cathode = negative electrode) The ray emanating from the cathode was repelled by the negative pole of an applied electrical field. So what did Thomson propose the ray was composed of? Determined the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron: c/m = -1.76 x 108 C/g Thomson (cont.) Since electrons could be produced from electrodes of various metals, all atoms must contain electrons, so they must have some positive charge. Postulated that an atom consisted of a diffuse cloud of positive charge with the negative electrons embedded randomly around it. (Plum Pudding Model) Robert Millikan Oil Drop Experiment: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=91E6KvCvRf0 Altered the voltage on charged plates to stop the fall of charged oil drops. Using the voltage and the mass of the oil drop, he was able to determine the charge on an oil drop. Using the charge on the oil drop and Thomson’s charge-to-mass ratio, Millikan calculated the mass of an electron as 9.11 x 10-31 kg. Ernest Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHcjiiP0HB4&fe ature=related Tested Thomson’s plum pudding model by directing α particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Expected result: particles would pass through Actual result: most passed through, but some were deflected and reflected These results indicated a concentration of positive charge (nucleus), with electrons moving around it at some distance. Niels Bohr Quantum Model: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cn6v5ygyZHQ The electron in a hydrogen atom moves around the nucleus only in certain allowed circular orbits (much like the planetary model) Bohr also postulated that atoms can become “excited” by an electrical current, absorbing energy and then releasing that energy in the form of light, with each element emitting certain, unique wavelengths (or spectrum). http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xUXnmPL9SE&NR=1 Schrodinger Said electrons were more like waves than particles James Chadwick Discovered the neutron This accounted for the previously unexplained difference between an element’s atomic number and its atomic mass http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HnmEI94URK 8&feature=related Werner Heisenberg Discovered both Bohr AND Schrodinger were correct: an electron is a particle with wave-like properties Photon: a “particle” of electromagnetic radiation Also said you cannot know both an electron’s location AND its spin at the same time. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fqr4MFg6GHI&fe ature=related Atomic Structure